The Disadvantages of Tourism – What Happens When Travel is not Sustainable
This post will highlight some of the common disadvantages of tourism, and the negative impacts it can have on destinations when it is not managed in a sustainable way.

Table of Contents

The problem with tourism
In 2019 (pre-COVID), international tourist arrivals grew to 1.5 billion and the industry generated 1.4 trillion USD dollars of tourism receipts ( UNWTO ). It was the tenth straight year of growth, with arrivals continuing to increase each year. The receipts from tourism were even growing at a faster rate than global GDP! Ten years of rapid growth, and in many destinations, limited restriction or control on that growth has left tourism causing some pretty serious damage to the destinations it occurs in. It is only in recent years that sustainable tourism has really become a serious priority for destinations and operators around the world. In many cases, it has been out of necessity, in an attempt to resolve the issues unsustainable tourism has caused over the years.
Now, I love to travel. And this list is by no means designed to try to make anyone stop travelling (COVID has already done that for us…). But I think it is really important as travellers to be aware of the issues we are contributing to. Either directly or indirectly. The negative impacts of tourism are usually classified into three different areas, economic, social and environmental. In this post, I will share four negative impacts tourism can have in each of these areas. This list is by no means exhaustive, and there are (unfortunately) many other disadvantages of tourism. But the idea of this post is to highlight the problems with unsustainable tourism.
Economic disadvantages of tourism
It might seem hard to believe that there can be economic disadvantages of tourism when it produces so much revenue. But the economic side of tourism is more than just profits. And unsustainable tourism driven by profits only can have dire consequences for the destinations it occurs in.
Over reliance on tourism
Countries can become over-reliant on tourism, with a large portion of their economy and GDP coming from tourism. The situation the world finds itself in now with COVID could not be a better illustrator of the damages of being over-reliant on tourism, a very volatile industry. But even before a global pandemic, this was still an issue. Tourist’s destination preferences change easily, and it doesn’t take much to sway them away from a particular destination. Relying on tourist’s to come back to the same place year after year is risky. Events such as natural disasters, terrorism, health concerns or even just a change in trend can leave countries that were thriving on tourism empty.

Low quality employment
It’s true that tourism generates employment for many. But often these jobs are low paying and seasonal. With employees completing menial tasks with little room for progression or career advancement. It’s not uncommon for establishments like resorts to hire international staff for senior, managerial roles. Usually from more economically developed countries. This leaves local workers stuck in low-level roles, paid peanuts and not guaranteed year-round work.
Tourism dollars leaking out of local economies
A major economic issue with the tourism industry is that of leakage. You can read about this issue in more detail here. But basically, leakage is when a portion of tourism income does not stay in the destination where the tourists visited. Money ‘leaks’ out to more developed countries. This usually occurs through international companies such as airlines and resorts taking their profits back to their headquartering countries. And the local destination and community do not get the economic benefits of the tourists that have visited.

Favoured over other industries
In countries where tourism is a major industry sector, the government can sometimes focus all their energy and funds on the industry. This is often at the peril of other important industries like education, infrastructure and healthcare. This can result in pristine tourist areas, new infrastructure and funding for the benefit of visitors. But what about the locals who live in the country? They might not enjoy anywhere near the same level of development.
Social disadvantages of tourism
The impacts of tourism on society and culture are often contested and deeply complicated. Tourism is just one of many forces that can impact on and change cultures, like globalisation, technology and the media. But there is no denying that tourism and culture and society are inseparable. And there are some major disadvantages of tourism in this area.
The commodification of culture
This is one of the most complex, morally challenging and difficult parts of tourism. It warrants an entire discussion of its own, but in short, tourism can turn culture into a commodity. When traditional culture becomes an attraction, that people pay to see, this raises complicated ethical issues. Often times the culture that is presented to tourists has been adapted to be more appealing to the visitor. Traditional dances and costumes are amended, ceremonies or rituals are shortened, and handicrafts are often made smaller or lighter to fit in suitcases. Only certain elements of a culture are deemed worthy of presenting to tourists. And usually, there is a whole host of problems behind closed doors that tourists are never exposed to or aware of. The culture of a destination as seen through the tourists’ eyes is not authentic at all.
Erosion of culture
This issue is different to the previous issue in that culture can not only be commodified but in many cases lost altogether as a result of tourism. The ‘demonstration effect’ occurs when locals, particularly in traditional or indigenous cultures, observe the behaviours of visitors, usually Western tourists. Exposing the locals to a completely different way of life can lead to changes in their local culture, particularly from younger members of the community. They can begin to mimic and replicate the cultures of the tourists who visit and move away from the customs and traditions of their own culture.

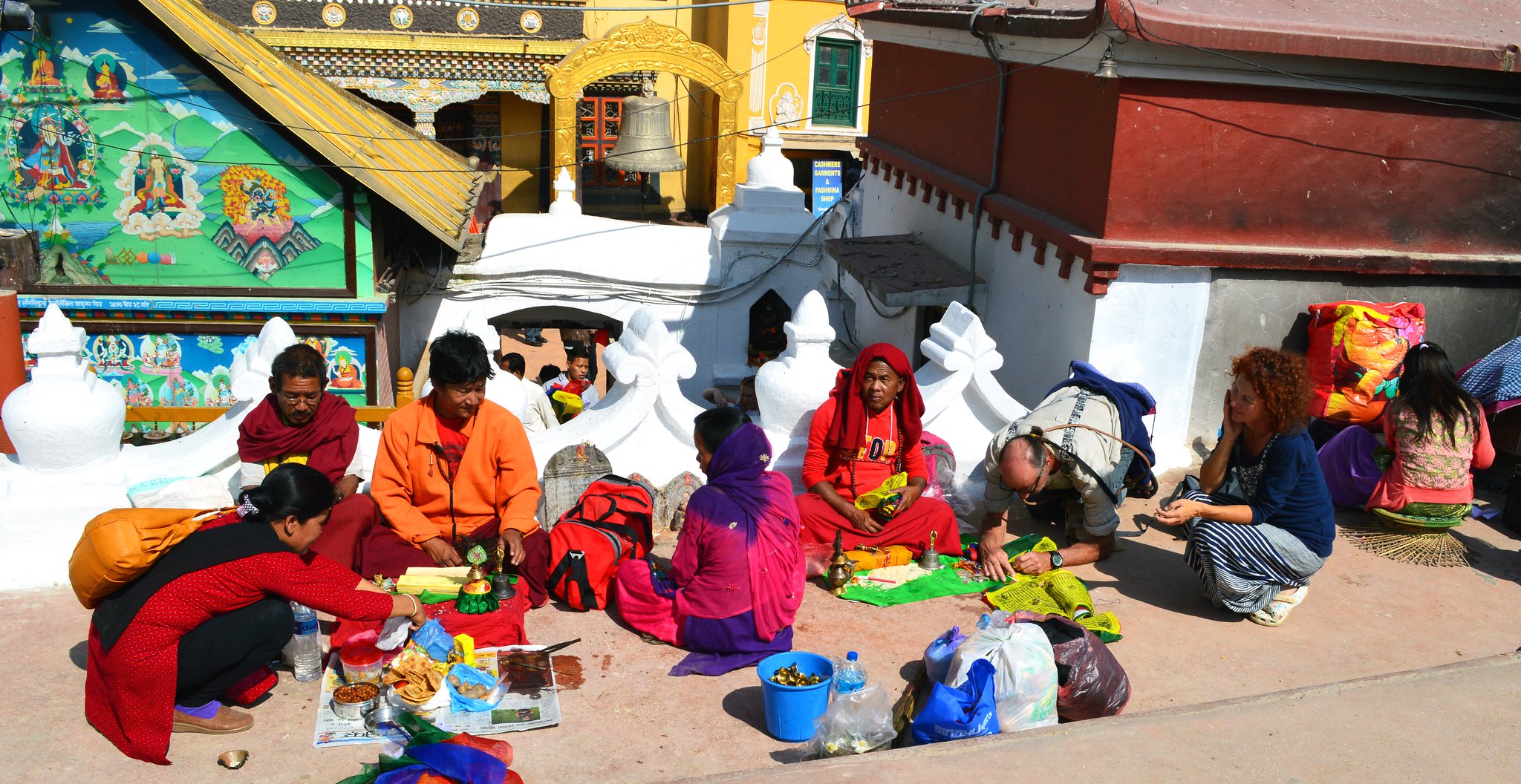
Tourists behaving badly
When people are on holiday they tend to leave their moral compass at home. They are relaxing, want to have a good time, and outside of their usual environment. This can lead to major clashes between tourists and locals, and leave the locals wishing the tourists had never arrived. Whether intentionally or unintentionally, tourists can offend locals and make them uncomfortable in their own homes. Dressing inappropriately, not being aware of culturally unacceptable behaviours and general bad behaviour through the use of alcohol and drugs are just some of the bad behaviours tourists bring to a destination.
Physical damage to built culture and heritage
The Colosseum, Petra, Angkor Wat, the Great Wall of China. Some of the biggest tourist attractions in the world are ancient, historical sites, built centuries ago by different civilisations. These physical representations of ancient cultures are old and fragile. And having thousands, sometimes millions, of tourists tramp through them each year places a lot of strain on the structures and can cause irreparable damage. Not all damage is deliberate on the part of the tourists, but simply having people walk over old stones, touch rock walls and lean on sites can cause irreversible erosion and damage. However many sites are suffering from the deliberate actions of tourists. Littering, graffitiing, taking pieces of the site home with them and climbing on off-limits structures.

Environmental disadvantages of tourism
The negative impacts of tourism on the environment are often the most publicised and talked about. They are easier for us to physically see and quantify, so it can be easier to talk about them. But the impacts that tourism can have on the environment are very complex and can be both direct and indirect. The environment is a complicated web of ecosystems, and one small action can have rippling effects throughout an entire area or species. This is by no means an exhaustive list of the negative things tourism can do to our environment. But some of the issues listed are a bit easier to quantify, where tourism has a direct impact.
Intense use of resources
Tourists, like all people, use resources such as water and energy. However many popular tourist destinations around the world are already dealing with resource scarcities, and tourism can severely exacerbate the problem. Tourism as an industry is a massive overuser of water. Swimming pools and golf courses require a lot of water, and I can’t think of something more synonymous with a holiday than a swimming pool. Tourists themselves tend to use more water than when they are at home, and doing their laundry can consume a lot of water and energy. Cooling and/or heating large hotels and resort complexes and their swimming pools also require a lot of electricity.

Physical damage to natural and marine areas
Tourism takes place in some of the most pristine, yet fragile natural areas in the world. Hiking in the rainforest, snorkelling in coral reefs and climbing alpine mountains are just some of the many activities that can physically impact and damage the natural environment. Vegetation can be damaged having tourists continually trampling over the same paths (and often going off the path too). Corals are damaged by boats and anchors, and tourists (accidentally or not) touching and breaking them. This damage has major flow-on effects on the wider ecosystems and can indirectly impact entire ecosystems and species.

Increased waste, pollution and emissions
From rubbish to sewerage, carbon emissions from transport carriers and water pollution – tourism produces a lot of unwanted waste. In many lesser developed countries around the world, tourism has come on quicker than their local infrastructure can handle, and disposing of the increased waste tourists bring has proven troublesome. Sewerage can end up in local rivers and lakes, and rubbish can be burnt or end up in the ocean. And transporting tourists from point A to B, by planes, in particular, releases a ton of carbon emissions into our atmosphere.
Land use and infrastructure development
Tourists need places to stay, airports for planes to land in and ports for boats to depart from. Natural areas are often cleared to make way for this construction, displacing animals and destroying forests or wetlands. A lot of tourism occurs in coastal areas, and building hotels and resorts right along the coastline can have major impacts on the ocean and surrounding reefs due to erosion and sand runoff. The same goes for constructing marinas and ports, where sand mining and dredging can have disastrous consequences for marine ecosystems.

The disadvantages of tourism: Conclusion
As I mentioned previously, this list is by no means exhaustive and unfortunately there is a range of other disadvantages of tourism. The problems tourism can cause in destinations around the world are complicated and entangled with other deep societal issues such as development, globalisation and colonialism. The purpose of sharing these negative impacts was to highlight that tourism is not a perfect industry. And as travellers, we should be aware of the damage that we can contribute to when we travel. But it’s not all bad news! Tourism, when managed sustainably, has the opportunity to contribute to positive change for our planet. And there are countless examples of the positive impacts of tourism!
What do you think? Have you experienced some of these disadvantages of tourism first hand? Can you think of any other negative impacts tourism can have on the economy, culture and environment? Let me know your thoughts in the comments below.

Sally Rodrick
Sally Rodrick is the voice behind Sally Sees. She has spent 12 months travelling in Mexico and Central America, and has her sights firmly set on South America. Sally helps thousands of readers discover the magic of Latin America. Sharing detailed guides to inspire and equip them with the knowledge they need to plan their own epic adventures in this incredible part of the world.
Leave a Comment Cancel Comment
The comments.
M.K.CHETTRI
It’s nice as you have studied and observed tourists and tourism from the very near…..it’s fantastic. but the thing is that, tourism must go strictly and very sincerely with modern technological facilities keeping in mind about our extremely valuable resources security and conservation.
Thankyou for your comment. I agree, for tourism to be beneficial for all parties involved, and the environment it has to be managed carefully with strict limitations in place to protect resources.
Thanks for simplifying it for me
My pleasure, I hope it was helpful 🙂
Hi Sally, I enjoy your travel blogs very much and appreciate the way you approach your travel experiences. They have been particularly helpful as I am planning a road trip to BCS.
Regarding the negative side of travel, it is much like the negative side of modern life in general. Our collective efforts and our individual choices can have an impact, however it is governments and large corporations who cause the most damage and reap the most profits from industry and development, and also have all the power to either continue down a path of environmental and cultural destruction or make crucial policy changes to preserve our world. Unfortunately, preservation isn’t lucrative but exploitation is. That’s why our environmental crisis is worsening, not improving, no matter how many reusable straws people are buying.
While I firmly believe that as individuals and consumers we must make conscious choices and also “vote with our dollars”, I find it frustrating that we as a collective society of caring individuals have fallen for the greatest psychological trick of industry: that it’s up to us, the consumer, to make sure our world doesn’t get destroyed, while governments and industries continue to knowingly create mass scale destruction, pollution, waste and overdevelopment.
This same problem applies to most areas of modern life, not just travel, and frankly it is extremely distressing. As someone who is very conscious of the dangerous effects of modern consumerism, I am often extremely troubled and sometimes paralyzed by it. So for me it becomes important to live with balance in this regard. I will always live consciously, but I need to be careful not to feel the enormous and distressing weight of these problems squarely on my shoulders alone. Ultimately, industry and government need to be held accountable more so than individuals. Plus, not all individuals are on board with these efforts. Many plainly do not care. Those individuals who contribute most to environmental and cultural destruction aren’t the ones who will be reading blogs like this, or refraining from purchasing multiple homes, or living beyond their share of resources. They don’t care and never will. We need our leadership to change and to lead us all into conservation and preservation.
Certainly we as caring citizens of the planet should live consciously but our small efforts are no match for the unbridled and unregulated industries that are the true source of our worlds demise.
I certainly appreciate the message you are putting forth here and everything you point out is absolutely accurate, but I fear the ones who need to hear it the most won’t be the ones this message will reach.
Thank you for being a conscious and caring citizen of the planet and thank you for your lovely and helpful blogs. Best wishes and happy trails.
Hi Marissa,
Thankyou for your insightful comment. I couldn’t have said it better myself and completely share your sentiment on the situation of our planet.
To be perfectly honest, I try not to think too much about what our governments and large corporations are doing to our earth. It often feels to overwhelming to even comprehend, when it is so far out of our control.
You are completely right in saying that they are the ones that are really doing the damage, and the only ones that have the potential for real change. But for that to happen profit must be sacrificed, and planet must come first. There are small hints of this happening in some places around the world, and I think countries with large tourism industry are amongst some of the first to say no to profitable industries that are detrimental to the environment. Finally they can see the long term condition of the environment is more valuable than a quick financial win in a destructive industry. A pristine environment with rich biodiversity will be worth financially more to tourists in the long term, so there is incentive to keep it that way.
That’s why I think travel can be so powerful. Sure, travelling produces emissions and has its own set of challenges for our environment. But as you say, modern living in any context, at home or while travelling, is damaging by its very nature. I believe pros of travel can outweigh the cons if done right.
It’s a very tough line between knowing that really, as individuals, we have very little power to make meaningful change. But if we swing too far in the opposite direction it turns into an attitude of not even bothering at all. Little steps can have little impacts, and whilst it won’t solve the enormous problems our earth is facing – it can’t hurt to do the right thing where and when we can.
Keep exploring our beautiful world, and take on board the issues you can solve. All the best, Sally x
Sinadi Aanya
This is grate I got a lot of information thank u so much 🙏🏻☺️
I’m so glad it was helpful Sinadi! All the best, Sally

Tourism: The Advantages, Disadvantages and How to Properly Travel

The Advantages
For developing countries, the advantages of tourism tend to be primarily monetary. A large scale tourism industry prevents larger, more harmful businesses from working off the land. Small tourist companies that reign on the land stops large capitalistic corporations from polluting the air or gentrifying people’s homes.
The tourism industry encompasses many different travel areas, which allows the majority of a country’s population to be employed . These employment places include hotels, car rental agencies, restaurants, tour companies, souvenir shops, and equipment shops, among others.
Profit earned from tourism can be reinvested into the country for better infrastructure, education, funding conservation efforts and creating more responsible ways of touring. Without tourism, many countries would not have the same level of access to education and infrastructure. Moreover, tourism allows hosts and visitors to share cultures and meet diverse groups of people. Through respectful interactions, a broader view of the world from both parties can be achieved. By reinvesting the money earned back into the country, tourism and its attractions can grow, creating a positive cycle for the country.
The Disadvantages
With the way the tourism industry is currently run, the disadvantages of tourism may greatly outweigh the advantages in a country. The first factor to take into consideration is environmental damage. When a country has a high tourist attraction, the number of people occupying a space increases immensely. As a result, the release of carbon monoxide gases can increase due to plane and car use affecting the country’s environment. Many countries with ancient ruins or natural attractions are also in danger of destruction or erosion with significant foot traffic and human interaction. Additionally, flora and fauna can decrease in areas or change their growth and migration patterns when there is an overflow of humans interact. Foot traffic and continuous touching can also slowly degrade the stability of ancient structures.
One of the advantages breached upon the sharing of cultures. While this is a great interaction of beliefs and customs, it can become destructive to a host country’s culture. One of the ways cultures can be disrespected is through the commercialization of countries’ cultures . When tourism booms, large industries swoop in and sell figures of the cultures’ icons or traditional wear, disrespecting the countries’ indigenous beliefs and can be harmful to the people living there. Moreover, poor behavior from tourists who don’t respect the spoken or unspoken codes of conduct held by indigenous peoples also undermines the sacred beliefs held within the country.
Also, for many countries, tourism is a seasonal occurrence. For people that work in the tourism industry, their jobs are only viable for a certain number of months, and after the season has ended, many are left without income. Many of these jobs also lack the benefits that other sector jobs supply. Tourism workers are often left without insurance or pension. Not to mention, foreign businesses tend to overtake the companies present in these countries, forcing small businesses to shut down. As a result, foreign businesses keep the majority of profits from tourism, while local businesses lose their income. This hurts small businesses and local economies.
As previously stated, the profit gained from tourism is often reinvested into the industry. However, with unequal infrastructure development, the tourism industry can inadvertently sustain itself without aiding a country’s other vital sectors. As such, many countries end up developing tourism hot spots while the rest of the country suffers. In these countries, there are visible socioeconomic gaps between the wealthy and the poor. Focusing mainly on the tourism industry and places of mass attraction leaves disadvantaged communities at risk of financial instability. Moreover, countries solely invested in tourism are vulnerable to quick economic falls as its working sectors are unevenly balanced. If a natural disaster, political unrest or unprecedented pandemic were to strike, the country would lose a massive income, causing an economic recession that some countries may significantly struggle to bounce back from.
Ways to Respectfully Travel
The most important step to being a respectful tourist is to be an educated tourist. Understanding and respecting the culture and the people of the country is vital. By not undermining tourism countries’ culture and beliefs, the people living there will be more welcoming to tourists, and cultures can flourish without fear of commercialization.
Being environmentally conscious is also important to the survival of these countries. Respecting a country’s land and structures preserve the countries’ beauty and keep the land clean and prepped for further development. Many countries are more environmentally strained, so reducing pollution or your carbon footprint in a foreign country can help ease the strain.
Supporting the small and local businesses found in these countries can help keep local communities employed and support the overall economy. As local businesses grow, more people will have the opportunity to be employed outside of the tourism sector, and the economy will be able to grow within itself.
By learning the advantages and disadvantages of tourism, and how one can improve the practice of traveling, the tourism industry will be able to change for the better and support the countries that host people from all over the world.
– Marlee Ingram Photo: Flickr
“The Borgen Project is an incredible nonprofit organization that is addressing poverty and hunger and working towards ending them.”
-The Huffington Post
Inside the borgen project.
- Board of Directors
Get Smarter
- Global Poverty 101
- Global Poverty… The Good News
- Global Poverty & U.S. Jobs
- Global Poverty and National Security
- Innovative Solutions to Poverty
- Global Poverty & Aid FAQ’s
Ways to Help
- Call Congress
- Email Congress
- 30 Ways to Help
- Volunteer Ops
- Internships
- Courses & Certificates
- The Podcast
National Geographic content straight to your inbox—sign up for our popular newsletters here

What's the problem with overtourism?
With visitor numbers around the world increasing towards pre-pandemic levels, the issue of overtourism is once again rearing its head.
When locals in the charming Austrian lakeside village of Hallstatt staged a blockade of the main access tunnel, brandishing placards asking visitors to ‘think of the children’, it highlighted what can happen when places start to feel overrun by tourists. Hallstatt has just 800 residents but has opened its doors to around 10,000 visitors a day — a population increase of over 1,000%. And it’s just one of a growing number of places where residents are up in arms at the influx of travellers.
The term ‘overtourism’ is relatively new, having been coined over a decade ago to highlight the spiralling numbers of visitors taking a toll on cities, landmarks and landscapes. As tourist numbers worldwide return towards pre-pandemic levels, the debate around what constitutes ‘too many’ visitors continues. While many destinations, reliant on the income that tourism brings, are still keen for arrivals, a handful of major cities and sites are now imposing bans, fines, taxes and time-slot systems, and, in some cases, even launching campaigns of discouragement in a bid to curb tourist numbers.
What is overtourism?
In essence, overtourism is too many people in one place at any given time. While there isn’t a definitive figure stipulating the number of visitors allowed, an accumulation of economic, social and environmental factors determine if and how numbers are creeping up.
There are the wide-reaching effects, such as climate change. Coral reefs, like the Great Barrier Reef and Maya Bay, Thailand, made famous by the Leonardo DiCaprio film, The Beach , are being degraded from visitors snorkelling, diving and touching the corals, as well as tour boats anchoring in the waters. And 2030 transport-related carbon emissions from tourism are expected to grow 25% from 2016 levels, representing an increase from 5% to 5.3% of all man-made emissions, according to the United Nations World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO). More localised issues are affecting locals, too. Renters are being evicted by landlords in favour of turning properties into holiday lets, and house prices are escalating as a result. As visitors and rental properties outnumber local residents, communities are being lost. And, skyrocketing prices, excessive queues, crowded beaches, exorbitant noise levels, damage at historical sites and the ramifications to nature as people overwhelm or stray from official paths are also reasons the positives of tourism can have a negative impact.
Conversely, ‘undertourism’ is a term applied to less-frequented destinations, particularly in the aftermath of the pandemic. The economic, social and environmental benefits of tourism aren't always passed on to those with plenty of capacity and, while tourist boards are always keen for visitors to visit their lesser-known attractions, it’s a more sustainable and rewarding experience for both residents and visitors.

What’s the main problem with it?
Overcrowding is an issue for both locals and tourists. It can ruin the experience of sightseeing for those trapped in long queues, unable to visit museums, galleries and sites without advance booking, incurring escalating costs for basics like food, drink and hotels, and faced with the inability to experience the wonder of a place in relative solitude. The absence of any real regulations has seen places take it upon themselves to try and establish some form of crowd control, meaning no cohesion and no real solution.
Justin Francis, co-founder and CEO of Responsible Travel, a tour operator that focuses on more sustainable travel, says “Social media has concentrated tourism in hotspots and exacerbated the problem, and tourist numbers globally are increasing while destinations have a finite capacity. Until local people are properly consulted about what they want and don’t want from tourism, we’ll see more protests.”
A French start up, Murmuration, which monitors the environmental impact of tourism by using satellite data, states that 80% of travellers visit just 10% of the world's tourism destinations, meaning bigger crowds in fewer spots. And, the UNWTO predicts that by 2030, the number of worldwide tourists, which peaked at 1.5 billion in 2019, will reach 1.8 billion, likely leading to greater pressure on already popular spots and more objection from locals.
Who has been protesting?
Of the 800 residents in the UNESCO-listed village of Hallstatt, around 100 turned out in August to show their displeasure and to push for a cap on daily visitors and a curfew on tour coach arrivals.
Elsewhere, residents in Venice fought long and hard for a ban on cruise ships, with protest flags often draped from windows. In 2021, large cruise ships over 25,000 tonnes were banned from using the main Giudecca Canal, leaving only smaller passenger ferries and freight vessels able to dock.
In France, the Marseille Provence Cruise Club introduced a flow management system for cruise line passengers in 2020, easing congestion around the popular Notre-Dame-de-la-Garde Basilica. A Cruise Lines International Association (CLIA) spokesperson said, “Coaches are limited to four per ship during the morning or afternoon at the Basilica to ensure a good visitor experience and safety for residents and local businesses. This is a voluntary arrangement respected by cruise lines.”
While in Orkney, Scotland, residents have been up in arms at the number of cruise ships docking on its shores. At the beginning of 2023, the local council confirmed that 214 cruise ship calls were scheduled for the year, bringing around £15 million in revenue to the islands. Following backlash from locals, the council has since proposed a plan to restrict the number of ships on any day.

What steps are being taken?
City taxes have become increasingly popular, with Barcelona increasing its nightly levy in April 2023 — which was originally introduced in 2012 and varies depending on the type of accommodation — and Venice expects to charge day-trippers a €5 fee from 2024.
In Amsterdam this summer, the city council voted to ban cruise ships, while the mayor, Femke Halsema, commissioned a campaign of discouragement, asking young British men who planned to have a 'vacation from morals’ to stay away. In Rome, sitting at popular sites, such as the Trevi Fountain and the Spanish Steps, has been restricted by the authorities.
And in Kenya’s Maasai Mara, meanwhile, the Narok County governor has introduced on-the-spot fines for off-roading. He also plans to double nightly park fees in peak season.
What are the forecasts for global tourism?
During the Covid pandemic, tourism was one of the hardest-hit industries — according to UNWTO, international tourist arrivals dropped 72% in 2020. However, traveller numbers have since been rapidly increasing, with double the number of people venturing abroad in the first three months of 2023 than in the same period in 2022. And, according to the World Travel Tourism Council, the tourism sector is expected to reach £7.5 trillion this year, 95% of its pre-pandemic levels.
While the tourism industry is forecast to represent 11.6% of the global economy by 2033, it’s also predicted that an increasing number of people will show more interest in travelling more sustainably. In a 2022 survey by Booking.com, 64% of the people asked said they would be prepared to stay away from busy tourist sites to avoid adding to congestion.
Are there any solutions?
There are ways to better manage tourism by promoting more off-season travel, limiting numbers where possible and having greater regulation within the industry. Encouraging more sustainable travel and finding solutions to reduce friction between residents and tourists could also have positive impacts. Promoting alternative, less-visited spots to redirect travellers may also offer some benefits.
Harold Goodwin, emeritus professor at Manchester Metropolitan University, says, “Overtourism is a function of visitor volumes, but also of conflicting behaviours, crowding in inappropriate places and privacy. Social anthropologists talk about frontstage and backstage spaces. Tourists are rarely welcome in backstage spaces. To manage crowds, it’s first necessary to analyse and determine the causes of them.
Francis adds: “However, we must be careful not to just recreate the same problems elsewhere. The most important thing is to form a clear strategy, in consultation with local people about what a place wants or needs from tourism.”
As it stands, overtourism is a seasonal issue for a small number of destinations. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, a range of measures are clearly an option depending on the scale of the problem. For the majority of the world, tourism remains a force for good with many benefits beyond simple economic growth.
Related Topics
- OVERTOURISM
- SUSTAINABLE TOURISM
You May Also Like

How can tourists help Maui recover? Here’s what locals say.

One of Italy’s most visited places is an under-appreciated wine capital
Fuel their curiosity with your gift.

What is tourist tax and will you have to pay it in Europe this summer?

In this fragile landscape, Ladakh’s ecolodges help sustain a way of life

Cinque Terre’s iconic ‘path of love’ is back. Don’t love it to death

25 breathtaking places and experiences for 2023

See the relentless beauty of Bhutan—a kingdom that takes happiness seriously
- Environment
- Perpetual Planet
- History & Culture
- Paid Content
History & Culture
- Gory Details
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
What is Tourism and its pros and cons elaborated
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tourism: A Comprehensive Overview
Tourism is a crucial part of the global economy, contributing significantly to job creation , economic growth, and cultural exchange. However, tourism also has its disadvantages, including environmental degradation, cultural erosion, and the potential for exploitation. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the advantages and disadvantages of tourism.
Advantages of Tourism
- Economic benefits: One of the most significant advantages of tourism is the economic benefits it provides. Tourism generates income for local businesses and creates job opportunities for people in the host community. It also boosts the local economy by increasing the demand for goods and services.
- Cultural exchange: Tourism can be an excellent way for people to experience different cultures and ways of life. It promotes understanding and tolerance between different groups and can help to break down cultural barriers.
- Preservation of heritage sites: Tourism can help to preserve heritage sites by providing the necessary funding and resources for their maintenance and restoration. This, in turn, helps to protect the cultural and historical significance of these sites for future generations.
- Environmental awareness: Tourism can promote environmental awareness by encouraging tourists to adopt sustainable travel practices. This includes reducing their carbon footprint, conserving natural resources, and minimizing waste.
Disadvantages of Tourism
- Environmental degradation: Tourism can have a negative impact on the environment , including increased pollution, depletion of natural resources, and destruction of wildlife habitats.
- Cultural erosion: Tourism can lead to the erosion of traditional cultures and ways of life. This is especially true in areas where tourism is the primary source of income, and local communities are forced to adapt to meet the needs of tourists.
- Exploitation: Tourism can lead to the exploitation of local communities, particularly in developing countries where labor laws are lax, and workers are not protected. This includes low wages, long working hours, and poor working conditions.
- Overcrowding: Tourism can lead to overcrowding, particularly in popular tourist destinations. This can result in traffic congestion, longer wait times, and increased noise levels.
Tourism has its advantages and disadvantages, and it is essential to strike a balance between the two. The benefits of tourism can be significant, but we must also be aware of its potential negative impacts. By adopting sustainable travel practices and promoting responsible tourism, we can ensure that tourism remains a positive force for economic development, cultural exchange, and environmental preservation.
Are you struggling with your paper? Let us handle it - WE ARE EXPERTS!
Get started
Starts at $9 /page
Recent Customer Feedback
See more customer feedback.., how our paper writing service works.
It's very simple!
Complete the order form by providing as much information as possible, and then click the submit button.
Select your preferred writer for the project, or let us assign the best writer for you.
Allocate funds to your wallet. You can release these funds to the writer incrementally, after each section is completed and meets your expected quality.
Download the finished work. Review the paper and request free edits if needed. Optionally, rate the writer and leave a review.
- Net Zero Features
- Conscious Living Essentials
- Geothermal Energy Installers
- Planet Earth
- Climate Policy
- Sustainability

The Pros and Cons of Tourism
We are reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn affiliate commission.
The tourism industry is one of the most lucrative and essential industries for the global economy since it can provide revenue almost year-round. It allows people to spend time in places they want to explore and enjoy. Every year, people from all over the world visit destinations like Paris, Hawaii, Mexico and Japan to experience a new culture through food, sightseeing and adventures.
Tourism provides thousands of jobs each year and allows people to explore the world at their leisure. It’s excellent for both the people touring an area themselves for happiness and well-being, and it’s great for the country’s population as a whole.
However, the disadvantages of tourism should be addressed, especially concerning the environment. Tourism industries in some countries often ignore these cons because they want to continue providing revenue for the peoples’ livelihoods. It’s easy to overlook the negative aspects when tourism has brought enormous wealth to developing countries.
If developing nations only rely on tourism and dismiss other aspects, like the environment, society and infrastructure development, the cons can quickly outweigh the pros. Fortunately, there are ways to be sustainable in the tourism industry. Here are the pros and cons of tourism.
The Pros of Tourism
From stimulating job growth to bridging cultural divides, tourism has many benefits for people, the economy and the environment. Below are five advantages of tourism.
1. Creates Jobs
One of the most significant benefits of tourism is creating jobs for people who may have previously been unemployed. Tourism accounts for about 10% of employment worldwide , whether directly or indirectly.
The tourism industry encompasses retailers, restaurant workers, transportation industries, entertainment facilities and hospitality workers. It can even include medical workers as some people travel for cosmetic surgery or medical advice and medications. This leads to the reduction of unemployment in many countries, which reduces the burden on the government.
2. Develops Countries
As more people get jobs in developing countries, they can further progress. The government can get the funds needed to advance their nation. The tourism industry offers more security and financial stability. Plus, the government can carry out various infrastructure projects to continue its progression by building roads, hospitals, hotels, restaurants, and entertainment businesses to allow more people to stay, generating more jobs and wealth.
3. Conserves the Environment
Some of the primary attractions in countries are the historical sights and beautiful landscapes. Often, countries try to conserve these sights and attractions to continue bringing in more tourists. Governments and private entities often use tourism money to maintain historical sight and protect the environment.
4. Broadens Knowledge and Appreciation of Nature
An airboat ride through the Florida Everglades delivers more than the perfect photo opportunity. Airboat captains share stories about the river’s history, wildlife facts, environmental issues plaguing the ecosystem, and how the average person can make a difference. Travel experiences like this are crucial for broadening one’s knowledge and deepening their appreciation for the natural world. The hope is for tourists to impart their knowledge to someone else and spark an interest in conservation and sustainable habits.
5. Encourages Culture-Learning
Finally, tourism encourages the learning of different cultures. It helps to create a sense of unity among people from various cultures and countries. Tourism encourages people of all backgrounds to visit a particular place, so tourist destinations become a melting pot of other cultures. People can begin to understand one another and may even make friends with people from other countries.
The Cons of Tourism
While welcoming visitors to explore a particular area has benefits — especially within the eco-tourism subsector — it’s not all rainbows and sunshine. Unfortunately, there are some cons of tourism that often get overlooked, such as the following.
1. Damages the Environment
Although countries do their best to conserve the environment, including animals, plants and natural scenes, tourists can still be disrespectful. As people flock to one place, waste and pollution accumulate. Sometimes, tours offer animal experiences as well, which put animals through suffering. Further, land is needed to accommodate tourists, so countries will destroy habitats to build hotels and restaurants.
2. Puts Pressure on Natural Resources
Another con of the tourism industry is that it puts an immense amount of pressure on natural resources. Anytime someone stays in an area, they inevitably use the area’s natural resources , like water and food. Cities and countries around the world have faced droughts. Additionally, tourism puts stress on the local land use, leading to soil erosion which can cause damage to infrastructure.
3. Strains Infrastructure
Too many tourists in one location can significantly strain infrastructure, including roadways, water resources and waste disposal. For instance, nearly 30 million tourists visit Venice, Italy, annually, crowding narrow canals and limited roadways. In the Caribbean, Antigua and Barbuda is among the most frequently vacationed and water-stressed countries, with under 1000 cubic meter of freshwater resources per capita. Without a municipal wastewater treatment center, most households rely on poorly built septic tanks.
4. Encourages Dependence on Tourism
It’s not a good thing to be solely dependent on tourism. Regions known for their tourist destinations learned that lesson once COVID-19 spread throughout the world. When people could no longer travel, the tourism industry in countries that depended on it had a more difficult time recovering and getting the necessary resources that locals needed to survive. Without tourists, those countries would receive no more income, which affects the entire country.
5. Leads to Loss of Cultural Identity
Often, locals in a tourist destination will begin copying the lifestyles of tourists and leave their local and cultural traditions behind. Instead of shops filled with daily necessities for the locals, they are filled with things tourists need, like travel-sized toiletries and souvenirs. Fast-food chains have taken over local cuisine as well. And unfortunately, tourism has led to a growth in prostitution and human trafficking.
Making Tourism a More Sustainable Industry
Tourism is a necessary part of the economy, but the adverse effects often go unnoticed. Fortunately, there are ways to make it a more sustainable industry. Tourists should support the local economy, avoid single-use plastics, take more eco-friendly modes of transportation and avoid all of the traditional “tourist” excursions. The next time you travel, make sustainability a priority.
This post was last updated on April 9, 2024 to provide more current information.
Thanks for subscribing! Please check your email for further instructions.
Like what you read? Join other Environment.co readers!
Get the latest updates on our planet by subscribing to the Environment.co newsletter!
About the author
What Groups Set Hunting Regulations in Most States?

Let These Green Neighborhood Projects Inspire You

What Are Microplastics? Here’s What We Know

How to Compost Leaves: 5 Steps to Keep Your Pile Healthy

Where to Take Plastic Bags for Recycling Near Me

What Are the Benefits of Using Reusable Water Bottles?

10 Economic impacts of tourism + explanations + examples
There are many economic impacts of tourism, and it is important that we understand what they are and how we can maximise the positive economic impacts of tourism and minimise the negative economic impacts of tourism.
Many argue that the tourism industry is the largest industry in the world. While its actual value is difficult to accurately determine, the economic potential of the tourism industry is indisputable. In fact, it is because of the positive economic impacts that most destinations embark on their tourism journey.
There is, however, more than meets the eye in most cases. The positive economic impacts of tourism are often not as significant as anticipated. Furthermore, tourism activity tends to bring with it unwanted and often unexpected negative economic impacts of tourism.
In this article I will discuss the importance of understanding the economic impacts of tourism and what the economic impacts of tourism might be. A range of positive and negative impacts are discussed and case studies are provided.
At the end of the post I have provided some additional reading on the economic impacts of tourism for tourism stakeholders , students and those who are interested in learning more.
Foreign exchange earnings
Contribution to government revenues, employment generation, contribution to local economies, development of the private sector, infrastructure cost, increase in prices, economic dependence of the local community on tourism, foreign ownership and management, economic impacts of tourism: conclusion, further reading on the economic impacts of tourism, the economic impacts of tourism: why governments invest.
Tourism brings with it huge economic potential for a destination that wishes to develop their tourism industry. Employment, currency exchange, imports and taxes are just a few of the ways that tourism can bring money into a destination.
In recent years, tourism numbers have increased globally at exponential rates, as shown in the World Tourism Organisation data below.
There are a number of reasons for this growth including improvements in technology, increases in disposable income, the growth of budget airlines and consumer desires to travel further, to new destinations and more often.

Here are a few facts about the economic importance of the tourism industry globally:
- The tourism economy represents 5 percent of world GDP
- Tourism contributes to 6-7 percent of total employment
- International tourism ranks fourth (after fuels, chemicals and automotive products) in global exports
- The tourism industry is valued at US$1trillion a year
- Tourism accounts for 30 percent of the world’s exports of commercial services
- Tourism accounts for 6 percent of total exports
- 1.4billion international tourists were recorded in 2018 (UNWTO)
- In over 150 countries, tourism is one of five top export earners
- Tourism is the main source of foreign exchange for one-third of developing countries and one-half of less economically developed countries (LEDCs)
There is a wealth of data about the economic value of tourism worldwide, with lots of handy graphs and charts in the United Nations Economic Impact Report .
In short, tourism is an example of an economic policy pursued by governments because:
- it brings in foreign exchange
- it generates employment
- it creates economic activity
Building and developing a tourism industry, however, involves a lot of initial and ongoing expenditure. The airport may need expanding. The beaches need to be regularly cleaned. New roads may need to be built. All of this takes money, which is usually a financial outlay required by the Government.
For governments, decisions have to be made regarding their expenditure. They must ask questions such as:
How much money should be spent on the provision of social services such as health, education, housing?
How much should be spent on building new tourism facilities or maintaining existing ones?
If financial investment and resources are provided for tourism, the issue of opportunity costs arises.
By opportunity costs, I mean that by spending money on tourism, money will not be spent somewhere else. Think of it like this- we all have a specified amount of money and when it runs out, it runs out. If we decide to buy the new shoes instead of going out for dinner than we might look great, but have nowhere to go…!
In tourism, this means that the money and resources that are used for one purpose may not then be available to be used for other purposes. Some destinations have been known to spend more money on tourism than on providing education or healthcare for the people who live there, for example.
This can be said for other stakeholders of the tourism industry too.
There are a number of independent, franchised or multinational investors who play an important role in the industry. They may own hotels, roads or land amongst other aspects that are important players in the overall success of the tourism industry. Many businesses and individuals will take out loans to help fund their initial ventures.
So investing in tourism is big business, that much is clear. What what are the positive and negative impacts of this?

Positive economic impacts of tourism
So what are the positive economic impacts of tourism? As I explained, most destinations choose to invest their time and money into tourism because of the positive economic impacts that they hope to achieve. There are a range of possible positive economic impacts. I will explain the most common economic benefits of tourism below.

One of the biggest benefits of tourism is the ability to make money through foreign exchange earnings.
Tourism expenditures generate income to the host economy. The money that the country makes from tourism can then be reinvested in the economy. How a destination manages their finances differs around the world; some destinations may spend this money on growing their tourism industry further, some may spend this money on public services such as education or healthcare and some destinations suffer extreme corruption so nobody really knows where the money ends up!
Some currencies are worth more than others and so some countries will target tourists from particular areas. I remember when I visited Goa and somebody helped to carry my luggage at the airport. I wanted to give them a small tip and handed them some Rupees only to be told that the young man would prefer a British Pound!
Currencies that are strong are generally the most desirable currencies. This typically includes the British Pound, American, Australian and Singapore Dollar and the Euro .
Tourism is one of the top five export categories for as many as 83% of countries and is a main source of foreign exchange earnings for at least 38% of countries.
Tourism can help to raise money that it then invested elsewhere by the Government. There are two main ways that this money is accumulated.
Direct contributions are generated by taxes on incomes from tourism employment and tourism businesses and things such as departure taxes.
Taxes differ considerably between destinations. I will never forget the first time that I was asked to pay a departure tax (I had never heard of it before then), because I was on my way home from a six month backpacking trip and I was almost out of money!
Japan is known for its high departure taxes. Here is a video by a travel blogger explaining how it works.
According to the World Tourism Organisation, the direct contribution of Travel & Tourism to GDP in 2018 was $2,750.7billion (3.2% of GDP). This is forecast to rise by 3.6% to $2,849.2billion in 2019.
Indirect contributions come from goods and services supplied to tourists which are not directly related to the tourism industry.
Take food, for example. A tourist may buy food at a local supermarket. The supermarket is not directly associated with tourism, but if it wasn’t for tourism its revenues wouldn’t be as high because the tourists would not shop there.
There is also the income that is generated through induced contributions . This accounts for money spent by the people who are employed in the tourism industry. This might include costs for housing, food, clothing and leisure Activities amongst others. This will all contribute to an increase in economic activity in the area where tourism is being developed.
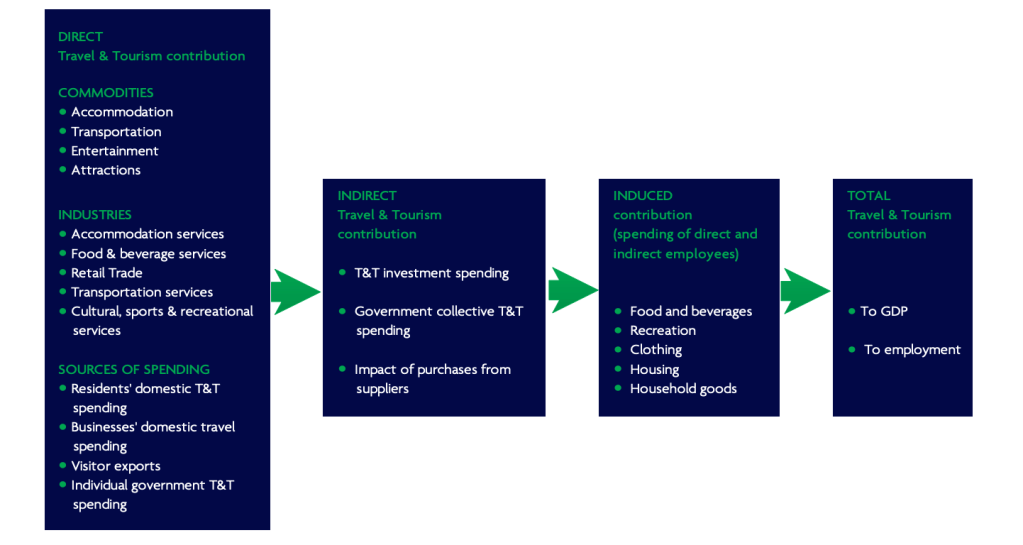
The rapid expansion of international tourism has led to significant employment creation. From hotel managers to theme park operatives to cleaners, tourism creates many employment opportunities. Tourism supports some 7% of the world’s workers.
There are two types of employment in the tourism industry: direct and indirect.
Direct employment includes jobs that are immediately associated with the tourism industry. This might include hotel staff, restaurant staff or taxi drivers, to name a few.
Indirect employment includes jobs which are not technically based in the tourism industry, but are related to the tourism industry. Take a fisherman, for example. He does not have any contact of dealings with tourists. BUT he does sell his fish to the hotel which serves tourists. So he is indirectly employed by the tourism industry, because without the tourists he would not be supplying the fish to the hotel.
It is because of these indirect relationships, that it is very difficult to accurately measure the economic value of tourism.
It is also difficult to say how many people are employed, directly and indirectly, within the tourism industry.
Furthermore, many informal employments may not be officially accounted for. Think tut tut driver in Cambodia or street seller in The Gambia – these people are not likely to be registered by the state and therefore their earnings are not declared.
It is for this reason that some suggest that the actual economic benefits of tourism may be as high as double that of the recorded figures!
All of the money raised, whether through formal or informal means, has the potential to contribute to the local economy.
If sustainable tourism is demonstrated, money will be directed to areas that will benefit the local community most.
There may be pro-poor tourism initiatives (tourism which is intended to help the poor) or volunteer tourism projects.
The government may reinvest money towards public services and money earned by tourism employees will be spent in the local community. This is known as the multiplier effect.
The multiplier effect relates to spending in one place creating economic benefits elsewhere. Tourism can do wonders for a destination in areas that may seem to be completely unrelated to tourism, but which are actually connected somewhere in the economic system.

Let me give you an example.
A tourist buys an omelet and a glass of orange juice for their breakfast in the restaurant of their hotel. This simple transaction actually has a significant multiplier effect. Below I have listed just a few of the effects of the tourist buying this breakfast.
The waiter is paid a salary- he spends his salary on schooling for his kids- the school has more money to spend on equipment- the standard of education at the school increases- the kids graduate with better qualifications- as adults, they secure better paying jobs- they can then spend more money in the local community…
The restaurant purchases eggs from a local farmer- the farmer uses that money to buy some more chickens- the chicken breeder uses that money to improve the standards of their cages, meaning that the chickens are healthier, live longer and lay more eggs- they can now sell the chickens for a higher price- the increased money made means that they can hire an extra employee- the employee spends his income in the local community…
The restaurant purchase the oranges from a local supplier- the supplier uses this money to pay the lorry driver who transports the oranges- the lorry driver pays road tax- the Government uses said road tax income to fix pot holes in the road- the improved roads make journeys quicker for the local community…
So as you can see, that breakfast that the tourist probably gave not another thought to after taking his last mouthful of egg, actually had the potential to have a significant economic impact on the local community!

The private sector has continuously developed within the tourism industry and owning a business within the private sector can be extremely profitable; making this a positive economic impact of tourism.
Whilst many businesses that you will come across are multinational, internationally-owned organisations (which contribute towards economic leakage ).
Many are also owned by the local community. This is the case even more so in recent years due to the rise in the popularity of the sharing economy and the likes of Airbnb and Uber, which encourage the growth of businesses within the local community.
Every destination is different with regards to how they manage the development of the private sector in tourism.
Some destinations do not allow multinational organisations for fear that they will steal business and thus profits away from local people. I have seen this myself in Italy when I was in search of a Starbucks mug for my collection , only to find that Italy has not allowed the company to open up any shops in their country because they are very proud of their individually-owned coffee shops.
Negative economic impacts of tourism
Unfortunately, the tourism industry doesn’t always smell of roses and there are also several negative economic impacts of tourism.
There are many hidden costs to tourism, which can have unfavourable economic effects on the host community.
Whilst such negative impacts are well documented in the tourism literature, many tourists are unaware of the negative effects that their actions may cause. Likewise, many destinations who are inexperienced or uneducated in tourism and economics may not be aware of the problems that can occur if tourism is not management properly.
Below, I will outline the most prominent negative economic impacts of tourism.

Economic leakage in tourism is one of the major negative economic impacts of tourism. This is when money spent does not remain in the country but ends up elsewhere; therefore limiting the economic benefits of tourism to the host destination.
The biggest culprits of economic leakage are multinational and internationally-owned corporations, all-inclusive holidays and enclave tourism.
I have written a detailed post on the concept of economic leakage in tourism, you can take a look here- Economic leakage in tourism explained .

Another one of the negative economic impacts of tourism is the cost of infrastructure. Tourism development can cost the local government and local taxpayers a great deal of money.
Tourism may require the government to improve the airport, roads and other infrastructure, which are costly. The development of the third runway at London Heathrow, for example, is estimated to cost £18.6billion!
Money spent in these areas may reduce government money needed in other critical areas such as education and health, as I outlined previously in my discussion on opportunity costs.

One of the most obvious economic impacts of tourism is that the very presence of tourism increases prices in the local area.
Have you ever tried to buy a can of Coke in the supermarket in your hotel? Or the bar on the beachfront? Walk five minutes down the road and try buying that same can in a local shop- I promise you, in the majority of cases you will see a BIG difference In cost! (For more travel hacks like this subscribe to my newsletter – I send out lots of tips, tricks and coupons!)
Increasing demand for basic services and goods from tourists will often cause price hikes that negatively impact local residents whose income does not increase proportionately.
Tourism development and the related rise in real estate demand may dramatically increase building costs and land values. This often means that local people will be forced to move away from the area that tourism is located, known as gentrification.
Taking measures to ensure that tourism is managed sustainably can help to mitigate this negative economic impact of tourism. Techniques such as employing only local people, limiting the number of all-inclusive hotels and encouraging the purchasing of local products and services can all help.
Another one of the major economic impacts of tourism is dependency. Many countries run the risk of becoming too dependant on tourism. The country sees $ signs and places all of its efforts in tourism. Whilst this can work out well, it is also risky business!
If for some reason tourism begins to lack in a destination, then it is important that the destination has alternative methods of making money. If they don’t, then they run the risk of being in severe financial difficulty if there is a decline in their tourism industry.
In The Gambia, for instance, 30% of the workforce depends directly or indirectly on tourism. In small island developing states, percentages can range from 83% in the Maldives to 21% in the Seychelles and 34% in Jamaica.
There are a number of reasons that tourism could decline in a destination.
The Gambia has experienced this just recently when they had a double hit on their tourism industry. The first hit was due to political instability in the country, which has put many tourists off visiting, and the second was when airline Monarch went bust, as they had a large market share in flights to The Gambia.
Other issues that could result in a decline in tourism includes economic recession, natural disasters and changing tourism patterns. Over-reliance on tourism carries risks to tourism-dependent economies, which can have devastating consequences.

The last of the negative economic impacts of tourism that I will discuss is that of foreign ownership and management.
As enterprise in the developed world becomes increasingly expensive, many businesses choose to go abroad. Whilst this may save the business money, it is usually not so beneficial for the economy of the host destination.
Foreign companies often bring with them their own staff, thus limiting the economic impact of increased employment. They will usually also export a large proportion of their income to the country where they are based. You can read more on this in my post on economic leakage in tourism .
As I have demonstrated in this post, tourism is a significant economic driver the world over. However, not all economic impacts of tourism are positive. In order to ensure that the economic impacts of tourism are maximised, careful management of the tourism industry is required.
If you enjoyed this article on the economic impacts of tourism I am sure that you will love these too-
- Environmental impacts of tourism
- The 3 types of travel and tourism organisations
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism glossary
- 50 fascinating facts about the travel and tourism industry
- 23 Types of Water Transport To Keep You Afloat

18 Advantages and Disadvantages of Tourism
Tourism is the act of traveling for leisure, recreation, or business purposes. It involves the movement of people to destinations outside their usual environment for a certain period of time.
The purpose of this article is to examine the advantages and disadvantages of tourism, with a focus on its economic, cultural, and social effects.
The article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the benefits and drawbacks of tourism, and to encourage readers to consider the impact of their travel on local communities and the environment.

- Redaction Team
- February 17, 2023
- Professional Development , Study in Germany
Advantages of Tourism
- Job creation and income generation : Tourism provides jobs in a variety of industries, such as hotels, restaurants, transportation, and entertainment. Tourist attractions, local businesses and historical sites can lead to increased source of income for local residents and a boost to the overall economy.
- Increase in foreign exchange : Tourism can also bring in foreign currency, as tourists typically spend money on goods and services while visiting a destination. This can help to stabilize the economy and lead to growth.
- Development of infrastructure : Tourism can also lead to the infrastructure development, such as roads, airports, and public transportation systems. This can improve the overall hospitality and quality of life for residents and make the destination more attractive to future tourists.
- Exposure to different cultures : Tourism allows people to experience different cultures and ways of life, which can broaden their perspectives and promote understanding and tolerance.
- Preservation of heritage sites : Tourism can also help to preserve tourism-related heritage sites, as the income generated by tourism can be used to fund their maintenance and restoration.
- Cultural exchange : Tourism also provides many countries opportunities for cultural exchange, as tourists and locals interact and share their customs and traditions.
- Promotion of international understanding : Tourism sector can promote international understanding by bringing people from different cultures together and fostering mutual respect and understanding.
- Increase in community involvement : Tourism can also increase community involvement, as residents may become more engaged in efforts to attract tourists and improve their destination.
- Development of tourism industry : Tourism also can lead to the development of the tourism industry, which can create hotels and places to stay, jobs and economic opportunities in a destination.
These are some examples of how tourism accounts can be beneficial and positively impact different aspects of society, however, it’s important to note that not all tourism activities are carried out in a sustainable and responsible way, which can lead to negative consequences.
Advantages of Jasper AI
- Damage to natural habitats and wildlife : Tourism can have a negative impact on the environment, as it can lead to the destruction of natural habitats and the displacement of wildlife. Activities such as excessive hiking, off-roading, and building of tourism infrastructure can generate environmental damage to natural resources.
- Pollution and waste management : Tourism can also lead to an increase in pollution and waste, as large numbers of tourists can generate a significant amount of trash, sewage, and other waste products. This can put a strain on local waste management systems and have negative impacts on the environment and generate natural disasters.
- Overcrowding of popular destinations : Popular tourist destinations can become overcrowded, which can lead to strain on local resources and the degradation of the natural environment. This can also make it difficult for tourists to fully enjoy their experience as they may feel like they are fighting for space with other visitors.
- Disruption of local communities : Tourism can disrupt local communities by altering traditional ways of life, and leading to the displacement of residents. This can cause social and cultural changes that may not be beneficial to everyone in the community.
- Exploitation of local resources and culture : Tourism can also lead to the exploitation of local resources, as well as the commercialization and commodification of local culture. This can lead to the loss of authenticity in tourist destinations and the erosion of traditional ways of life.
- Loss of authenticity in tourist destinations : Some places can become too commercialized and lose their authenticity, being transformed into tourist traps, this can lead to a loss of charm and interest for the tourists, and local residents might feel like they are living in a theme park.
- Dependence on tourism industry : A destination can become too dependent on tourism, and if the tourism industry were to decline, it could have a severe economic impact on the community.
- Widening income gap : Tourism can also lead to a widening income gap, as the benefits of tourism may not be distributed equally among all members of a community. This can lead to an increase in poverty, and social inequality.
- Inflation : Tourism can also lead to inflation, as the demand for goods and services increases, prices may rise, making it more difficult for residents to afford necessities.
Conclusion of Pros and Cons of Tourism
Tourism can bring many benefits to a destination, including economic growth, cultural exchange, and increased community involvement. However, it can also have negative impacts, such as environmental degradation, disruption of local communities, and exploitation of local resources and culture.
To minimize the negative impacts of tourism and to promote sustainable development, it is important to plan and manage tourism marketing activities in a responsible and sustainable way. This includes measures such as setting limits on the number of tourists, protecting natural habitats and wildlife, and involving local communities in tourism planning.
Overall, tourism can be a valuable tool for economic and social development, but it’s important to consider its potential negative consequences and to strive for sustainable tourism practices. This way, tourists, locals, and the environment can all benefit from tourism activities.

Privacy Overview

Pros and Cons of Tourism
Be it Niagara Falls, The Grand Canyon, or the Amazon Rainforest, these places have numerous reasons to attract tourists every year. Tourists love to visit such spots looking for fun, amusement, and even finding peace of mind. Tourism has turned into a thriving industry in many countries. Governments and local communities reap the benefits of tourism in many different ways. But those advantages come with certain risks as well. However, like everything else, there are pros and cons of tourism . You should be taking a closer look at the good and the bad of tourism before you set a vacation schedule alone or with your friends and families.
What are the Pros of Tourism?
In 2021, tourism to Grand Canyon National Park made a significant contribution of $710 million to the local economy, reports National Park Service.
1. Economic Boost
Tourism is a significant contributor to the economy of a country. By attracting tourists, nations can create sustainable revenue streams, generate job opportunities, and boost growth across several sectors. According to a report by NPS, the park welcomed approximately 4.5 million visitors to the Grand Canyon, spending an estimated $710 million in the surrounding gateway regions.
2. Cultural Exchange
Travel can bring people together and provide a unique opportunity to share ideas and experiences. Travelers often have an open mind about different cultures and customs, so they are eager to explore new places. This type of exchange can break down cultural barriers between countries by allowing each party to understand the other's culture better. This exchange of cultural values can be counted as one of the major advantages of tourism.
3. Environmental Conservation
All natural heritages are tourist spots, and people come to admire the view. One of the significant advantages of tourism is that it can help protect and preserve the environment. Local governments can invest the revenue generated by tourism for the betterment of environmentally sensitive regions and areas with fragile ecosystems.
4. Improved Infrastructure is Among the Pros of Tourism
With the influx of tourists, countries can consider upgrading their infrastructure to accommodate visitors' needs. This includes constructing new airports, roads, accommodations, and public facilities such as parks and museums. This positive change can be felt both by the tourists and the inhabitants.
5. Global Recognition
Tourism is an essential part of many countries economies, and it can also provide significant global recognition for the destination. A well-designed tourism strategy that attracts a high volume of international visitors can bring in foreign money, create jobs, and help to develop infrastructure. It also raises awareness about an area, leading to increased interest from the rest of the world.
What are the Cons of Tourism?
Besides the positive changes, tourism also has its share of downsides. Most of the cons of the tourism industry are associated with the misuse of natural resources. Some of the other problems with tourism include:
1. Environmental Damage
Tourism can lead to environmental damage in many ways. For example, it can impact water resources through increased water and wastewater production demand. It can also add to pollution by generating emissions from transportation as visitors travel around the area. Additionally, tourists may increase pressure on local land resources, leading to deforestation and loss of habitats for native species.
2. Displaced Communities
Tourism often brings economic benefits to local communities. Still, when done in a way that does not consider the local community's needs and aspirations, it can cause displacement. Communities may be displaced from their traditional lands or homes, pushing them away from the resources they need for subsistence. This can be particularly detrimental if these resources are already scarce or difficult to access.
3. Cultural Erosion
Cultural Erosion is one of the most dreaded cons of tourism. A tourist destination with a distinct local culture is prone to changes due to the influx of tourists. The more tourism activities are higher the chances of community displacement.
This phenomenon is often compounded by the fact that many tourists come from cultures very different to those of the local community, and their presence can lead to a sudden change in cultural values. This rapid transition can significantly damage a community as its members may no longer feel represented or respected.
4. Economic Dependence
The COVID-19 pandemic best explains how tourism can suddenly burden an economy. As the pandemic wiped out all income for many countries' businesses, many had to rely heavily on government support and bailouts as their primary sources of revenue. This has resulted in rising debts due to emergency aid distributions and other fiscal measures associated with relief during this crisis.

5. Overcrowding
Visiting a particular area can harm the environment and local culture as tourism grows. One of the main disadvantages of tourism is overcrowding, which can strain resources, increase pollution, and damage natural habitats.
Overcrowding can decrease the quality of life for residents, as tourists take up public space and resources. It can also affect the health and safety of visitors who may be exposed to increased levels of crime or air pollution.
Conclusion on the Pros and Cons of Tourism
The pros and cons of tourism are complex if you evaluate them thoroughly. It is easy to see that people benefit from increased access to new cultures, experiences, and destinations.
On the other hand, there are real risks associated with tourist activities like over-tourism and the destruction of natural spaces. Therefore, it's up to individuals to assess these impacts on their own terms. It's up to every citizen to become responsible travelers who understand tourism's positive and negative effects.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the cons of tourism.
Tourism frequently exerts excessive strain on natural resources due to overconsumption, particularly in areas with limited resources. It places immense pressure on local land utilization, resulting in soil erosion, heightened pollution levels, loss of natural habitats, and increased jeopardy for endangered species.
What are the pros of tourism?
It fosters job creation, bolsters the local economy, facilitates infrastructure development, preserves the natural environment and cultural heritage, and works towards alleviating poverty and inequality.
What are the social benefits of tourism?
Tourism brings forth numerous social benefits, showcasing its positive impacts on society. These encompass the preservation of local culture and heritage, the fostering of vibrant communities, the provision of essential social services, the promotion of cultural and artistic commerce, the revitalization of customs and art forms, as well as the safeguarding of our precious heritage.
Who does tourism help?
Tourists contribute to the local economy by spending their money, leading to job creation and economic growth. This support is particularly crucial for small businesses, which often struggle to generate substantial profits.
What's your reaction?
Quick links.
- » Home
- » About us
- » Contact us
- » Post Article
- » Privacy policy
- » Terms and Conditions
- » Health and Wellness
- » Education and Communication
- » Computers and Electronics
- » Personal Care and Style
- » Travel Updates and Tourism Guide
- » Finance and Business Sector
- » Food and Entertainment
- » Home and Garden
- » Automobiles Sector
Tourism; Pros and Cons, Facts and Environmental Impact.
- by Ahsen Soomro

Table of Contents Show
1. wealth generation, 2. the progression of a country, 3. creation of jobs, 4. unity among different societies, 5. conservation, 6. improves geographical identity worldwide, 7. damage to the environment by tourists, 8. exploitation of local culture, 9. non-compliance of tourists, 10. lack of job security/seasonal only, 11. confined to service jobs, 12. unequal infrastructure growth, 13. foreign business owners, 14. neglecting of other sectors, 5+ fun facts on tourism, environmental damage, invasive organisms, negative impact on wildlife, loss of natural resources, challenging stereotypes, gaining cultural sensitivity, authentic experience of cultures.
Tourism is the department or an organization that facilitates people to allow them to visit or spend vacations at places they like.
Tourism is one of the most important industries in any country. It is a large contributor to the economy of a country as it can provide revenue throughout the year. Tourism helps in keeping the employment rate of countries stable as several job opportunities are created due to the tourism industry.
Sometimes, tourism can be a major source of foreign income for the country. This is like Maldives where 40% of the economy is generated from the Tourism industry.
This transaction doesn’t only facilitate the vacation or relaxation of tourists visiting these regions, but also helps to provide a better livelihood to everyone involved in the tourism sector.
Developed countries like USA and UK have greatly benefitted from medical tourism. Medical tourism involves people travelling to developed countries to get treatments unavailable in their home country. These are usually people from developing countries with sub-standard health care. You can also call them a medical tourist !
However, even with the great number of benefits of tourism, there are several drawbacks to it. These disadvantages are sometimes ignored by the tourism sector of that country as their sole purpose becomes profit. We must consider all aspects of tourism which include environmental responsibilities, profit and sustainability.
Today, we will look at some of the Pros and Cons of Tourism;
Advantages of Tourism
One of the major advantages of Tourism is a constant flow of cash. It is very important not just for the economy of the country as a whole but for all those working in the tourism sectors.
Commercial and private airlines operating from these countries tend to make a ton of revenue as people from around the world fly to a tourist attraction. Hotels and guest homes in the hospitality industry make a constant income as travelers flood hotel lobbies looking for a place to stay. This makes sure hotels make money throughout the year.
These small sectors, that come under the umbrella of tourism help to generate money for the country throughout the year. This cash flow is even more essential for small, developing, and third world nations as for some of them the tourist sector might be the biggest contributor to their local economy.
As wealth influx starts in the country, it helps the government to procure necessary funds for development and progression of the country. The tourism sector gives security and stability to the economy of the nation, preventing it from tanking in times of crisis.
The government also gets necessary funds to carry out large scale infrastructure projects like restaurants, hotels, casinos and theater which may further improve the tourism sector, providing more places for travelers to stay and more activities to indulge in. This will help to generate further cash influx.
Other than that, this wealth can also be used to improve the infrastructure of the country. This includes building roads, rail roads, better hospitals and education centers for natives as well as the tourists.
Tourism has provided various jobs to people who were previously unemployed. The natives gifted with constant stable jobs have greatly improved their livelihood ( there is a possible catch to this, I’ve explained in the cons ).
These jobs include working in areas such as hotels, restaurants, bars, casinos, theatres, zoos, parks, entertainment facilities, and more. Some of those you might remember from your last trip, especially the travel agent who booked your tickets or the tour operator who ensured that your trip went smooth or the captain of your cruise ship in the Caribbean. They work relentlessly, away from their families, to make sure you enjoy your vacations.
This has also led to the overall reduction of unemployment in the country, thus reducing burden on the government.
Did you know? 1 in 10 jobs are supported by Tourism industry across the world!
The unique feature of tourism is that it helps to create unity among people from different countries, cultures, backgrounds, traditions, and ethnicities who are all visiting to have some fun.
It allows people to learn different histories, traditions, cultures, diets, and lifestyles of the nations they are visiting. This helps to create understanding and oneness among people which can have a long-lasting impact socially.

Cross-cultural connections are developed as the natives interact with the tourists and may lead to further large-scale collaborations as well!
The main star of attraction for tourists visiting a country is its historical sites and landscapes, particularly the landmarks of the country. These landmarks may be in the form of churches, mosques, cathedrals, monuments, buildings, skyscrapers, beaches, amusement parks, and other attractions to say the least.
This means it becomes the government’s utmost priority to conserve these sites, for the tourism industry to be sustainable.
The government carries out regular maintenance of such areas and rules are placed concerned with damaging or vandalism of the property in order to protect these spots. Once these areas become a part of the tourism sector, they are no less than a cash generator for the country.
Tourists often go back home and praise about the vacation that they had. Every person that goes back home brags to at-least 10 more people about the wonderful vacation they had, usually through social media. This allows more people to know more about the country and helps it earn its name and make a place for itself on the map!
Increased recognition leads to further foreign investment and development, followed with increased tourism activity in the area.
Major Cons of Tourism
When it comes to tourism thousands of people may visit, even millions in some spots. This high influx of tourists can lead to immense environmental destruction, especially in destinations where tourists are more prone to visit.
This environmental burden is not solely due to the high influx of tourists, but it is associated with various other factors working together to bring environmental harm.
These factors include increased presence and use of cars, buses, trains, and other vehicles which may raise carbon emissions. A large number of flights at the airport could become a large contributor of air pollution as well.
Tourists can cause a lot of land pollution; as they throw a massive amount of garbage and waste, which is mostly non-biodegradable, leading to a massive number of landfills. All these activities may combine to greatly impact the environment of the region.
Soil erosion, Different kinds of Pollution , habitat loss and destruction as well as forest fires are just some of the environmental effects of tourism.

If these regions are not conserved and taken care of properly, they will lose their natural essence and subsequently be abandoned by tourists. This can lead to permanent damage of the natural tourist attractions!
Fortunately, we have been observing a rise in demand of sustainable tourism. We’ll be discussing that very soon.
Some countries, seeing the vast amount of tourists coming in their country to observe their unorthodox lifestyle and traditions, begin to commercialize their culture. It can be in the form of souvenirs. Usually, the natives are not offended by this.
However, in some regions this can be considered an outright disgrace and mocking of their culture. This is especially true for the regions where locals consider their culture to be their identity. Commercializing may result in people just wearing costumes and exhibiting traditions just to entertain tourists. Observing that the governments are using their culture as a tool for profiteering can cause them to feel sad and ridiculed by their nation.
Sometimes, tourists do not honor cultures and traditions of countries/regions they visit. They may break certain rules and unspoken codes of conduct to which the locals have very high regard. Tourists get drunk in public and do horrendous acts at times. This creates certain hatred among the locals for the incoming tourists.
Racist remarks by tourists and the socioeconomic gap between the tourists and the natives may further exacerbate the issue. The tourists may consider themselves in much higher regard than the natives. Such thoughts may provoke the tourists to act wildly and unlawfully, and sometimes even end up mocking the nation.
Look at it this way; if you go to a friend’s house, you don’t outright break stuff at his home or start shouting remarks to his/her family. You respectfully meet your friend and have a good time, in good spirits. That’s the way you should treat natives when you’re visiting another country, because you’re visiting their home !
Although we did mention that tourism leads to an increase in the employment rate; sometimes these jobs can be seasonal depending on the region and hence, cannot be a dependable income throughout the year. This is more concerning in countries that have specific durations and seasons of high influx of tourists from around the world. These seasonal jobs, hence, offer minimal job security and employees can be left without a proper pension or insurance.
Although tourism generates jobs for locals, most of these jobs are confined to service industry with minimal wages. These low-wage and minimum-skill workers have little ambition to promotion and getting higher up the chain.
Massive income generated from tourism offers countries to build upon infrastructure of the tourist destination only. Sadly, the countries do not use the revenue generated from this infrastructure to build and develop other regions which require maintenance and development.
The wealth generated from tourism is put back into tourism-related things and regions that desperately need improvement are constantly neglected. The locals who don’t live in tourist-economy regions are neglected which leads to imbalance of infrastructure development.
Sometimes most of the places which are heavily infiltrated by tourists are owned by foreign businesses. This means most of the profits and money coming into the country are being used by foreigners thereby causing significant loss of local businesses.
Local industries miss out on the primary source of income that is required for them to stay afloat and to grow. This can lead to businesses going bankrupt and losing, overall damaging the country’s economy.
Countries see that tourist is the major source of income for them, tend to ignore other various sectors upon which they are built. This leads to nations neglecting these sectors, thus causing a loss of income, jobs, and growth amongst these sectors. The country aims to put all of its resources in one basket which is the tourism industry, will leaving all others behind for them to crumble and diminish.
This over-reliance on a specific sector for the stability of the nations can sometimes cause a massive impact, especially during times of war, political instability, or natural disasters as it will be led to the long term closure of the tourism of those countries due to unrest. This can eventually drain the country down as its only resource which is tourism is no longer function, and it didn’t have any other sector nor did they built any other sector in a way for them to become sustainable in times of economic crisis.
- Tourism is responsible for 5% of the Global GDP!
- China stays as the world’s top tourism spender, spending more than 260 Billion Dollars!
- Global tourism industry being the largest industry contributes more than 7.5 trillion dollars in the world economy.
- Almost 10% of world’s jobs are sourced from Tourism Industry.
- Tourists spend the most cash in Dubai. Around 28.5 Billion dollars yearly!
- Osaka in Japan is emerging as the hottest tourist spot in the world.
Negative Environmental Impacts of Tourism
The government may choose to put the wealth generated from tourism into preservation of the environment. However, tourism still goes on to put sufficient burden on the natural resources of our planet and prompts over-consumption of natural resources in regions with already limited resources.
Once tourism becomes unsustainable, the surrounding environment starts to deteriorate. Tourism has a wide impact on the air quality, vegetation, water supply, wildlife, and the natural ecosystems of the region.
Most of the tourist activities have a negative impact on ecosystems. These include fishing, hiking, and snorkeling; all of which tend to affect and deplete the local scenery.
To run a tropical golf course for tourists requires water that can feed up to 60,000 locals. There is a trail in the Himalayas known as “the toilet paper trail” which shows how much damage tourism has caused to the environment.

Once there is an influx of tourists to a common destination, there is an overuse of transportation systems which heavily contributes to pollution (Mainly air pollution). Tourism accounts for 60% of air travel worldwide, and flying one mile in a plane can produce 53 pounds of carbon dioxide.
Even travelers conscious of hurting the environment also cause a negative impact. Tourists that travel to natural sites located remotely, tend to cause damage to natural ecosystems they come to see.
The increased human presence on many geographical regions can alter the number of native plants in the region and introduce non native species in those areas.
Even species brought in as pets into the country are sometime released into the wild and could bring havoc upon the ecosystem if they turned out to be invasive species.

Human intervention and presence can disrupt food webs, ecological communities, and harm keystone species in an area. Others take an active approach and hunt foreign animals as a tourist activity. They can also damage the natural habitat of native wildlife by engaging with it. All of these contribute to wildlife endangerment and extinction.
Tourism can shrink the natural resources by causing over-consumption. This is particularly damaging in areas with food and water scarcity.
This may also lead to hatred among the locals for tourists who use up the limited water supply for luxuries. A natural resource like water could be used to fill up Jacuzzis at a 5-star hotel but could much better be used in feeding a child who suffers from dehydration.
Cultural Benefits of Traveling

When you get to visit another country and observe their culture, you get the opportunity to be exposed to unfamiliar perspectives and traditions and gain a more broad, much informed, and kinder view of the locals and places you encounter.
Perceptions and stereotypes might be replaced by first hand view of the people by the tourists themselves.
People get to see traditions and learn manners of different cultures. Manners and etiquette tourists may not have practiced in their native countries.
Pointing with your index fingers at the indigenous people, showing excessive skin, wearing shoes indoors, and making noises may be considered rude in some places.
So it is important to do a little bit of research on the local customs and traditions before visiting so you can try to avoid being offensive or inappropriate.
It can be a wonderful way to experience the insights of a different culture through the experience of traditions, rituals, festivals, celebrations, and rites. It gives the visitor a chance to understand the cultural heritage of a region much more deeply.
Tourism has its benefits to the economy but the environmental component of tourism shouldn’t be ignored. Think about that the next time you book your tickets. We are also working on reducing your environmental footprint when you travel…Can’t reveal more. Stay tuned!
For now I’d like to leave this picture for you to ponder about Eco-tourism.

Ahsen Soomro
My love for nature is not newfound. I have lived on the countryside for over a decade of my life where I realized how human activities impacted the environment. Later during my stint in medical school, I realized that many of our health concerns originate from neglecting our environmental responsibilities and this was just not sustainable in the long run. Raising awareness, not locally but globally, was the mission. This led to the foundation of EnvironmentBuddy!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Differences between Deforestation, Afforestation and Reforestation!
Afforestation; importance, advantages & disadvantages. current efforts, you may also like.

- 4 minute read
Bottled Water vs Tap Water; What to drink?
- No comments

- 7 minute read
13 Major Pros and Cons of Gated Communities

- 13 minute read
31 Must-Have Mock Cherry Trees You’ll Love

- 9 minute read
6 Signs of Bad Parenting and How they Affect the Child

- 5 minute read
What is Water Scarcity? 9 Reasons Behind It

Plastic Bag Decomposition Process
- What Are The Negative Effects Of Tourism On The Environment?

Tourism is usually regarded as a boon to a region’s economy. Tourism brings prosperity to the region and provides employment to the locals of the region. However, when tourism becomes unsustainable in nature, it can have disastrous consequences on the environment. When the tourist industry active in the region crosses the legal and ethical barriers to earn more profit, it can lead to massive degradation of the environment in the area. Local human population, flora, and fauna, suffer greatly due to such irresponsible and unsustainable tourism. Some of the ways in which tourism adversely impacts the environment have been mentioned below:
Tourism And Pollution
Transport of tourists results in air pollution.
The movement of tourists from their home to the tourist destination involves transport via road, rail, or air, or a combination of these modes of transport. When a large number of tourists are involved, it invariably leads to a greater use of the transportation system. We all are aware of the fact that emissions from automobiles and airplanes are one of the biggest causes of air pollution. When a large number tourists use these modes of transport to reach a particular attraction, it pollutes the air both locally and globally. Due to the rapid growth in international tourism, tourists now account for nearly 60% of air travel. In many places, buses or other vehicles leave their motors running to ensure that tourists return to comfortable air-conditioned vehicles. Such practices further pollute the air.
Tourism Leads To Noise Pollution
Tourists destinations are often subject to significant noise pollution. Tourists vehicles entering and leaving natural areas create a lot of noise. Such noise is the source of distress for wildlife. Loud music played by tourists in forested areas also disturb the animals living in the area. Often, noise generated by tourist activities for long-term alters the natural activity patterns of animals.
Littering Of Tourist Spots By Irresponsible Tourists
Irresponsible tourists often litter the tourist spots visited by them. Waste disposal is a great problem in the natural environment. According to estimates, cruise ships in the Caribbean produce over 70,000 tons of waste annually. If waste is disposed of irresponsibly in the sea, it can lead to the death of marine animals. Even the Mount Everest is not free of human-generated waste. Trekkers leave behind their oxygen cylinders, garbage, and camping equipment on the mountains and hills. Some trails in the Himalayas and the Andes have been nicknamed the "Toilet paper trail” or the "Coca-Cola trail,” referring to the garbage left behind on such trails.
Sewage Generated At Tourist Spots Contaminate The Natural Environment
Rampant construction of tourist facilities like hotels, cafes, restaurants, etc., in an area without proper arrangement for safe disposal of sewage, can lead to disastrous consequences. Wastewater carrying sewage from such areas often pollutes nearby water bodies. It can lead to the eutrophication of water bodies and the loss of the balance in aquatic ecosystems. Pollution of water bodies with sewage can also lead to health issues and even epidemics that can ultimately wipe out large populations of aquatic flora and fauna and also impact human health adversely.
Tourism Can Spoil The Aesthetics Of The Environment
Tourist facilities built to earn a profit without any concern about integrating the design with the natural features of the place can lead to aesthetic pollution. Large resorts of disparate designs can dominate the landscape and spoil the natural beauty of a place.
Tourism And Natural Resources
When tourism is encouraged in an area with inadequate resources, it will have a negative impact on the ecosystem of the area. In such areas, the local flora and fauna might be deprived of the resources needed to sustain their lives. For example, large volumes of water are consumed to cater to the needs of the tourists, run hotels, swimming pools, maintain golf courses, etc. This can degrade the quality of water and decrease the volume of water that is available for the local population, plants, and animals. It is not only the water resources that are depleted. Unsustainable practices by the tourist industry can also put pressure on other resources like food, energy, etc.
Tourism And Physical Degradation Of The Ecosystem
Every ecosystem works on a delicate natural balance. Every species in the ecosystem has a specific role to play in the system. However, tourism often disturbs this delicate balance and creates a great disaster in the ecosystem. When the tourist industry active in an area is completely profit-minded, it pays little heed to the needs of nature. For example, often hotels and resorts are built illegally very close to the beach or inside the core areas of forests. Large patches of natural vegetation need to be cleared to allow space for the sprawling resorts or hotels. As old tourist spots get degraded due to overuse by tourists, newer ‘upcoming’ destinations with fewer crowds become the next favorite of tourists and the tourism industry. The same situation is repeated once more. Unsustainable practices by the tourism industry can thus lead to deforestation, sand erosion, loss of species, changes in sea currents and coastlines, destruction of habitats, etc. Even activities like nature walks can be harmful to the environment if tourists trample on the local vegetation during their walk. Such trampling can lead to reduced plant vigor, breakage of stems, reduced regeneration, etc. Tourists breaking off corals during snorkeling or scuba diving activities can also contribute to ecosystem degradation. Commercial harvesting of corals for sale to tourists also causes harm to coral reefs. Even the anchorage of cruise ships to coral reefs can degrade large sections of the reef.
- Environment
More in Environment

Importance Of Wetlands

Meet 12 Incredible Conservation Heroes Saving Our Wildlife From Extinction

India's Leopard God, Waghoba, Aids Wildlife Conservation In The Country

India's Bishnoi Community Has Fearlessly Protected Nature For Over 500 Years

Wildfires And Habitat Loss Are Killing Jaguars In The Amazon Rainforest

In India's Sundarbans: Where People Live Face-To-Face With Wild Tigers

Africa's "Thunderbird" Is At Risk Of Extinction

Why Is Biodiversity Critical To Life On Earth?
Understanding and overcoming negative impacts of tourism in city destinations: conceptual model and strategic framework
Journal of Tourism Futures
ISSN : 2055-5911
Article publication date: 15 November 2017
Issue publication date: 15 December 2017
The purpose of this paper is to clarify the mechanisms of conflict between residents and tourists and to propose a conceptual model to assess the impact of such conflicts on city tourism and to suggest a framework to develop strategies to deal with such conflicts and mitigate negative impacts.
Design/methodology/approach
Based on desk research a conceptual model was developed which describes the drivers of conflicts between residents and visitors. Building blocks of the model are visitors and their attributes, residents and their attributes, conflict mechanisms and critical encounters between residents and visitors, and indicators of the quality and quantity of tourist facilities. Subsequently the model was used to analyse the situation in Hamburg. For this analysis concentration values were calculated based on supply data of hotels and AirBnB, app-data, and expert consultations.
The study shows that in Hamburg there are two key mechanisms that stimulate conflicts: (1) the number of tourists in relation to the number of residents and its distribution in time and space; (2) the behaviour of visitors measured in the norms that they pose onto themselves and others (indecent behaviour of tourists).
Research limitations/implications
The model that was developed is a conceptual model, not a model with which hypotheses can be tested statistically. Refinement of the model needs further study.
Practical implications
Based on the outcomes of the study concrete strategies were proposed with which Hamburg could manage and control the balance of tourism.
Originality/value
City tourism has been growing in the last decades, in some cases dramatically. As a consequence, conflicts between tourists, tourism suppliers and inhabitants can occur. The rise of the so-called sharing economy has recently added an additional facet to the discussion. The ability to assess and deal with such conflicts is of importance for the way city tourism can develop in the future. This study is an attempt to contribute to the understanding of the mechanism behind and the nature of those conflicts, and the way they can be managed and controlled. Besides it illustrates how data generated by social media (apps) can be used for such purposes.
- City tourism
Conflict mechanisms
- Host-guest relations
- Overtourism
- Tourism impact studies
- Visitor management
Postma, A. and Schmuecker, D. (2017), "Understanding and overcoming negative impacts of tourism in city destinations: conceptual model and strategic framework", Journal of Tourism Futures , Vol. 3 No. 2, pp. 144-156. https://doi.org/10.1108/JTF-04-2017-0022
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2017, Albert Postma Dirk Schmuecker
Published in the Journal of Tourism Futures. Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Introduction
Tourism is subject to massive growth. Projections made by the World Tourism Organisation anticipate a growth to 1.8 billion international arrivals worldwide till 2030. Based on its World Tourism Monitor, IPK states that city tourism is the fastest growing market segment in tourism ( IPK International, 2016 ). The direct and indirect effects of this increase in visitor numbers seem to cause an increase in annoyance among residents, which could lead to conflicts between tourists, tourism suppliers and inhabitants. The rise of the so-called sharing economy has recently added an additional facet to the discussion. During the past few years various media have reported on incidents, residents protests and the like. However, the humming-up of media may occasionally obscure the difference between actual conflicts perceived in the population and what interested actors in the media make of it. Here, only a careful analysis of the actual situation would help. On the other hand, such conflicts and the discussion about it are neither new nor limited to large cities. Yet, the focus of the discussion has shifted over the last decades: from tourism to developing countries, residents of villages in the Alps which have found themselves into ski-circuses, or greenlanders suffering from the rush of cruise ships. Recently, the discussion has shifted to where a large proportion of tourists go: from and to the European cities. Data from the German Reiseanalyse, an annual survey on holiday travel in Germany ( Schmücker et al. , 2016 ), suggest that in 2014, 31 per cent of the population and 33 per cent of German holiday makers were at home in cities with more than 100,000 inhabitants. In the cities, holiday travel is more than 80 per cent higher than in the countryside.
Tourism generates income and employment for cities, and thanks to tourism the liveliness and liveability in cities is boosted because many shops, services and facilities would not exist without that additional customer base. However, with an eye on the (social) sustainability of city tourism development, it is important to understand whether and how residents’ annoyance comes about and with which measures residents’ attitude could be kept within the margins of their tolerance level. Postma (2013) studied residents’ experiences with tourism in four tourism destinations. He identified three categories of so called “critical encounters”, four levels of annoyance, four levels on tolerance, and three levels of loyalty towards tourism development. The European Tourism Futures Research Network did a pilot study in Riga, Berlin and Amsterdam to investigate the applicability of Postma’s outcomes in an urban context. When this proved valid, the approach was used by the Dutch Centre of Expertise in Leisure, Tourism and Hospitality (CELTH) in a European study on visitor pressure in the city centres of Copenhagen, Berlin, Munich, Amsterdam, Barcelona and Lisbon. A second phase of this study just started in the Flemish cities of art (Antwerp, Bruges, Ghent, Leuven and Mechelen), Tallin and Salzburg. In this study residents were consulted to identify critical encounters and the support for various kinds of strategies to deal with it. Finally, NIT and ETFI conducted a study in Hamburg addressing these issues in 2015/2016.
The domain of tourism impact studies
The study presented here is an example of a tourism impact study. The domain of tourism impact studies has evolved since the second world war, echoing the development of tourism, its characteristics and its perception. During the first phase (1960-1970) the emphasis of tourism impact studies was on the positive economic impacts of tourism. Tourism was mainly seen as a means to strengthen economies. In the 1970s and 1980s, the focus gradually shifted to the negative social, cultural and environmental impacts. This reflected the growing concern of industrialisation, sustainability and quality of life. Ultimately in the 1980s and 1990s the interest of tourism impact studies moved to integrating the economic perspective with the social and environmental one. Tourism had continued to grow, had become more diffuse, and had become more interconnected with societies and economies. The divide in tourism impact studies between economic and social and environmental perspectives, and the emphasis on tourism and destinations as two different worlds impacting upon each other (nicely illustrated in binary terminology such as host and guest) gradually moved to a growing interest into the multidimensional relation between tourism and communities; the process by which tourism is shaped by the interactions between, tourism, host environments, economy and societies; and the meaning of tourism for society ( Postma, 2013 ; Pizam, 1978 ; Jafari, 1990, 2005, 2007 ; Butler, 2004 ; Hudson and Lowe, 2004 ; Ateljevic, 2000 ; Crouch, 1999, 2011 ; Williams, 2009 ; Sherlock, 2001 ). This so called cultural turn in tourism impact studies ( Milne and Ateljevic, 2001 ) opened the door to new research areas raising attention on themes and issues that were largely overlooked or marginalised before ( Causevic and Lynch, 2009 ), for instance, “the multiple readings of local residents while working, living, playing or, in other words, consuming and producing their localities through encounter with tourism” ( Ateljevic, 2000 , pp. 381-382).
According to Deery et al. (2012) , tourism impact studies have grown into a massive and mature field of study covering a wide spectrum of economic, social and environmental dimensions. However, Williams asserts that there is still a lack of understanding of the relationship between tourism and destination communities, both because the number of empirical studies, inconclusive or conflicting results of empirical studies, and a contested conceptual basis ( Williams, 2009 ). Postma (2013) confirms that mainstream tourism impact literature does not offer useful theoretical frameworks for tourism impact studies that focus on the tourism community relations.
Sustainable tourism
Although the notion of sustainable development has led to considerable debate since its introduction which in part is due to its vagueness for concrete action, it is incorporated as an important starting point in contemporary policy and planning worldwide. This also applies to tourism, where the basic ideas of sustainable development were gradually translated into the concept of sustainable tourism development. The first ideas were introduced by Krippendorf (1984) , and they were elaborated in the Brundtland report ( World Commission on Environment and Development, 1987 ) and the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development in Rio de Janeiro in 1992. The ideas presented in the Rio Declaration on Environment and Development and in Agenda 21 guided the World Conference on Sustainable Tourism in Lanzarote in 1995, where the core principles were established ( France, 1997 ; Martin, 1995 ). In line with sustainable development, sustainable tourism development tries to establish a suitable balance between economic, environmental and social aspects of tourism development to guarantee its long-term sustainability ( World Tourism Organisation, 2004 ). The World Tourism Organisation’s core principles of sustainable tourism development are: to improve the quality of life of the host community; to provide high quality experience for visitors; and to maintain the quality of the environment, on which both the host community and the visitors depend ( Mill and Morrison, 2002 ).
Sustainable development and sustainable tourism development do not aim at prosperity and material gains but primarily at well-being and quality of life ( Postma, 2001, 2003 ; Postma and Schilder, 2007 ; Jackson, 1989 ; Burns, 1999 ). In this view residents should be both the starting point and the checkpoint for tourism policy and planning. As the negative perception of tourism affects the way in which residents perceive their quality of community life ( Kim, 2002 ), the long-term sustainability of tourism might be negatively affected by any impacts from tourism causing irritation, annoyance, or anger among local residents. The threshold level at which enthusiasm and support for tourism turns into irritation could be regarded as an indicator of the edge of sustainable development. Therefore, sustainable tourism development requires both greater efforts to incorporate the input of residents in the planning process both in communities exposed to tourism for the first time and in established destinations experiencing increased volumes of tourists ( Burns and Holden, 1997 ; Harrill, 2004 ), as well as to studying host community attitudes and the antecedents of residents’ reactions ( Zhang et al. , 2006 ). As Haywood (1988) states: “Local governments should be more responsible to the local citizens whose lives and communities may be affected by tourism in all its positive and negative manifestations” (in Burns and Holden, 1997 ).
Thus, understanding current and potential conflicts between residents and tourists is an integral part of the sustainable tourism debate. By definition, sustainable tourism development does have an ecological, economic and social dimension. It may be argued that the inclusion of the needs of the inhabitants stimulates the traditional understanding of a tourism market between buyers and sellers: while consumers look for tourism experiences and providers look for business opportunities, the claims of residents are more extensively focussed on an adequate quality of life ( Postma, 2003 ). The larger the interfaces between these three stakeholder groups, the more conflict-free tourism will be able to develop ( Figure 1 ).
For (city) tourism, it seems advisable to define the concept of sustainability in a broad and comprehensive way. Sustainable tourism thus entails “acceptance by the population”, and the population is clearly a part of the social dimension. The participation of the population and securing/increasing the acceptance of tourism is therefore also one of the objectives for Hamburg’s sustainable tourism development. To develop tourism in a sustainable way, in Hamburg as in other cities, the challenge is to bring the quality of life demands of the inhabitants (social dimension) and the quality-of-opportunity requirements of the providers (economic dimension) as far as possible into line.
The case of Hamburg
The aim of this viewpoint paper is to contribute to the conceptualisation of tourism community relations and to clarify the mechanisms of conflict between residents and tourists and to propose a conceptual model to assess the impact of such conflicts on city tourism and to suggest a framework to develop strategies to deal with such conflicts and mitigate negative impacts. This model was developed for a study in Hamburg that addressed the balanced and sustainable growth of tourism in the city. Hamburg is one of the most popular city destinations in Germany. The city, located in the north of the country, is faced with a gradual increase of visitor numbers, especially during the past few years. Internal papers of Hamburg’s Destination Management Organisation, Hamburg Tourismus ( HHT, 2015 ), show that between 2001 and 2015, the number of overnight stays in Hamburg increased with over 150 per cent, which is more than, for example, Barcelona (+112 per cent), Venice (+120 per cent), Amsterdam (+54 per cent) and Berlin (+153 per cent). Although the negative implications of tourism are not as visible as in some other European cities, critiques are getting louder in selected parts of the city, as shown by a regular resident monitoring implemented by HHT. Strategies to distribute tourism flows in time and space could help to prevent or to counteract. The study, commissioned by HHT, is an attempt to contribute to the understanding of the mechanisms behind and the nature of possible conflicts between tourists, tourism suppliers and residents and the way they can be managed and controlled, for example, by making use of data generated by social media. Based on desk research, a conceptual model was developed which describes the drivers of conflict between residents and visitors. Building blocks of the model are visitors and their attributes, residents and their attributes, conflict mechanisms and areas of conflict between both parties, and indicators of quality and quantity of tourist facilities. Subsequently the model was used to analyse the situation in Hamburg.
Conflict drivers and irritation factors
To develop a better understanding of the mechanism of conflict between tourists, tourism suppliers and residents, desk research was conducted into potential areas of conflict between locals and tourists, which factors would characterize particularly vulnerable residents and particularly disturbing locals, and what would be strategic options to manage and control the (occurrence) of such conflicts.
There is danger that for a focus on only negative aspects in the interaction between tourists and locals would cause bias. Therefore, it should be stressed that – for the destination – tourism is not an end in itself, but primarily an economic and, second, a social potential. Economically, tourism usually has positive effects for the inhabitants, mainly through the money flowing in from the outside, which tourists spend in the city and for the city. This money leads to tourist turnover, which is reflected in income. This income can be in the form of salaries, income from self-employment, company profits, or from the leasing or sale of land, buildings or flats. Indirectly, tourism revenues also contribute to the creation and maintenance of infrastructures and (tourist) offers which can also be used by residents. This applies to most cultural institutions (from the opera to the zoo), but also for public transport offers, gastronomy, etc. Socially, tourism can lead to desirable effects in the destination as well. This includes the (simple) encounter with others (provided they are “encounters on eye”), a general stimulation and a social enrichment and liveliness of the city.
It is especially in the economic dimension, where the dilemma to which involvement with tourism could sometimes lead, becomes clear. If an apartment is rented as a holiday home rather than as a permanent living space, because the landlord will get a higher income (in some cases at lower costs and lower risk), this is undoubtedly disadvantageous for the regular tenants and land-lords of houses undoubtedly advantageous. An assessment of this dilemma is therefore not only possible based on (short-term) economic considerations, but must consider long-term and non-economic aspects. The understanding of such balancing processes and the existence of potentially positive and negative effects of tourism is fundamental to the overall further consideration.
The study of the interaction between tourists and the residents of the destination has already shown a longer academic tradition (see Harrill, 2004 ; Zhang et al. , 2006 ; Andereck et al. , 2005 ; Vargas-Sánchez et al. , 2008 ). However, Postma notes: “A review of the literature concerning residents’ attitude toward tourism revealed an absence of research exploring factors that specifically contribute or cause irritation development, with the exception of Doxey’s (1975) article and the authors who quote him or elaborated and described his model in more detail, such as Murphy (1985) , Fridgen (1991) , Ryan (1991) , Matthieson and Wall (1982) , Wall and Mathieson (2006) , Vanderwerf (2008) and Milligan (1989) . Based on empirical investigations he designed an irritation index, describing four stages in the development of irritation: euphoria, apathy, annoyance, and antagonism. The model of this “irridex” describes the changing attitude of residents ensuing from reciprocal impacts between tourists and residents and varying degrees of compatibility between the residents and outsiders. According to Doxey (1975) irritation differs from person to person: it is affected by various personal characteristics and various characteristics of the tourist destination.
Much literature is devoted to investigating the positive and negative impacts of tourism. Rátz and Puczkó (2002) have summarised these impacts. This overview indicates that irritation might develop along four dimensions: population impacts, transformation of the labour market, changes in community characteristics and community structure, impacts at the individual and family level, and impacts on the natural and cultural resources ( Postma, 2013 , p. 25) lists the socio-cultural impacts of tourism, which is the focus of this study.
Model construction
The results of the desk research were put together in a conceptual framework to conceptualise the complex issue under study, that has largely been unexplored in this way so far. The model helps to identify and visualise possible irritation points on the part of the inhabitants and their (possibly disturbing) interaction with visitors. Just like other models, this conceptual model is a schematic abstraction of reality. It takes individual, relevant aspects into account, while other aspects might be neglected. The intention is not to be complete, but to visualise reality and identify relevant issues. So, the model presented here is abstract and descriptive. It is not a scientific structure or measurement model from which statistical hypotheses can be derived, but rather a “thinking structure” for further investigation.
The overview of positive and negative possible effects of tourism on the social dimension of tourism by Rátz and Puczkó (2002) is a first starting point for the modelling process. A second starting point is the Tourist Destination Model as developed by NIT, which has been evolved throughout many years ( Schmücker, 2011 ). Further starting points for the modelling process were reports and survey results from cities in which there have already been clearly observed annoyances among the local population because of tourism. A particularly prominent example is Barcelona (even a film was recorded), but also cities like Venice, Vienna, Amsterdam or Berlin are not only reported in the local, national and international press.
For the elaboration of a conceptual model, it is first necessary to clarify which content should be taken into account. First, the key actors: tourists and their characteristics, and residents and their characteristics. Second, attributes of the tourist product because their quantity and quality of the tourism opportunity spectrum are the prerequisite for tourists to visit the city at all. This includes both the specific tourist offer (hotel industry, semi-professional, private and sharing offers, MICE offers) as well as the offers which are aimed at both tourists and locals (cultural offers, gastronomy, mobility, etc.).
With these building blocks, the essential conflict mechanisms and concrete fields of conflict can be described, as well as strategic courses of action against the objectives of sustainable tourism development. The model is displayed in Figure 2 .
The model shows the interaction between local residents and tourists, its conditions and consequences. Conditioned by the attributes of both parties, and of conflict mechanisms between the two (sensitivity to) areas of conflict do arise. The model helps to understand how this process works. Based on intensive data collection and data analysis the model was applied in Hamburg to make an analysis of the distribution in time and space of overnight stay accommodation, events and visitor flows, the annoyance tourism caused among local residents, and the strategies that could be taken to manage tourism flows in a sustainable way. In the following sections the components of the model will be described in detail.
Relevant characteristics of tourists
“Adaptivity”: the ability of tourists to adapt to the people in the destination and their habits. “Adaptive” behaviour can be divided into general and specific. General adaptive behaviour is at work in many cultures, for example, general friendliness and restraint. Specific adaptive behaviour can include behaviour accepted by some cultures, but by others (e.g. preparing food in the hotel room or visiting sacred buildings with/without head cover). The larger the cultural distance between the locals and the tourists, the greater their adaptiveness should be to avoid conflicts.
“Tourism culture”: it seems plausible to attribute a greater potential for irritation to tourists with certain behaviours, travel situations or group sizes than others. In particular tourist trips that are mainly aimed at enjoyment in the city. Eye-catching examples can be actions such as bachelor parties, visits to sporting events and the like. In connection with conspicuous behaviour (e.g. shouting, drinking, etc.) the irritation potential increases significantly. This behaviour is often different from home. “[It] can be labelled as a tourist culture, a subset of behavioural patterns and values that tend to emerge only when the visitors are travelling but which, when viewed by local people in receiving areas, project a false and misleading image of the visitors and the societies they represent” ( Postma, 2013 , p. 144). Group size belongs to the same category: it can be assumed that tourists coming in (large) groups, tend to generate irritation easier than individual tourists.
Other demographic, socio-cultural and personal characteristics: of course there are other characteristics of tourists that could cause irritation or annoyance. However, it seems plausible to consider, for example, purely demographic attributes (such as age, gender, household type and size) as background variables rather than primary features in the model. The same applies to other attributes that contribute to the adaptivity, to socio-cultural attributes (nationality, ethnicity, language, attitude to women), to socio-economic attributes (such as income and consumption patterns) and to the regional origin of the visitors. Regardless of the adaptivity, the regional origin can be a relevant driver of irritation. Even if tourists behave in a very friendly and reserved manner, their appearance may be irritating some inhabitants due to specific characteristics (such as skin colour, language/dialect or clothing). Even if there is no objective cause for complaint, strangeness as such can cause irritation.
It is important to emphasise that these background variables are not directly affecting behaviour in a direct way. Stephen Williams (2009 , p. 144) comments: “The behaviour patterns of visitors often divert from their socio-cultural norms and do not accurately represent the host societies from which they originate, with conspicuous increases in levels of expenditure and consumption, or adoption of activities that might be on the margins pf social acceptability at home (e.g. drinking, overeating, gambling, atypical dress codes, nudity, semi nudity)”.
Relevant characteristics of inhabitants
On the part of the inhabitants, a fairly large number of potential attributes can be identified in the literature which could influence their attitude towards the tourists.
demographic characteristics: gender, age, education;
socio-economic characteristics: employment and income situation, housing situation (place of residence, duration of residence, property/rented), personal relationship to the city/district, attitude to economic growth;
socio-psychological and socio-cultural characteristics: orientation (new vs traditional) and lifestyle, origin (born and raised or migrant, born in city or country), personality traits such as self-image and group identity; and
tourism-specific characteristics: knowledge about tourism and its effects, income dependence from tourism, spatial distance to tourist hotspots and actual contacts with tourists, involvement in decisions about tourism development.
Harrill (2004) , Zhang et al. (2006) , Andereck et al. (2005) , Vargas-Sánchez et al. (2008) , Faulkner and Tideswell (1997) .
Investigations into residents’ perceptions of tourism have been approached from several perspectives: the balance between positive and negative perceived impacts (social exchange theory), the shared social representations of tourism with other community members (social representations theory; Moscovici, 1981, 1983, 1984, 1988 ), the speed and intensity of tourism growth, especially in the early phases of tourism development (social disruption theory; England and Albrecht, 1984 ; Kang, Long and Perdue, 1996 ) and increasing investments and associated commodification and destruction of the landscape and idyll (theory of creative destruction ( Mitchell, 1998 )).
“Cultural Distance” as a collective term for the cultural difference between tourists and locals. It can take the form of a lack of adaptivity, appearance in (large) groups, disturbing behaviour on the part of the tourists, and a sensitivity on the part of the local (which has its roots in the factors mentioned above) Altogether, cultural distance can be understood as the socio-cultural difference between locals and tourists. The term goes back to Stephen Williams (2009) : the larger the cultural distance, the greater the potential for conflict.
Spatial and temporal distribution. This refers to the crowding (the sheer number of tourists) or the concentration of tourists in space and/or time. This crowding can lead to irritation irrespective of “cultural distance”: even with the highest degree of “correct behaviour” by highly adaptive individual tourists without further disturbing characteristics, crowding can occur.
Each aspect can potentially cause irritation on its own, but in combination the effects become potentially stronger.
Concrete fields of conflict
The components of the model described in the previous section point at conflicts in a more abstract way (which characteristics and features could lead to conflicts and how does this work in general?). This section will focus on the actual (concrete) conflict fields that can occur. The basis for the collection of these fields of conflict is derived from the illustrated antecedents, yet it is mainly about what has been reported by destinations (especially big cities) and survey results.
The numerous arguments, which are mentioned in the literature, but above all in reports and interviews on areas of conflict, can be divided into possible direct restrictions (those which are perceived at the moment of occurrence) and indirect consequences. Table I shows the concrete fields of conflict that were identified in an overview. The fields of conflict are characterised as “potential”, because it is a structured collection without any further statement as to whether and how far these are relevant to Hamburg. Moreover, it is not an overview of fears by the authors, but about fears of local residents as they experienced in their daily lives (e.g. the authors do not believe that the employment of people with an immigration background is a negative consequence of tourism).
It becomes clear that the number of possible conflict fields is large and their structure heterogeneous and not always clearly assignable. In addition, specific developments do not only impact upon the direct interests of the local residents, but also upon the relations between different tourist actors and economic groups. For example, it is not clear yet how the renting through sharing portals has an impact upon the price development in the hotel industry ( Zervas et al. , 2016 ), and how much “sharing” (as opposed to businesses) there really is in the sharing economy ( O’Neill and Ouyang, 2016 ; European Commission, 2016 ).
In the case of Hamburg, conflicts arose from both temporary or seasonal and permanent sources of conflict. Examples of temporary sources of conflict can be large events, but also groups of cruise passengers who flood the city during daytime in the summer season. In the Hamburg case, there are few very large events in the course of the year which can be conflicting with the interests of the inhabitants, although mitigation and management measures have been taken. But also, a permanent area of conflict can be found in the concrete case, e.g. the misbehaviour of groups of drunken or otherwise intoxicated young males (mostly), entering the red-light district around Reeperbahn.
Strategic approaches
For the residents: to secure and increase the acceptance of tourism.
For tourists and touristic providers: to secure and increase tourist value creation.
Against this background, it is important to ask which measures are appropriate to achieve these goals (see also Figure 1 ).
Although this project is primarily aimed at the equalisation of tourism flows, further strategies and actions are conceivable that mitigate the perceived negative effects of tourism.
improved spatial distribution of visitors (Spreading visitors around the city and beyond);
better time distribution of visitors (time-based rerouting);
regulation (regulation);
incentives through creating itineraries;
improved audience segmentation (visitor segmentation);
making the benefit of the inhabitants clearer (make residents benefit from the visitor economy);
tourist offers with benefits for the inhabitants (create city experiences);
communicating with and involving local stakeholders;
communication approaches towards visitors (communicating with and involving visitors); and
improvement of infrastructure (Improve city infrastructure and facilities).
Each of those strategies is linked to specific actions (CELTH, 2016).
Conclusions and discussion
Currently tourism is on the rise and city tourism has a large share in this increase. The UN World Tourism Organisation anticipates a further growth during the years to come. Emerging economies play a major role in the vast increase of tourism. Driven by an increase of wealth the middle classes in these economies are discovering the world and for example, in Europe it is evident that this is causing a growing level of annoyance among residents of (urban) destinations. Because of the rise of international tourism it is likely that the situation will worsen if visitor flows are not managed properly. This requires a thorough understanding of the forces, the conditions and mechanisms at work. This paper is an attempt to contribute to this understanding by means of a case study in Hamburg and the construction of a model that could help to manage visitor flows and anticipate possible effects of potential measures. Future studies are needed to refine the model.
The model developed in this paper is a conceptual model. It is based upon desk research on and expert interviews in various European cities and a literature review. As a conceptual model, it’s main value lies in sorting and arranging the many possible aspects of visitor pressure occurring in city tourism. It can be (and in the case of Hamburg has been) used as a working structure to assess possible fields of conflict arising from the conflict mechanisms contained in the model. Furthermore, it is intended to help clarify the relation between stakeholders (i. e. the residents, the tourism suppliers and the visitors) and their respective objectives. Being conceptual, however, it is not intended to serve as a structural model delivering graphical representations of hypotheses or structural relationships.
Obviously, in order to assess the situation in a specific destination, the conceptual model is only one basic tool. For concrete applications, two more steps need to be taken, building on the model.
First, the concrete fields of conflict have to be identified. These fields will differ in their importance from city to city and from destination to destination. While in one city, cruise tourists flooding the city centre impose problems, it might be stag parties or beer bikes in another destination and the rise of housing prices because of increasing numbers of Airbnbs in the next. Typically, public discussion about “visitor pressure” or “overtourism” starts with one publicly visible field of conflict. The conceptual model can then help to embed this problem into a larger framework and thus prevent it from being discussed in isolation. In other cases, cities want to assess their current status and vulnerability to unbalanced tourism development. Then, the conceptual model can help to get a more holistic view to the problem.
Second, indicators and metrics have to be applied to the concrete fields of conflict. If, e.g. crowding is identified as a field of conflict, then indicators and measurement for crowding need to be found. These can be visitor counts or usage data from apps and mobile phones. If shared accommodation seems to be the problem, then the number of hosts, listings and overnights at Airbnb and other platforms can be appropriate metrics. A major drawback, however, in the current situation seems to be the lack of comparable metrics. Each city and destination has to rely on its own assessment of “how much is too much”. In terms of overnight stays in hotels, a reasonably well maintained European database exists (TourMIS). Furthermore, some methodological approaches to assess some fields of visitor pressure have been published by McElroy (2006) or Boley et al. (2014) . However, comparable indicators and metrics specific for the field of visitor pressure are not at hand at the moment.
Third, taking action and implementing measures is a logical consequence in cases where the assessment phase has shown problems of visitor pressure. These actions might be in the fields of regulation, visitor management, pricing or communication. The model does not give suggestions as to which actions to take. It can work, however, as a guideline for the strategic objectives of such actions, namely to secure (and possibly increase) the economic value from tourism for the city and its tourism suppliers on the one hand and to secure (and possibly increase) tourism acceptance on the residents’ side on the other hand.
Quality of life: equal demands on tourism
Conceptual model of conflict drivers and irritation factors
Potential areas of conflict
Source: Adapted from Postma (2013)
Andereck , K.L. , Valentine , K.M. , Knopf , R.C. and Vogt , C.A. ( 2005 ), “ Residents’ perceptions of community tourism impacts ”, Annals of Tourism Research , Vol. 32 No. 4 , pp. 1056 - 76 .
Ateljevic , I. ( 2000 ), “ Circuits of tourism: stepping beyond the ‘production/consumption’ dichotomy ”, Tourism Geographies , Vol. 2 No. 4 , pp. 369 - 88 .
Boley , B.B. , McGehee , N.G. , Perdue , R.R. and Long , P. ( 2014 ), “ Empowerment and resident attitudes toward tourism: strengthening the theoretical foundation through a Weberian lens ”, Annals of Tourism Research , Vol. 49 , pp. 33 - 50 , available at: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2014.08.005
Burns , P. ( 1999 ), An Introduction to Tourism and Anthropology , Routledge , London .
Burns , P.M. and Holden , A. ( 1997 ), “ Alternative and sustainable tourism development – the way forward? ”, in France , L. (Ed.), The Earthscan Reader in Sustainable Tourism , Earthscan Publications Ltd , London , pp. 26 - 8 .
Butler , R. ( 2004 ), “ Geographical research on tourism, recreation and leisure: origins, eras and directions ”, Tourism Geographies , Vol. 6 No. 2 , pp. 143 - 62 .
Causevic , S. and Lynch , P. ( 2009 ), “ Hospitality as a human phenomenon: host-guest relationships in a post-conflict setting ”, Tourism and Hospitality Planning & Development , Vol. 6 No. 2 , pp. 121 - 32 .
Crouch , D. (Ed.) ( 1999 ), Leisure/Tourism Geographies: Practices and Geographical Knowledge , Routledge , London .
Crouch , D. ( 2011 ), “ Tourism, performance and the everyday ”, Leisure Studies , Vol. 30 No. 3 , pp. 378 - 80 .
Deery , M. , Jago , L. and Fredline , L. ( 2012 ), “ Rethinking social impacts of tourism research: a new research agenda ”, Tourism Management , Vol. 33 , pp. 64 - 73 .
Doxey , G.V. ( 1975 , 8-11 September), “ A causation theory of visitor-resident irritants: methodology and research inferences ”, Proceedings of the Travel Research Association, ‘The impact of tourism’, 6th Annual Conference , San Diego, CA , pp. 196 - 8 .
England , J.L. and Albrecht , S.L. ( 1984 ), “ Boomtown and social disruption ”, Rural Sociology , Vol. 49 , pp. 230 - 46 .
European Commission ( 2016 ), “ A European agenda for the collaborative economy ”, COM(2016) 356 final and the Staff Working Document (SWD(2016)) 184 final .
Faulkner , B. and Tideswell , C. ( 1997 ), “ A framework for monitoring community impacts of tourism ”, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , Vol. 5 No. 1 , pp. 3 - 28 .
France , L. ( 1997 ), “ Introduction ”, in France , L. (Ed.), The Earthscan Reader in Sustainable Tourism , Earthscan Publications Ltd , London , pp. 1 - 22 .
Fridgen , J. ( 1991 ), Dimensions of Tourism , American Hotel and Motel Association Educational Institute , East Lansing, MI .
Harrill , R. ( 2004 ), “ Residents’ attitudes toward tourism development: a literature review with implications for tourism planning ”, Journal of Planning Literature , Vol. 18 No. 3 , pp. 251 - 66 .
Haywood , K.M. ( 1988 ), “ Responsible and responsive tourism planning in the community ”, Tourism Management , Vol. 9 , pp. 105 - 18 .
HHT ( 2015 ), Wirtschaftsfaktor Tourismus. Hamburg und die Metropolregion , dwif-Consulting GmbH, München/Berlin , Datengrundlage .
Hudson , J. and Lowe , S. ( 2004 ), Understanding the Policy Process. Analysing Welfare Policy and Practice , 2nd ed. , The Policy Press , Bristol .
IPK International ( 2016 ), “ ITB world travel trends report 2015-2015 ”, Messe Berlin GmbH, Berlin .
Jackson , E.L. ( 1989 ), “ Environmental attitudes, values and recreation ”, in Jackson , E.L. and Burton , T.L. (Eds), Understanding Leisure and Recreation. Mapping the Past, Charting the Future , E&F Spon Ltd , London , pp. 357 - 83 .
Jafari , J. ( 1990 ), “ Research and scholarship. The basis of tourism education ”, The Journal of Tourism Studies , Vol. 1 No. 1 , pp. 33 - 41 .
Jafari , J. ( 2005 ), “ Bridging out, nesting afield: powering a new platform ”, Journal of Tourism Studies , Vol. 16 No. 2 , pp. 1 - 5 .
Jafari , J. ( 2007 ), “ Entry into a new field of study: leaving a footprint ”, in Nash , D. (Ed.), The Study of Tourism: Anthropological and Sociological Beginnings , Elsevier , Oxford , pp. 108 - 21 .
Kang , Y.-S. , Long , P.T. and Perdue , R.R. ( 1996 ), “ Resident attitudes toward legal gambling ”, Annals of Tourism Research , Vol. 23 No. 1 , pp. 71 - 85 .
Kim , K. ( 2002 ), “ The effects of tourism impacts upon quality of life of residents in the community ”, PhD thesis, Electronic Theses and Dissertations at Virginia Tech, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, available at: http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/theses/available/etd-12062002-123337/unrestricted/Title_and_Text.pdf
Koens , K. and Postma , A. ( 2016 ), Understanding and Managing Visitor Pressure in Urban Tourism. A Study into the Nature and Methods used to Manage Visitor Pressure in Six Major European Cities , CELTH , Leeuwarden/Breda/Vlissingen .
Krippendorf , J. ( 1984 ), The Holidaymakers. Understanding the Impact of Leisure and Travel , Heinemann , London .
McElroy , J.L. ( 2006 ), “ Small Island tourism economies across the lifecycle ”, Asia Pacific Viewpoint , Vol. 47 No. 1 , pp. 61 - 77 .
Martin , C. ( 1995 ), “ Charter for sustainable tourism. World Conference on Sustainable Tourism ”, Lanzarote, 27-28 April, available at: www.world-tourism.org/sustainable/doc/Lanz-en.pdf
Matthieson , A. and Wall , G. ( 1982 ), Tourism: Economic, Physical and Social Impacts , Longman , Harlow .
Mill , R.C. and Morrison , A.M. ( 2002 ), The Tourism System , 4th ed. , Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company , Dubuque, IA .
Milligan , J. ( 1989 ), “ Migrant workers in the Guernsey hotel industry ”, PhD thesis, Nottingham Business School, Nottingham .
Milne , S. and Ateljevic , I. ( 2001 ), “ Tourism, economic development and the global-local nexus: theory embracing complexity ”, Tourism Geographies , Vol. 3 No. 4 , pp. 369 - 93 .
Mitchell , C.J.A. ( 1998 ), “ Entrepreneurialism, commodification and creative destruction: a model of post-modern community development ”, Journal of Rural Studies , Vol. 14 , pp. 273 - 86 .
Moscovici , S. ( 1981 ), “ On social representations ”, in Forgas , J.P. (Ed.), Social Cognition: Perspectives on Everyday Understanding , Academic Press , London , pp. 181 - 209 .
Moscovici , S. ( 1983 ), “ The coming era of social representations ”, in Codol , J.P. and Leyens , J.P. (Eds), Cognitive Approaches to Social Behaviour , Nijhoff , The Hague , pp. 115 - 50 .
Moscovici , S. ( 1984 ), “ The phenomenon of social representations ”, in Farr , R.M. and Moscovici , S. (Eds), Social Representations , Cambridge University Press , Cambridge , pp. 3 - 70 .
Moscovici , S. ( 1988 ), “ Notes toward a description of social representations ”, European Journal of Psychology , Vol. 18 , pp. 211 - 50 .
Murphy , P.E. ( 1985 ), Tourism: A Community Approach , Methuen , London .
O’Neill , J.W. and Ouyang , Y. ( 2016 ), “ From air mattresses to unregulated business: an analysis of the other Side of Airbnb ”, Penn State University School of Hospitality Management, State College, PA .
Pizam , A. ( 1978 ), “ Tourism impacts: the social costs to the destination community as perceived by its residents ”, Journal of Travel Research , Vol. 16 No. 4 , pp. 8 - 12 .
Postma , A. ( 2001 ), “ An approach for integrated development of quality tourism ”, in Andrews , S. , Flanagan , S. and Ruddy , J. (Eds), Tourism Destination Planning: Proceedings of ATLAS 10th Anniversary International Conference Tourism, Innovation and Regional Development, held in Dublin , Vol. 2 , DIT , Dublin , 3-5 October , pp. 205 - 17 .
Postma , A. ( 2003 ), “ Quality of life, competing value perspectives in leisure and tourism ”, Keynote presentation, ATLAS 10th International Conference, “Quality of Life, competing value perspectives in leisure and tourism” , Leeuwarden , June .
Postma , A. ( 2013 ), “ ‘When the tourists flew in’. Critical encounters in the development of tourism ”, PhD thesis, Faculty of Spatial Sciences, University of Groningen, Groningen .
Postma , A. and Schilder , A.K. ( 2007 ), “ Critical Impacts of tourism; the case of Schiermonnikoog ”, in Casado-Diaz , M. , Everett , S. and Wilson , J. (Eds), Social and Cultural Change: Making Space(s) for Leisure and Tourism , Leisure Studies Association publication , Vol. 98, No. 3 , University of Brighton , Eastborne , pp. 131 - 50 .
Rátz , T. and Puczkó , L. ( 2002 ), The Impacts of Tourism: An Introduction , Hame Polytechnic , Hämeenlinna .
Ryan , C. ( 1991 ), Recreational Tourism , Routledge , London .
Schmücker , D. , Grimm , B. and Beer , H. ( 2016 ), “ Reiseanalyse 2016 ”, in Schrader , R. (Ed.), Summary of the Findings of the RA 2016 German Holiday Survey , FUR , Kiel , pp. 7 - 8 .
Schmücker , D. ( 2011 ), Einflussanalyse Tourismus: Einfluss einer Festen Fehmarnbeltquerung auf den Tourismus in Fehmarn und Großenbrode , NIT , Kiel .
Sherlock , K. ( 2001 ), “ Revisiting the concept of hosts and guests ”, Tourist Studies , Vol. 1 No. 3 , pp. 271 - 95 .
Vanderwerf , J. ( 2008 ), “ Creative destruction and rural tourism planning: the case of Creemore, Ontario ”, master thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario, available at: http://uwspace.uwaterloo.ca/handle/10012/3809 (accessed 17 June 2009 ).
Vargas-Sánchez , A. , De los Angeles Plaza-Meija , M. and Porras-Bueno , N. ( 2008 ), “ Understanding residents’ attitudes toward the development of industrial tourism in a former mining community ”, Journal of Travel Research , Vol. 47 No. 3 , pp. 373 - 87 .
Wall , G. and Mathieson , A. ( 2006 ), Tourism: Changes, Impacts, and Opportunities , Pearson Education Unlimited , Essex .
Williams , S.W. ( 2009 ), Tourism Geography: A new Synthesis , 2nd ed. , Routledge , New York, NY .
World Commission on Environment and Development ( 1987 ), Our Common Future , Oxford University Press , Oxford , available at: http://worldinbalance.net/intagreements/1987-brundtland.pdf, www.un-documents.net/wced-ocf.htm (accessed 15 May 2005 ).
World Tourism Organisation ( 2004 ), “ Sustainable development of tourism. Concepts and definitions ”, available at: www.world-tourism.org/sustainable/top/concepts.html (accessed 15 May 2005 ).
Zervas , G. , Proserpio , D. and Byers , J. ( 2016 ), “ The rise of the sharing economy: estimating the impact of Airbnb on the hotel industry ”, Research Paper No. 2013-16, Boston University School of Management, Boston .
Zhang , J. , Inbakaran , J. and Jackson , M.S. ( 2006 ), “ Understanding community attitudes toward tourism and host-guest interaction in the urban-rural border region ”, Tourism Geographies , Vol. 8 No. 2 , pp. 182 - 204 .
Acknowledgements
© Albert Postma and Dirk Schmuecker. Published in the Journal of Tourism Futures . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Corresponding author
About the authors.
Albert Postma is a Professor of Applied Sciences at the European Tourism Futures Institute, Stenden University of Applied Sciences, Leeuwarden, The Netherlands.
Dirk Schmuecker is the Head of Research at the NIT Institute for Tourism Research in Northern Europe, Kiel, Germany.
Related articles
All feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
Overtourism Effects: Positive and Negative Impacts for Sustainable Development
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 02 October 2020
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Ivana Damnjanović 7
Part of the book series: Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals ((ENUNSDG))
303 Accesses
1 Citations
Responsible tourism ; Tourism overcrowding ; Tourism-phobia ; Tourist-phobia
Definitions
Tourism today is paradoxically dominated by two opposite aspects: its sustainable character and overtourism. Since its creation by Skift in 2016 (Ali 2016 ), the term “overtourism” has been a buzzword in media and academic circles, although it may only be a new word for a problem discussed over the past three decades.
Overtourism is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon destructive to tourism resources and harmful to destination communities’ well-being through overcrowding and overuse (Center for Responsible Travel 2018 ; International Ecotourism Society 2019 ) as certain locations at times cannot withstand physical, ecological, social, economic, psychological, and/or political pressures of tourism (Peeters et al. 2018 ). Overtourism is predominantly a problem producing deteriorated quality of life of local communities (Responsible Tourism n.d. ; The International Ecotourism Society 2019 ; UNWTO 2018...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Ali R (2016) ‘Exploring the coming perils of over tourism’, Skift, 23-08-2016 (online). Available at: www.skift.com (10-09-2019)
Google Scholar
Bowitz E, Ibenholt K (2009) Economic impacts of cultural heritage – research and perspectives. J Cult Herit 10(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2008.09.002
Article Google Scholar
Center for Responsible Travel – CREST (2018) The case for responsible travel: Trends & Statistics 2018. Retrieved from https://www.responsibletravel.org
Center for Responsible Travel – CREST (n.d.) Center for Responsible Travel. Retrieved 11 Sept 2019, from https://www.responsibletravel.org/
Cheer JM, Milano C, Novelli M (2019) Tourism and community resilience in the anthropocene: accentuating temporal overtourism. J Sustain Tour 27:554–572. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2019.1578363
Croes R, Manuel A, Rivera KJ, Semrad KJ, Khalilzadeh J (2017) Happiness and tourism: evidence from Aruba. Retrieved from the dick pope Sr. Institute for Tourism Studies website. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.29257.85602
Epler Wood M, Milstein M, Ahamed-Broadhurst K (2019) Destinations at risk: the invisible burden of tourism. The Travel Foundation
Giulietti, S., Romagosa, F., Fons Esteve, J., & Schröder, C. (2018). Tourism and the environment: towards a reporting mechanism in Europe (ETC/ULS report |01/2018). Retrieved from European Environment Agency website: http://www.sepa.gov.rs/download/strano/ETC_TOUERM_report_2018.pdf
Global Sustainable Tourism Council – GSTC (2017) Official website. Retrieved August 23, 2019, from https://www.gstcouncil.org/
Goodwin, H. (2017) The challenge of overtourism (working paper). Responsible tourism partnership. Available at https://haroldgoodwin.info/pubs/RTP'WP4Overtourism01'2017.pdf
Interagency Visitor Use Management Council (2016) Visitor use management framework: a guide to providing sustainable outdoor recreation, 1st edn
Jordan P, Pastras P, Psarros M (2018) Managing tourism growth in Europe: the ECM toolbox. Retrieved from European Cities Marketing website: https://www.ucm.es/data/cont/media/www/pag-107272/2018-Managing%20Tourism%20Growth%20in%20Europe%20The%20ECM%20Toolbox.pdf
Kim D, Lee C, Sirgy MJ (2016) Examining the differential impact of human crowding versus spatial crowding on visitor satisfaction at a festival. J Travel Tour Mark 33(3):293–312. https://doi.org/10.1080/10548408.2015.1024914
Leung Y, Spenceley A, Hvenegaard G, Buckley, R, Groves C (eds) (2018) Tourism and visitor management in protected areas: guidelines for sustainability. Best practice protected area guidelines series, vol 27. IUCN, Gland. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.CH.2018.PAG.27.en
Li L, Zhang J, Nian S, Zhang H (2017) Tourists’ perceptions of crowding, attractiveness, and satisfaction: a second-order structural model. Asia Pac J Tour Res 22(12):1250–1260. https://doi.org/10.1080/10941665.2017.1391305
Milano C (2017) Overtourism and tourismphobia: global trends and local contexts. Retrieved from Barcelona: Ostelea School of Tourism and Hospitality website. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.13463.88481
Book Google Scholar
Milano C, Novelli M, Cheer JM (2019) Overtourism and tourismphobia: a journey through four decades of tourism development, planning and local concerns. Tour Plan Dev 16(4):353–357. Retrieved from. https://doi.org/10.1080/21568316.2019.1599604
Muler Gonzalez V, Coromina L, Galí N (2018) Overtourism: residents’ perceptions of tourism impact as an indicator of resident social carrying capacity – case study of a Spanish heritage town. Tour Rev 73(3):277–296. https://doi.org/10.1108/tr-08-2017-0138
Oklevik O, Gössling S, Hall CM, Steen Jacobsen JK, Grøtte IP, McCabe S (2019) Overtourism, optimisation, and destination performance indicators: a case study of activities in fjord Norway. J Sustain Tour:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2018.1533020
Peeters P, Gössling S, Klijs J, Milano C, Novelli M, Dijkmans C, Eijgelaar E, Hartman S, Heslinga J, Isaac R, Mitas O, Moretti S, Nawijn J, Papp B, Postma A (2018) Research for TRAN committee – overtourism: impact and possible policy responses. European Parliament, Policy Department for Structural and Cohesion Policies, Brussels
Perkumienė D, Pranskūnienė R (2019) Overtourism: between the right to travel and residents’ rights. Sustainability 11(7):21–38. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072138
Popp M (2012) Positive and negative urban tourist crowding: Florence, Italy. Tour Geogr 14(1):50–72. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616688.2011.597421
Responsible Tourism (n.d.) Over Tourism (online). Available at: www.responsibletourismpartnership.org/overtourism
Seraphin H, Sheeran P, Pilato M (2018) Over-tourism and the fall of Venice as a destination. J Destin Mark Manag 9:374–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2018.01.011
Souza T, Thapa B, Rodrigues CG, Imori D (2018) Economic impacts of tourism in protected areas of Brazil. J Sustain Tour 27(6):735–749. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2017.1408633
Spenceley A, Snyman S, Rylance A (2017) Revenue sharing from tourism in terrestrial African protected areas. J Sustain Tour 27(6):720–734. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2017.1401632
The International Ecotourism Society (2019) Ecotourism is the solution to Overtourism. Retrieved 10 Sept 2019, from https://ecotourism.org/news/ecotourism-is-the-solution-to-overtourism/
The Travel Foundation. (2016). What is sustainable tourism? . Retrieved 13 July 2020, from https://www.thetravelfoundation.org.uk/resources-categories/what-is-sustainable-tourism/
Thomas, C. C., Koontz, L., and Cornachione, E. (2018). 2017 National park visitor spending effects: economic contributions to local communities, states, and the nation. Retrieved from U.S. Department of the Interior, National Park Service website: https://www.nps.gov/nature/customcf/NPS_Data_Visualization/docs/NPS_2017_Visitor_Spending_Effects.pdf
UN World Tourism Organization (2018a) Tourism for SDGs platform. Retrieved 13 Sept 2019, from http://tourism4sdgs.org/
UN World Tourism Organization (2018b) Measuring sustainable tourism. Retrieved from http://statistics.unwto.org/mst
UN World Tourism Organization (2018c) UNWTO tourism highlights, 2018 edition. UNWTO, Madrid, p 4. https://doi.org/10.18111/9789284419876
UN World Tourism Organization; Centre of Expertise Leisure, Tourism & Hospitality; NHTV Breda University of Applied Sciences; and NHL Stenden University of Applied Sciences (2018d), ‘Overtourism’? – Understanding and Managing Urban Tourism Growth beyond Perceptions, Executive Summary, UNWTO, Madrid. https://doi.org/10.18111/9789284420070
UN World Tourism Organization (2019). ‘Key tourism figures’, infographic (online). Available at http://www2.unwto.org
UN World Tourism Organization; Centre of Expertise Leisure, Tourism & Hospitality; NHTV Breda University of Applied Sciences; and NHL Stenden University of Applied Sciences (2018) ‘Overtourism’? – understanding and managing urban tourism growth beyond perceptions, executive summary. UNWTO, Madrid. https://doi.org/10.18111/9789284420070
UNEP and UNWTO (2005) Making tourism more sustainable: a guide for policy makers. World Tourism Organization Publications, Madrid
United Nations (2018) About the sustainable development goals. Retrieved 13 Sept 2019, from http://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/
UNWTO (2004) Tourism congestion management at natural and cultural sites. World Tourism Organization Publications, Madrid
Waller I (2011) Less law, more order. Acta Criminologica South Afr J Criminol 24(1):I–IV. Retrieved from https://hdl.handle.net/10520/EJC29060
World Travel & Tourism Council (2019) Global Economic Impact & Trends 2019 (march 2019). Available at https://www.wttc.org/economic-impact/country-analysis/
World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC) and McKinsey Company (2017) Coping with success: managing overcrowding in tourism destinations. Retrieved from https://www.wttc.org/-/media/files/reports/policy-research/coping-with-success%2D%2D-managing-overcrowding-in-tourism-destinations-2017.pdf
WWF – World Wide Fund For Nature (2019) Blue planet: coasts. Retrieved 12 Sept 2019, from http://wwf.panda.org/our_work/oceans/coasts/
Zehrer A, Raich F (2016) The impact of perceived crowding on customer satisfaction. Retrieved from. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2016.06.007
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Health and Business Studies, Singidunum University, Valjevo, Serbia
Ivana Damnjanović
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ivana Damnjanović .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
European School of Sustainability, Hamburg University of Applied Sciences, Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
Walter Leal Filho
Center for Neuroscience & Cell Biology, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
Anabela Marisa Azul
Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Passo Fundo University Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Passo Fundo, Brazil
Luciana Brandli
HAW Hamburg, Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
Amanda Lange Salvia
International Centre for Thriving, University of Chester, Chester, UK
Section Editor information
Department of Health Professions, Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Haruna Musa Moda
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Damnjanović, I. (2020). Overtourism Effects: Positive and Negative Impacts for Sustainable Development. In: Leal Filho, W., Azul, A.M., Brandli, L., Lange Salvia, A., Wall, T. (eds) Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71059-4_112-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71059-4_112-1
Received : 10 October 2019
Accepted : 16 October 2019
Published : 02 October 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-71059-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-71059-4
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Earth and Environm. Science Reference Module Physical and Materials Science Reference Module Earth and Environmental Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Advantages And Disadvantages Of International Tourism
- Miscellaneous
- Aug 13, 2023
- Noshin Bashir

Several countries heavily rely on tourism as a significant part of their economies. These countries often have stunning natural landscapes, rich cultural heritage, unique infrastructure, historical sites, or unique attractions that draw in a large number of tourists. Some examples of countries that heavily rely on tourism include MALDIVES, Spain, Switzerland, Thailand, Switzerland, etc.
With its breathtaking beaches and luxurious resorts, tourism is the backbone of the Maldives’ economy, contributing a substantial portion of its GDP. Apart from the Maldives, Spain, and Thailand are major tourist destinations known for their beaches, historic cities, and cultural sites. Ancient history, stunning islands, and archaeological sites of Greece attract tourists from around the world.

Tourism brings about a range of benefits to both the host country or destination and the tourists themselves. Here are some of the key advantages of tourism. For instance, tourism is a significant contributor to economic growth, generating revenue and creating employment opportunities in various sectors, such as hospitality, transportation, entertainment, and retail.
Tourism also brings in foreign exchange through expenditures by tourists on accommodations, food, transportation, attractions, and souvenirs. This revenue can bolster a country’s balance of payments and support local economies.
Additionally, the need to cater to tourists often leads to improved infrastructure such as transportation networks, airports, roads, and public facilities, which can benefit both tourists and local residents. Tourism provides opportunities for a wide range of job types, from hotel staff and tour guides to artisans and performers, contributing to job diversification within local communities.
Above all, tourism promotes cultural exchange and encourages the preservation and maintenance of historical sites, landmarks, and cultural heritage, as they become valuable assets for attracting visitors.
While these advantages are notable, it’s important to implement sustainable tourism practices that minimize the negative impacts and ensure that the benefits of tourism are distributed equitably among local communities, economies, and the environment.
It’s important to note that while tourism can bring economic benefits to these countries, it also poses challenges, such as managing environmental impact, preserving local culture, and ensuring equitable distribution of tourism-related income.
While tourism offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its share of disadvantages. Here are some common drawbacks associated with tourism. First, tourism can lead to environmental degradation through increased pollution, deforestation, habitat destruction, and overuse of natural resources. Popular tourist destinations often experience increased waste generation and strain on local ecosystems.
Second, excessive tourism can lead to the commodification and commercialization of local cultures, resulting in the loss of authentic traditions and values. Communities may start catering primarily to tourists, diluting their own cultural practices.

Besides, the sheer volume of tourists in some places can overwhelm infrastructure, damage historical sites, and disrupt the lives of local residents. This phenomenon, known as over-tourism, can lead to negative impacts on both the environment and the community. Moreover, as demand for goods and services rises due to tourism, the cost of living in a destination can increase, making it challenging for local residents to afford basic necessities.
Tourists sometimes may unintentionally disrespect local customs, traditions, and etiquette due to a lack of awareness, causing tensions between visitors and locals. Above all, natural disasters can really turn the tourism industry upside down as has been in the case of the recent pandemic. T he COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the vulnerability of economies heavily dependent on tourism, as travel restrictions and health concerns have led to a significant decrease in tourist arrivals.
Many countries imposed strict travel restrictions and lockdown measures to contain the spread of the virus. This resulted in the closure of borders, suspension of international flights, and restrictions on movement, bringing international travel to a halt. This led to a massive decrease in tourist arrivals, causing a severe decline in revenue for tourism-dependent economies. Airlines too faced a sharp decline in demand for flights, leading to financial struggles, layoffs, and even bankruptcies for many airlines around the world.
Share This Post:
Related posts.

11 Signs To Know If He Is Cheating On You?
Matric paper of english bise sargodha, read surah muzammil online.

Experience Is The Best Teacher
Recent posts.

What Is D8 Organization? What Does It Aim For?

What Should You Do In Case Of Road Injury?
List of airports in iran, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Number of tourist arrivals
Somewhere on Earth this year
The World Counts • Impact through Awareness
The world counts impact through awareness, 45 arrivals every second.
There are over 1.4 billion tourists arriving at their destination every year. That’s 45 arrivals every single second.
Exponential growth of tourism
In 1950 there were 25 million international tourist arrivals, in 1970 the number was 166 million, and by 1990 it had grown to 435 million. From 1990 to 2018 numbers more than tripled reaching 1.442 billion. By 2030, 1.8 billion tourist arrivals are projected.
Negative environmental impacts of tourism
The negative environmental impacts of tourism are substantial. They include the depletion of local natural resources as well as pollution and waste problems. Tourism often puts pressure on natural resources through over-consumption, often in places where resources are already scarce.
Tourism puts enormous stress on local land use, and can lead to soil erosion, increased pollution, natural habitat loss, and more pressure on endangered species. These effects can gradually destroy the environmental resources on which tourism itself depends.
Tourism often leads to overuse of water
An average golf course in a tropical country, for example, uses as much water as 60,000 rural villagers. It also uses 1500 kilos of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides per year.
Tourism and climate change
Tourism contributes to more than 5 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions, with transportation accounting for 90 percent of this.
By 2030, a 25% increase in CO2-emissions from tourism compared to 2016 is expected. From 1,597 million tons to 1,998 million tons.
1,101,463,991
Tons of waste dumped
Globally, this year
2,171,754.47
Square kilometers of land area being degraded
2,213,318,846,717
Tons of freshwater used
Worldwide, this year
22,392,968,159
Tons of CO2 emitted into the atmosphere
The alternative: Eco-tourism
Eco-tourism offers a greener alternative. Eco-tourism is a rapidly growing industry, with potential benefits for both the environment and the economies of the tourist destinations.
Number of eco-tourist arrivals
- World Population
- The Consumer Economy
- Our Global Challenges
- The Project
- Keep the optimism
- Support green companies

- Embedded System
- Interview Q
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share

Learn Latest Tutorials
Transact-SQL
Reinforcement Learning
R Programming
React Native
Python Design Patterns
Python Pillow
Python Turtle
Preparation

Verbal Ability

Interview Questions

Company Questions
Trending Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Cloud Computing
Data Science
Machine Learning
B.Tech / MCA
Data Structures
Operating System
Computer Network
Compiler Design
Computer Organization
Discrete Mathematics
Ethical Hacking
Computer Graphics
Software Engineering
Web Technology
Cyber Security
C Programming
Control System
Data Mining
Data Warehouse

UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Tourism’s Importance for Growth Highlighted in World Economic Outlook Report
- All Regions
- 10 Nov 2023
Tourism has again been identified as a key driver of economic recovery and growth in a new report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). With UNWTO data pointing to a return to 95% of pre-pandemic tourist numbers by the end of the year in the best case scenario, the IMF report outlines the positive impact the sector’s rapid recovery will have on certain economies worldwide.
According to the World Economic Outlook (WEO) Report , the global economy will grow an estimated 3.0% in 2023 and 2.9% in 2024. While this is higher than previous forecasts, it is nevertheless below the 3.5% rate of growth recorded in 2022, pointing to the continued impacts of the pandemic and Russia's invasion of Ukraine, and from the cost-of-living crisis.
Tourism key sector for growth
The WEO report analyses economic growth in every global region, connecting performance with key sectors, including tourism. Notably, those economies with "large travel and tourism sectors" show strong economic resilience and robust levels of economic activity. More specifically, countries where tourism represents a high percentage of GDP have recorded faster recovery from the impacts of the pandemic in comparison to economies where tourism is not a significant sector.
As the report Foreword notes: "Strong demand for services has supported service-oriented economies—including important tourism destinations such as France and Spain".
Looking Ahead
The latest outlook from the IMF comes on the back of UNWTO's most recent analysis of the prospects for tourism, at the global and regional levels. Pending the release of the November 2023 World Tourism Barometer , international tourism is on track to reach 80% to 95% of pre-pandemic levels in 2023. Prospects for September-December 2023 point to continued recovery, driven by the still pent-up demand and increased air connectivity particularly in Asia and the Pacific where recovery is still subdued.
Related links
- Download the News Release on PDF
- UNWTO World Tourism Barometer
- IMF World Economic Outlook
Category tags
Related content, international tourism reached 97% of pre-pandemic level..., international tourism to reach pre-pandemic levels in 2024, international tourism to end 2023 close to 90% of pre-p..., international tourism swiftly overcoming pandemic downturn.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Advantages And Disadvantages of Tourism: It is no secret that the tourism industry in the world has been on a steady rise. In order to understand what the future will be like for tourism, it is important to examine the current landscape and consider how new technological advancements may affect the industry. Students can also […]
The problem with tourism. In 2019 (pre-COVID), international tourist arrivals grew to 1.5 billion and the industry generated 1.4 trillion USD dollars of tourism receipts ().It was the tenth straight year of growth, with arrivals continuing to increase each year.
The Advantages. For developing countries, the advantages of tourism tend to be primarily monetary. A large scale tourism industry prevents larger, more harmful businesses from working off the land. Small tourist companies that reign on the land stops large capitalistic corporations from polluting the air or gentrifying people's homes.
While the tourism industry is forecast to represent 11.6% of the global economy by 2033, it's also predicted that an increasing number of people will show more interest in travelling more ...
This includes reducing their carbon footprint, conserving natural resources, and minimizing waste. Disadvantages of Tourism. Environmental degradation: Tourism can have a negative impact on the environment, including increased pollution, depletion of natural resources, and destruction of wildlife habitats. Cultural erosion: Tourism can lead to ...
2. Puts Pressure on Natural Resources. Another con of the tourism industry is that it puts an immense amount of pressure on natural resources. Anytime someone stays in an area, they inevitably use the area's natural resources, like water and food. Cities and countries around the world have faced droughts.
The tourism industry showed an unbridled growth from a mere 500,000 international travellers just after World War II, to more than one billion international arrivals each year just before the virus shut down travel globally. This amount of growth led to a focus of profits over people, in which multinational companies profited from the ...
Source: UNWTO. Here are a few facts about the economic importance of the tourism industry globally: The tourism economy represents 5 percent of world GDP. Tourism contributes to 6-7 percent of total employment. International tourism ranks fourth (after fuels, chemicals and automotive products) in global exports.
The global tourism industry generates one trillion in U.S. dollars. Tourism supports between 6% and 7% of global workers (including workers indirectly employed by the industry) Tourism is a top five export earner in about 77% of the world's countries. ... The Disadvantages of Tourism.
Dependence on tourism industry: A destination can become too dependent on tourism, and if the tourism industry were to decline, it could have a severe economic impact on the community. Widening income gap: Tourism can also lead to a widening income gap, as the benefits of tourism may not be distributed equally among all members of a community ...
the disadvantages of tourism may outweigh the advantages. For example, tourism leads to social inequality (Pham-Do & Pham, 2020), crime, immoral behaviour , and change
However, tourism could also have a negative effect on the economy. Its boom may lead to a deindustrialization in other sectors (Copeland, 1991); this phenomenon is often called 'Dutch Disease effect'.Despite contractions of the manufacturing sector are not found in the long-run period, the authors warn that the danger of this effect could still be valid in either short or medium run (Song ...
Besides the positive changes, tourism also has its share of downsides. Most of the cons of the tourism industry are associated with the misuse of natural resources. Some of the other problems with tourism include: 1. Environmental Damage. Tourism can lead to environmental damage in many ways.
Conclusion. There are both advantages and disadvantages to tourism. On the plus side, tourism can have both a favorable impact on the economy and drawbacks. Because of this, it's crucial to manage tourism operations responsibly and sustainably through careful planning, community involvement, and the implementation of sustainable tourism ...
5+ Fun Facts on Tourism . Tourism is responsible for 5% of the Global GDP! China stays as the world's top tourism spender, spending more than 260 Billion Dollars! Global tourism industry being the largest industry contributes more than 7.5 trillion dollars in the world economy. Almost 10% of world's jobs are sourced from Tourism Industry.
However, when tourism becomes unsustainable in nature, it can have disastrous consequences on the environment. When the tourist industry active in the region crosses the legal and ethical barriers to earn more profit, it can lead to massive degradation of the environment in the area. Local human population, flora, and fauna, suffer greatly due ...
In terms of economic disadvantages, local communities need to be able to fund the tourist demands, which leads to an increase of taxes. The overall price of living increases in tourist destinations in terms of rent and rates, as well as property values going up. ... Mass tourism, including the cruise industry, tends to put a strain on fragile ...
The domain of tourism impact studies has evolved since the second world war, echoing the development of tourism, its characteristics and its perception. During the first phase (1960-1970) the emphasis of tourism impact studies was on the positive economic impacts of tourism. Tourism was mainly seen as a means to strengthen economies.
Tourism today is paradoxically dominated by two opposite aspects: its sustainable character and overtourism. Since its creation by Skift in 2016 (Ali 2016), the term "overtourism" has been a buzzword in media and academic circles, although it may only be a new word for a problem discussed over the past three decades.. Overtourism is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon destructive to ...
Above all, natural disasters can really turn the tourism industry upside down as has been in the case of the recent pandemic. T he COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the vulnerability of economies heavily dependent on tourism, as travel restrictions and health concerns have led to a significant decrease in tourist arrivals.
Exponential growth of tourism. In 1950 there were 25 million international tourist arrivals, in 1970 the number was 166 million, and by 1990 it had grown to 435 million. ... Eco-tourism is a rapidly growing industry, with potential benefits for both the environment and the economies of the tourist destinations. 52,475,406.
Disadvantages of Tourism. 1. Tourists' Negligence of the Environment. When it comes to tourism, thousands or even millions of people may travel somewhere. Particularly in places where tourists are more likely to travel, this high tourist influx has the potential to cause significant environmental damage.
10 Nov 2023. Tourism has again been identified as a key driver of economic recovery and growth in a new report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). With UNWTO data pointing to a return to 95% of pre-pandemic tourist numbers by the end of the year in the best case scenario, the IMF report outlines the positive impact the sector's rapid ...