
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview

1.1 What is Tourism?
Before engaging in a study of tourism , let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure (United Nations World Tourism Organization, 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is not just the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure), but the overall agglomeration of activities, services, and involved sectors that make up the unique tourist experience.
Tourism, Travel, and Hospitality: What are the Differences?
It is common to confuse the terms tourism , travel , and hospitality or to define them as the same thing. While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, p. 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry (Go2HR, 2020). You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 , respectively.
Definition of Tourist and Excursionist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” (LinkBC, 2008, p.8). The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
Excursionists on the other hand are considered same-day visitors (UNWTO, 2020). Sometimes referred to as “day trippers.” Understandably, not every visitor stays in a destination overnight. It is common for travellers to spend a few hours or less to do sightseeing, visit attractions, dine at a local restaurant, then leave at the end of the day.
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities and sectors.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 159 countries and over 500 affiliates such as private companies, research and educational institutions, and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website .
NAICS: The North American Industry Classification System
Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups (also commonly known as sectors) are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

It is typical for the entire tourist experience to involve more than one sector. The combination of sectors that supply and distribute the needed tourism products, services, and activities within the tourism system is called the Tourism Supply Chain. Often, these chains of sectors and activities are dependent upon each other’s delivery of products and services. Let’s look at a simple example below that describes the involved and sometimes overlapping sectoral chains in the tourism experience:
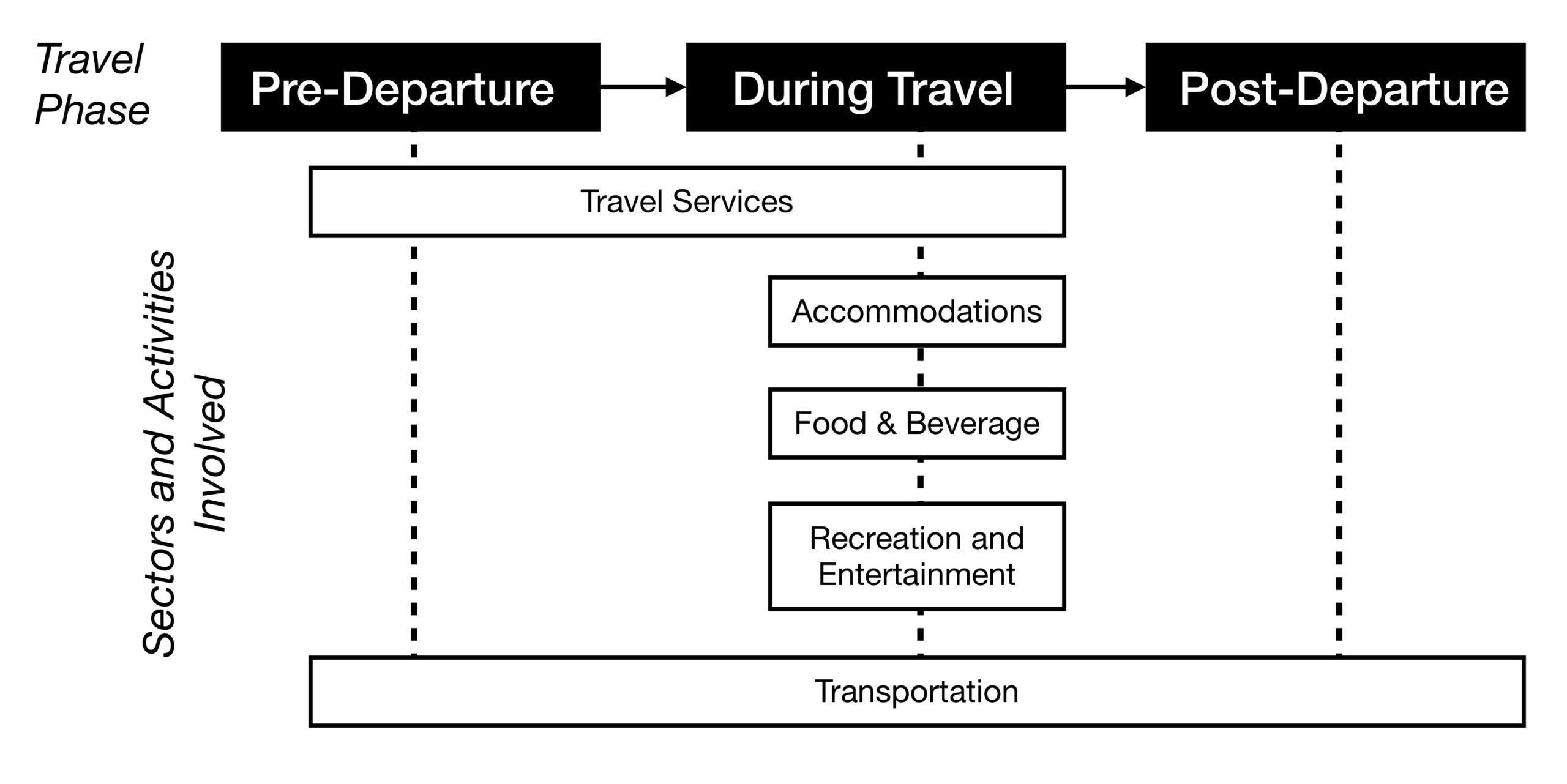
Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Long Descriptions
Figure 1.2 long description: Diagram showing the tourism supply chain. This includes the phases of travel and the sectors and activities involved during each phase.
There are three travel phases: pre-departure, during travel, and post-departure.
Pre-departure, tourists use the travel services and transportation sectors.
During travel, tourists use the travel services, accommodations, food and beverage, recreation and entertainment, and transportation sectors.
Post-departure, tourists use the transportation sector.
[Return to Figure 1.2]
Media Attributions
- Front Desk by Staying LEVEL is licensed under a CC BY-NC 4.0 Licence .
Tourism according the the UNWTO is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes.
UN agency responsible for promoting responsible, sustainable, and universally accessible tourism worldwide.
Moving between different locations for leisure and recreation.
The accommodations and food and beverage industry groupings.
someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons
A same-day visitor to a destination. Their trip typically ends on the same day when they leave the destination.
A way to group tourism activities based on similarities in business practices, primarily used for statistical analysis.
Introduction to Tourism and Hospitality in BC - 2nd Edition Copyright © 2015, 2020, 2021 by Morgan Westcott and Wendy Anderson, Eds is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1. History and Overview
1.1 What is Tourism?
Before engaging in a study of tourism , let’s have a closer look at what this term means.
Definition of Tourism
There are a number of ways tourism can be defined, and for this reason, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) embarked on a project from 2005 to 2007 to create a common glossary of terms for tourism. It defines tourism as follows:
Tourism is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes. These people are called visitors (which may be either tourists or excursionists; residents or non-residents) and tourism has to do with their activities, some of which imply tourism expenditure (United Nations World Tourism Organization, 2008).
Using this definition, we can see that tourism is not just the movement of people for a number of purposes (whether business or pleasure), but the overall agglomeration of activities, services, and involved sectors that make up the unique tourist experience.
Tourism, Travel, and Hospitality: What are the Differences?
It is common to confuse the terms tourism , travel , and hospitality or to define them as the same thing. While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as “the business of helping people to feel welcome and relaxed and to enjoy themselves” (Discover Hospitality, 2015, p. 3). Simply put, the hospitality industry is the combination of the accommodation and food and beverage groupings, collectively making up the largest segment of the industry (Go2HR, 2020). You’ll learn more about accommodations and F & B in Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 , respectively.
Definition of Tourist and Excursionist
Building on the definition of tourism, a commonly accepted description of a tourist is “someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons” [1] . The United Nations World Tourism Organization (1995) helps us break down this definition further by stating tourists can be:
- Domestic (residents of a given country travelling only within that country)
- Inbound (non-residents travelling in a given country)
- Outbound (residents of one country travelling in another country)
Excursionists on the other hand are considered same-day visitors (UNWTO, 2020). Sometimes referred to as “day trippers.” Understandably, not every visitor stays in a destination overnight. It is common for travellers to spend a few hours or less to do sightseeing, visit attractions, dine at a local restaurant, then leave at the end of the day.
The scope of tourism, therefore, is broad and encompasses a number of activities and sectors.
Spotlight On: United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
UNWTO is the United Nations agency responsible “for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism” (UNWTO, 2014b). Its membership includes 159 countries and over 500 affiliates such as private companies, research and educational institutions, and non-governmental organizations. It promotes tourism as a way of developing communities while encouraging ethical behaviour to mitigate negative impacts. For more information, visit the UNWTO website .
The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). Given the sheer size of the tourism industry, it can be helpful to break it down into broad industry groups using a common classification system. The North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) was jointly created by the Canadian, US, and Mexican governments to ensure common analysis across all three countries (British Columbia Ministry of Jobs, Tourism and Skills Training, 2013a). The tourism-related groupings created using NAICS are (in alphabetical order):
- Accommodation
- Food and beverage services (commonly known as “F & B”)
- Recreation and entertainment
- Transportation
- Travel services
These industry groups (also commonly known as sectors) are based on the similarity of the “labour processes and inputs” used for each (Government of Canada, 2013). For instance, the types of employees and resources required to run an accommodation business whether it be a hotel, motel, or even a campground are quite similar. All these businesses need staff to check in guests, provide housekeeping, employ maintenance workers, and provide a place for people to sleep. As such, they can be grouped together under the heading of accommodation. The same is true of the other four groupings, and the rest of this text explores these industry groups, and other aspects of tourism, in more detail.

It is typical for the entire tourist experience to involve more than one sector. The combination of sectors that supply and distribute the needed tourism products, services, and activities within the tourism system is called the Tourism Supply Chain. Often, these chains of sectors and activities are dependent upon each other’s delivery of products and services. Let’s look at a simple example below that describes the involved and sometimes overlapping sectoral chains in the tourism experience:
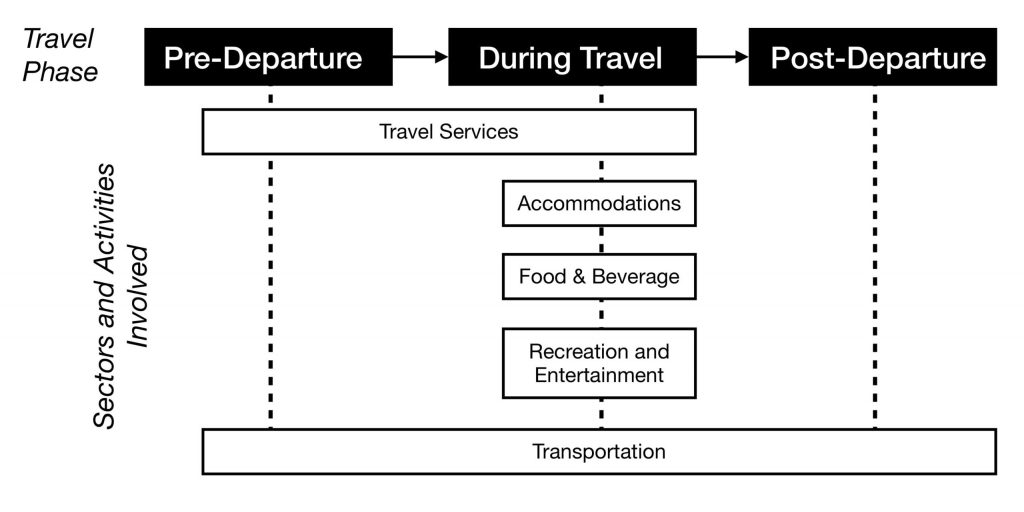
Before we seek to understand the five tourism sectors in more detail, it’s important to have an overview of the history and impacts of tourism to date.
Media Attributions
Front Desk © Staying LEVEL is licensed under a CC BY-NC (Attribution NonCommercial) license
- (LinkBC, 2008, p.8) ↵
Tourism according the the UNWTO is a social, cultural and economic phenomenon which entails the movement of people to countries or places outside their usual environment for personal or business/professional purposes.
UN agency responsible for promoting responsible, sustainable, and universally accessible tourism worldwide.
Moving between different locations for leisure and recreation.
The accommodations and food and beverage industry groupings.
someone who travels at least 80 km from his or her home for at least 24 hours, for business or leisure or other reasons
A same-day visitor to a destination. Their trip typically ends on the same day when they leave the destination.
A way to group tourism activities based on similarities in business practices, primarily used for statistical analysis.
Introduction to Tourism Copyright © 2020 by NSCC is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Travel Marketing, Tourism Economics and the Airline Product pp 3–27 Cite as
The Tourism Industry: An Overview
- Mark Anthony Camilleri 2
- First Online: 30 September 2017
101k Accesses
78 Citations
5 Altmetric
Part of the book series: Tourism, Hospitality & Event Management ((THEM))
This chapter introduces its readers to the concept of tourism. It sheds light on the rationale for tourism, as it explains the tourists’ inherent motivations to travel. It also describes different aspects that together make up the tourism industry. Tourists travel to destinations that are accessible to them. They require accommodation if they are visiting a place for more than 24 h. Leisure and business travellers may also visit attractions, and engage themselves in recreational activities. Hence, the tourist destinations should have the right amenities and facilities. In this light, this chapter clarifies how destinations may offer different products to satisfy a wide array of tourists. Tourism products can include; urban (or city) tourism, seaside tourism , rural tourism , ecotourism , wine tourism , culinary tourism , health tourism, medical tourism , religious tourism , cultural (or heritage) tourism , sports tourism , educational tourism , business tourism (including meetings, incentives, conferences and events), among others. In conclusion, this chapter lists major points of interest in North America to clarify how diverse destinations may be appealing to different tourists, for many reasons.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Corporate Communication, University of Malta, Msida, Malta
Mark Anthony Camilleri
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mark Anthony Camilleri .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Camilleri, M.A. (2018). The Tourism Industry: An Overview. In: Travel Marketing, Tourism Economics and the Airline Product. Tourism, Hospitality & Event Management. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49849-2_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49849-2_1
Published : 30 September 2017
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-49848-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-49849-2
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Agriculture and the Environment
- Case Studies
- Chemistry and Toxicology
- Environment and Human Health
- Environmental Biology
- Environmental Economics
- Environmental Engineering
- Environmental Ethics and Philosophy
- Environmental History
- Environmental Issues and Problems
- Environmental Processes and Systems
- Environmental Sociology and Psychology
- Environments
- Framing Concepts in Environmental Science
- Management and Planning
- Policy, Governance, and Law
- Quantitative Analysis and Tools
- Sustainability and Solutions
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
The role of tourism in sustainable development.
- Robert B. Richardson Robert B. Richardson Community Sustainability, Michigan State University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780199389414.013.387
- Published online: 25 March 2021
Sustainable development is the foundational principle for enhancing human and economic development while maintaining the functional integrity of ecological and social systems that support regional economies. Tourism has played a critical role in sustainable development in many countries and regions around the world. In developing countries, tourism development has been used as an important strategy for increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, creating jobs, and improving food security. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of biological diversity, natural resources, and cultural heritage sites that attract international tourists whose local purchases generate income and support employment and economic development. Tourism has been associated with the principles of sustainable development because of its potential to support environmental protection and livelihoods. However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is multifaceted, as some types of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, many of which are borne by host communities.
The concept of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which involves the participation of large numbers of people, often in structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has been associated with economic leakage and dependence, along with negative environmental and social impacts. Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to these economic, environmental, and social impacts. Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms. Tourism has played an important role in sustainable development in some countries through the development of alternative tourism models, including ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others that aim to enhance livelihoods, increase local economic growth, and provide for environmental protection. Although these models have been given significant attention among researchers, the extent of their implementation in tourism planning initiatives has been limited, superficial, or incomplete in many contexts.
The sustainability of tourism as a global system is disputed among scholars. Tourism is dependent on travel, and nearly all forms of transportation require the use of non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels for energy. The burning of fossil fuels for transportation generates emissions of greenhouse gases that contribute to global climate change, which is fundamentally unsustainable. Tourism is also vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include the impacts of natural disasters, disease outbreaks, and civil unrest. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to global shocks include the impacts of climate change, economic crisis, global public health pandemics, oil price shocks, and acts of terrorism. It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, debatable, and potentially contradictory.
- conservation
- economic development
- environmental impacts
- sustainable development
- sustainable tourism
- tourism development
Introduction
Sustainable development is the guiding principle for advancing human and economic development while maintaining the integrity of ecosystems and social systems on which the economy depends. It is also the foundation of the leading global framework for international cooperation—the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (United Nations, 2015 ). The concept of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future (World Commission on Environment and Development [WCED], 1987 , p. 29), which defined it as “paths of human progress that meet the needs and aspirations of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.” Concerns about the environmental implications of economic development in lower income countries had been central to debates about development studies since the 1970s (Adams, 2009 ). The principles of sustainable development have come to dominate the development discourse, and the concept has become the primary development paradigm since the 1990s.
Tourism has played an increasingly important role in sustainable development since the 1990s, both globally and in particular countries and regions. For decades, tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, non-extractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ). Many developing countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development is increasingly viewed as an important tool in increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, and improving food security. Tourism enables communities that are poor in material wealth, but rich in history and cultural heritage, to leverage their unique assets for economic development (Honey & Gilpin, 2009 ). More importantly, tourism offers an alternative to large-scale development projects, such as construction of dams, and to extractive industries such as mining and forestry, all of which contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and the cultural values of Indigenous Peoples.
Environmental quality in destination areas is inextricably linked with tourism, as visiting natural areas and sightseeing are often the primary purpose of many leisure travels. Some forms of tourism, such as ecotourism, can contribute to the conservation of biodiversity and the protection of ecosystem functions in destination areas (Fennell, 2020 ; Gössling, 1999 ). Butler ( 1991 ) suggests that there is a kind of mutual dependence between tourism and the environment that should generate mutual benefits. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of species diversity, natural resources, and protected areas. Such ideas imply that tourism may be well aligned with the tenets of sustainable development.
However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is complex, as some forms of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions, freshwater use, land use, and food consumption (Butler, 1991 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ; Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Assessments of the sustainability of tourism have highlighted several themes, including (a) parks, biodiversity, and conservation; (b) pollution and climate change; (c) prosperity, economic growth, and poverty alleviation; (d) peace, security, and safety; and (e) population stabilization and reduction (Buckley, 2012 ). From a global perspective, tourism contributes to (a) changes in land cover and land use; (b) energy use, (c) biotic exchange and extinction of wild species; (d) exchange and dispersion of diseases; and (e) changes in the perception and understanding of the environment (Gössling, 2002 ).
Research on tourism and the environment spans a wide range of social and natural science disciplines, and key contributions have been disseminated across many interdisciplinary fields, including biodiversity conservation, climate science, economics, and environmental science, among others (Buckley, 2011 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Given the global significance of the tourism sector and its environmental impacts, the role of tourism in sustainable development is an important topic of research in environmental science generally and in environmental economics and management specifically. Reviews of tourism research have highlighted future research priorities for sustainable development, including the role of tourism in the designation and expansion of protected areas; improvement in environmental accounting techniques that quantify environmental impacts; and the effects of individual perceptions of responsibility in addressing climate change (Buckley, 2012 ).
Tourism is one of the world’s largest industries, and it has linkages with many of the prime sectors of the global economy (Fennell, 2020 ). As a global economic sector, tourism represents one of the largest generators of wealth, and it is an important agent of economic growth and development (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). Tourism is a critical industry in many local and national economies, and it represents a large and growing share of world trade (Hunter, 1995 ). Global tourism has had an average annual increase of 6.6% over the past half century, with international tourist arrivals rising sharply from 25.2 million in 1950 to more than 950 million in 2010 . In 2019 , the number of international tourists reached 1.5 billion, up 4% from 2018 (Fennell, 2020 ; United Nations World Tourism Organization [UNWTO], 2020 ). European countries are host to more than half of international tourists, but since 1990 , growth in international arrivals has risen faster than the global average, in both the Middle East and the Asia and Pacific region (UNWTO, 2020 ).
The growth in global tourism has been accompanied by an expansion of travel markets and a diversification of tourism destinations. In 1950 , the top five travel destinations were all countries in Europe and the Americas, and these destinations held 71% of the global travel market (Fennell, 2020 ). By 2002 , these countries represented only 35%, which underscores the emergence of newly accessible travel destinations in Africa, Asia, the Middle East, and the Pacific Rim, including numerous developing countries. Over the past 70 years, global tourism has grown significantly as an economic sector, and it has contributed to the economic development of dozens of nations.
Given the growth of international tourism and its emergence as one of the world’s largest export sectors, the question of its impact on economic growth for the host countries has been a topic of great interest in the tourism literature. Two hypotheses have emerged regarding the role of tourism in the economic growth process (Apergis & Payne, 2012 ). First, tourism-led growth hypothesis relies on the assumption that tourism is an engine of growth that generates spillovers and positive externalities through economic linkages that will impact the overall economy. Second, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis emphasizes policies oriented toward well-defined and enforceable property rights, stable political institutions, and adequate investment in both physical and human capital to facilitate the development of the tourism sector. Studies have concluded with support for both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Durbarry, 2004 ; Katircioglu, 2010 ) and the economic-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Katircioglu, 2009 ; Oh, 2005 ), whereas other studies have found support for a bidirectional causality for tourism and economic growth (e.g., Apergis & Payne, 2012 ; Lee & Chang, 2008 ).
The growth of tourism has been marked by an increase in the competition for tourist expenditures, making it difficult for destinations to maintain their share of the international tourism market (Butler, 1991 ). Tourism development is cyclical and subject to short-term cycles and overconsumption of resources. Butler ( 1980 ) developed a tourist-area cycle of evolution that depicts the number of tourists rising sharply over time through periods of exploration, involvement, and development, before eventual consolidation and stagnation. When tourism growth exceeds the carrying capacity of the area, resource degradation can lead to the decline of tourism unless specific steps are taken to promote rejuvenation (Butler, 1980 , 1991 ).
The potential of tourism development as a tool to contribute to environmental conservation, economic growth, and poverty reduction is derived from several unique characteristics of the tourism system (UNWTO, 2002 ). First, tourism represents an opportunity for economic diversification, particularly in marginal areas with few other export options. Tourists are attracted to remote areas with high values of cultural, wildlife, and landscape assets. The cultural and natural heritage of developing countries is frequently based on such assets, and tourism represents an opportunity for income generation through the preservation of heritage values. Tourism is the only export sector where the consumer travels to the exporting country, which provides opportunities for lower-income households to become exporters through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists. Tourism is also labor intensive; it provides small-scale employment opportunities, which also helps to promote gender equity. Finally, there are numerous indirect benefits of tourism for people living in poverty, including increased market access for remote areas through the development of roads, infrastructure, and communication networks. Nevertheless, travel is highly income elastic and carbon intensive, which has significant implications for the sustainability of the tourism sector (Lenzen et al., 2018 ).
Concerns about environmental issues appeared in tourism research just as global awareness of the environmental impacts of human activities was expanding. The United Nations Conference on the Human Environment was held in Stockholm in 1972 , the same year as the publication of The Limits to Growth (Meadows et al., 1972 ), which highlighted the concerns about the implications of exponential economic and population growth in a world of finite resources. This was the same year that the famous Blue Marble photograph of Earth was taken by the crew of the Apollo 17 spacecraft (Höhler, 2015 , p. 10), and the image captured the planet cloaked in the darkness of space and became a symbol of Earth’s fragility and vulnerability. As noted by Buckley ( 2012 ), tourism researchers turned their attention to social and environmental issues around the same time (Cohen, 1978 ; Farrell & McLellan, 1987 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Young, 1973 ).
The notion of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future , the report of the World Commission on Environment and Development, also known as the Brundtland Commission (WCED, 1987 ). The report characterized sustainable development in terms of meeting “the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” (WCED, 1987 , p. 43). Four basic principles are fundamental to the concept of sustainability: (a) the idea of holistic planning and strategy making; (b) the importance of preserving essential ecological processes; (c) the need to protect both human heritage and biodiversity; and (d) the need to develop in such a way that productivity can be sustained over the long term for future generations (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ). In addition to achieving balance between economic growth and the conservation of natural resources, there should be a balance of fairness and opportunity between the nations of the world.
Although the modern concept of sustainable development emerged with the publication of Our Common Future , sustainable development has its roots in ideas about sustainable forest management that were developed in Europe during the 17th and 18th centuries (Blewitt, 2015 ; Grober, 2007 ). Sustainable forest management is concerned with the stewardship and use of forests in a way that maintains their biodiversity, productivity, and regeneration capacity as well as their potential to fulfill society’s demands for forest products and benefits. Building on these ideas, Daly ( 1990 ) offered two operational principles of sustainable development. First, sustainable development implies that harvest rates should be no greater than rates of regeneration; this concept is known as maximum sustainable yield. Second, waste emission rates should not exceed the natural assimilative capacities of the ecosystems into which the wastes are emitted. Regenerative and assimilative capacities are characterized as natural capital, and a failure to maintain these capacities is not sustainable.
Shortly after the emergence of the concept of sustainable development in academic and policy discourse, tourism researchers began referring to the notion of sustainable tourism (May, 1991 ; Nash & Butler, 1990 ), which soon became the dominant paradigm of tourism development. The concept of sustainable tourism, as with the role of tourism in sustainable development, has been interpreted in different ways, and there is a lack of consensus concerning its meaning, objectives, and indicators (Sharpley, 2000 ). Growing interest in the subject inspired the creation of a new academic journal, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , which was launched in 1993 and has become a leading tourism journal. It is described as “an international journal that publishes research on tourism and sustainable development, including economic, social, cultural and political aspects.”
The notion of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which is characterized by the participation of large numbers of people, often provided as structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has risen sharply in the last half century. International arrivals alone have increased by an average annual rate of more than 25% since 1950 , and many of those trips involved mass tourism activities (Fennell, 2020 ; UNWTO, 2020 ). Some examples of mass tourism include beach resorts, cruise ship tourism, gaming casinos, golf resorts, group tours, ski resorts, theme parks, and wildlife safari tourism, among others. Little data exist regarding the volume of domestic mass tourism, but nevertheless mass tourism activities dominate the global tourism sector. Mass tourism has been shown to generate benefits to host countries, such as income and employment generation, although it has also been associated with economic leakage (where revenue generated by tourism is lost to other countries’ economies) and economic dependency (where developing countries are dependent on wealthier countries for tourists, imports, and foreign investment) (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Khan, 1997 ; Peeters, 2012 ). Mass tourism has been associated with numerous negative environmental impacts and social impacts (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Ghimire, 2013 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ). Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to many of these economic, environmental, and social impacts.
Much of the early research on sustainable tourism focused on defining the concept, which has been the subject of vigorous debate (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Inskeep, 1991 ; Liu, 2003 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). Early definitions of sustainable tourism development seemed to fall in one of two categories (Sharpley, 2000 ). First, the “tourism-centric” paradigm of sustainable tourism development focuses on sustaining tourism as an economic activity (Hunter, 1995 ). Second, alternative paradigms have situated sustainable tourism in the context of wider sustainable development policies (Butler, 1991 ). One of the most comprehensive definitions of sustainable tourism echoes some of the language of the Brundtland Commission’s definition of sustainable development (WCED, 1987 ), emphasizing opportunities for the future while also integrating social and environmental concerns:
Sustainable tourism can be thought of as meeting the needs of present tourists and host regions while protecting and enhancing opportunity for the future. Sustainable tourism development is envisaged as leading to management of all resources in such a way that we can fulfill economic, social and aesthetic needs while maintaining cultural integrity, essential ecological processes, biological diversity and life support systems. (Inskeep, 1991 , p. 461)
Hunter argued that over the short and long terms, sustainable tourism development should
“meet the needs and wants of the local host community in terms of improved living standards and quality of life;
satisfy the demands of tourists and the tourism industry, and continue to attract them in order to meet the first aim; and
safeguard the environmental resource base for tourism, encompassing natural, built and cultural components, in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.” (Hunter, 1995 , p. 156)
Numerous other definitions have been documented, and the term itself has been subject to widespread critique (Buckley, 2012 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, there have been numerous calls to move beyond debate about a definition and to consider how it may best be implemented in practice (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Liu, 2003 ). Cater ( 1993 ) identified three key criteria for sustainable tourism: (a) meeting the needs of the host population in terms of improved living standards both in the short and long terms; (b) satisfying the demands of a growing number of tourists; and (c) safeguarding the natural environment in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.
Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ). Similar criticisms have been leveled at the concept of sustainable development, which has been described as an oxymoron with a wide range of meanings (Adams, 2009 ; Daly, 1990 ) and “defined in such a way as to be either morally repugnant or logically redundant” (Beckerman, 1994 , p. 192). Sharpley ( 2000 ) suggests that in the tourism literature, there has been “a consistent and fundamental failure to build a theoretical link between sustainable tourism and its parental paradigm,” sustainable development (p. 2). Hunter ( 1995 ) suggests that practical measures designed to operationalize sustainable tourism fail to address many of the critical issues that are central to the concept of sustainable development generally and may even actually counteract the fundamental requirements of sustainable development. He suggests that mainstream sustainable tourism development is concerned with protecting the immediate resource base that will sustain tourism development while ignoring concerns for the status of the wider tourism resource base, such as potential problems associated with air pollution, congestion, introduction of invasive species, and declining oil reserves. The dominant paradigm of sustainable tourism development has been described as introverted, tourism-centric, and in competition with other sectors for scarce resources (McKercher, 1993a ). Hunter ( 1995 , p. 156) proposes an alternative, “extraparochial” paradigm where sustainable tourism development is reconceptualized in terms of its contribution to overall sustainable development. Such a paradigm would reconsider the scope, scale, and sectoral context of tourism-related resource utilization issues.
“Sustainability,” “sustainable tourism,” and “sustainable development” are all well-established terms that have often been used loosely and interchangeably in the tourism literature (Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, the subject of sustainable tourism has been given considerable attention and has been the focus of numerous academic compilations and textbooks (Coccossis & Nijkamp, 1995 ; Hall & Lew, 1998 ; Stabler, 1997 ; Swarbrooke, 1999 ), and it calls for new approaches to sustainable tourism development (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). The notion of sustainable tourism has been reconceptualized in the literature by several authors who provided alternative frameworks for tourism development (Buckley, 2012 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ; Sharpley, 2000 ).
Early research in sustainable tourism focused on the local environmental impacts of tourism, including energy use, water use, food consumption, and change in land use (Buckley, 2012 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ). Subsequent research has emphasized the global environmental impacts of tourism, such as greenhouse gas emissions and biodiversity losses (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Additional research has emphasized the impacts of environmental change on tourism itself, including the impacts of climate change on tourist behavior (Gössling et al., 2012 ; Richardson & Loomis, 2004 ; Scott et al., 2012 ; Viner, 2006 ). Countries that are dependent on tourism for economic growth may be particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change (Richardson & Witkoswki, 2010 ).
The early focus on environmental issues in sustainable tourism has been broadened to include economic, social, and cultural issues as well as questions of power and equity in society (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Sharpley, 2014 ), and some of these frameworks have integrated notions of social equity, prosperity, and cultural heritage values. Sustainable tourism is dependent on critical long-term considerations of the impacts; notions of equity; an appreciation of the importance of linkages (i.e., economic, social, and environmental); and the facilitation of cooperation and collaboration between different stakeholders (Elliott & Neirotti, 2008 ).
McKercher ( 1993b ) notes that tourism resources are typically part of the public domain or are intrinsically linked to the social fabric of the host community. As a result, many commonplace tourist activities such as sightseeing may be perceived as invasive by members of the host community. Many social impacts of tourism can be linked to the overuse of the resource base, increases in traffic congestion, rising land prices, urban sprawl, and changes in the social structure of host communities. Given the importance of tourist–resident interaction, sustainable tourism development depends in part on the support of the host community (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ).
Tourism planning involves the dual objectives of optimizing the well-being of local residents in host communities and minimizing the costs of tourism development (Sharpley, 2014 ). Tourism researchers have paid significant attention to examining the social impacts of tourism in general and to understanding host communities’ perceptions of tourism in particular. Studies of the social impacts of tourism development have examined the perceptions of local residents and the effects of tourism on social cohesion, traditional lifestyles, and the erosion of cultural heritage, particularly among Indigenous Peoples (Butler & Hinch, 2007 ; Deery et al., 2012 ; Mathieson & Wall, 1982 ; Sharpley, 2014 ; Whitford & Ruhanen, 2016 ).
Alternative Tourism and Sustainable Development
A wide body of published research is related to the role of tourism in sustainable development, and much of the literature involves case studies of particular types of tourism. Many such studies contrast types of alternative tourism with those of mass tourism, which has received sustained criticism for decades and is widely considered to be unsustainable (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ). Still, some tourism researchers have taken issue with the conclusion that mass tourism is inherently unsustainable (Sharpley, 2000 ; Weaver, 2007 ), and some have argued for developing pathways to “sustainable mass tourism” as “the desired and impending outcome for most destinations” (Weaver, 2012 , p. 1030). In integrating an ethical component to mass tourism development, Weaver ( 2014 , p. 131) suggests that the desirable outcome is “enlightened mass tourism.” Such suggestions have been contested in the literature and criticized for dubious assumptions about emergent norms of sustainability and support for growth, which are widely seen as contradictory (Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ).
Models of responsible or alternative tourism development include ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others. Most models of alternative tourism development emphasize themes that aim to counteract the perceived negative impacts of conventional or mass tourism. As such, the objectives of these models of tourism development tend to focus on minimizing environmental impacts, supporting biodiversity conservation, empowering local communities, alleviating poverty, and engendering pleasant relationships between tourists and residents.
Approaches to alternative tourism development tend to overlap with themes of responsible tourism, and the two terms are frequently used interchangeably. Responsible tourism has been characterized in terms of numerous elements, including
ensuring that communities are involved in and benefit from tourism;
respecting local, natural, and cultural environments;
involving the local community in planning and decision-making;
using local resources sustainably;
behaving in ways that are sensitive to the host culture;
maintaining and encouraging natural, economic, and cultural diversity; and
assessing environmental, social, and economic impacts as a prerequisite to tourism development (Spenceley, 2012 ).
Hetzer ( 1965 ) identified four fundamental principles or perquisites for a more responsible form of tourism: (a) minimum environmental impact; (b) minimum impact on and maximum respect for host cultures; (c) maximum economic benefits to the host country; and (d) maximum leisure satisfaction to participating tourists.
The history of ecotourism is closely connected with the emergence of sustainable development, as it was born out of a concern for the conservation of biodiversity. Ecotourism is a form of tourism that aims to minimize local environmental impacts while bringing benefits to protected areas and the people living around those lands (Honey, 2008 ). Ecotourism represents a small segment of nature-based tourism, which is understood as tourism based on the natural attractions of an area, such as scenic areas and wildlife (Gössling, 1999 ). The ecotourism movement gained momentum in the 1990s, primarily in developing countries in Latin America and sub-Saharan Africa, and nearly all countries are now engaged in some form of ecotourism. In some communities, ecotourism is the primary economic activity and source of income and economic development.
The term “ecotourism” was coined by Hector Ceballos-Lascuráin and defined by him as “tourism that consists in travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific object of studying, admiring, and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 13). In discussing ecotourism resources, he also made reference to “any existing cultural manifestations (both past and present) found in these areas” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 14). The basic precepts of ecotourism had been discussed long before the actual use of the term. Twenty years earlier, Hetzer ( 1965 ) referred to a form of tourism “based principally upon natural and archaeological resources such as caves, fossil sites (and) archaeological sites.” Thus, both natural resources and cultural resources were integrated into ecotourism frameworks from the earliest manifestations.
Costa Rica is well known for having successfully integrated ecotourism in its overall strategy for sustainable development, and numerous case studies of ecotourism in Costa Rica appear in the literature (Chase et al., 1998 ; Fennell & Eagles, 1990 ; Gray & Campbell, 2007 ; Hearne & Salinas, 2002 ). Ecotourism in Costa Rica has been seen as having supported the economic development of the country while promoting biodiversity conservation in its extensive network of protected areas. Chase et al. ( 1998 ) estimated the demand for ecotourism in a study of differential pricing of entrance fees at national parks in Costa Rica. The authors estimated elasticities associated with the own-price, cross-price, and income variables and found that the elasticities of demand were significantly different between three different national park sites. The results reveal the heterogeneity characterizing tourist behavior and park attractions and amenities. Hearne and Salinas ( 2002 ) used choice experiments to examine the preferences of domestic and foreign tourists in Costa Rica in an ecotourism site. Both sets of tourists demonstrated a preference for improved infrastructure, more information, and lower entrance fees. Foreign tourists demonstrated relatively stronger preferences for the inclusion of restrictions in the access to some trails.
Ecotourism has also been studied extensively in Kenya (Southgate, 2006 ), Malaysia (Lian Chan & Baum, 2007 ), Nepal (Baral et al., 2008 ), Peru (Stronza, 2007 ), and Taiwan (Lai & Nepal, 2006 ), among many other countries. Numerous case studies have demonstrated the potential for ecotourism to contribute to sustainable development by providing support for biodiversity conservation, local livelihoods, and regional development.
Community-Based Tourism
Community-based tourism (CBT) is a model of tourism development that emphasizes the development of local communities and allows for local residents to have substantial control over its development and management, and a major proportion of the benefits remain within the community. CBT emerged during the 1970s as a response to the negative impacts of the international mass tourism development model (Cater, 1993 ; Hall & Lew, 2009 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ).
Community-based tourism has been examined for its potential to contribute to poverty reduction. In a study of the viability of the CBT model to support socioeconomic development and poverty alleviation in Nicaragua, tourism was perceived by participants in the study to have an impact on employment creation in their communities (Zapata et al., 2011 ). Tourism was seen to have had positive impacts on strengthening local knowledge and skills, particularly on the integration of women to new roles in the labor market. One of the main perceived gains regarding the environment was the process of raising awareness regarding the conservation of natural resources. The small scale of CBT operations and low capacity to accommodate visitors was seen as a limitation of the model.
Spenceley ( 2012 ) compiled case studies of community-based tourism in countries in southern Africa, including Botswana, Madagascar, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. In this volume, authors characterize community-based and nature-based tourism development projects in the region and demonstrate how community participation in planning and decision-making has generated benefits for local residents and supported conservation initiatives. They contend that responsible tourism practices are of particular importance in the region because of the rich biological diversity, abundant charismatic wildlife, and the critical need for local economic development and livelihood strategies.
In Kenya, CBT enterprises were not perceived to have made a significant impact on poverty reduction at an individual household level, in part because the model relied heavily on donor funding, reinforcing dependency and poverty (Manyara & Jones, 2007 ). The study identified several critical success factors for CBT enterprises, namely, awareness and sensitization, community empowerment, effective leadership, and community capacity building, which can inform appropriate tourism policy formulation in Kenya. The impacts of CBT on economic development and poverty reduction would be greatly enhanced if tourism initiatives were able to emphasize independence, address local community priorities, enhance community empowerment and transparency, discourage elitism, promote effective community leadership, and develop community capacity to operate their own enterprises more efficiently.
Pro-Poor Tourism
Pro-poor tourism is a model of tourism development that brings net benefits to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ; Harrison, 2008 ). Although its theoretical foundations and development objectives overlap to some degree with those of community-based tourism and other models of AT, the key distinctive feature of pro-poor tourism is that it places poor people and poverty at the top of the agenda. By focusing on a very simple and incontrovertibly moral idea, namely, the net benefits of tourism to impoverished people, the concept has broad appeal to donors and international aid agencies. Harnessing the economic benefits of tourism for pro-poor growth means capitalizing on the advantages while reducing negative impacts to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ). Pro-poor approaches to tourism development include increasing access of impoverished people to economic benefits; addressing negative social and environmental impacts associated with tourism; and focusing on policies, processes, and partnerships that seek to remove barriers to participation by people living in poverty. At the local level, pro-poor tourism can play a very significant role in livelihood security and poverty reduction (Ashley & Roe, 2002 ).
Rogerson ( 2011 ) argues that the growth of pro-poor tourism initiatives in South Africa suggests that the country has become a laboratory for the testing and evolution of new approaches toward sustainable development planning that potentially will have relevance for other countries in the developing world. A study of pro-poor tourism development initiatives in Laos identified a number of favorable conditions for pro-poor tourism development, including the fact that local people are open to tourism and motivated to participate (Suntikul et al., 2009 ). The authors also noted a lack of development in the linkages that could optimize the fulfilment of the pro-poor agenda, such as training or facilitation of local people’s participation in pro-poor tourism development at the grassroots level.
Critics of the model have argued that pro-poor tourism is based on an acceptance of the status quo of existing capitalism, that it is morally indiscriminate and theoretically imprecise, and that its practitioners are academically and commercially marginal (Harrison, 2008 ). As Chok et al. ( 2007 ) indicate, the focus “on poor people in the South reflects a strong anthropocentric view . . . and . . . environmental benefits are secondary to poor peoples’” benefits (p. 153).
Harrison ( 2008 ) argues that pro-poor tourism is not a distinctive approach to tourism as a development tool and that it may be easier to discuss what pro-poor tourism is not than what it is. He concludes that it is neither anticapitalist nor inconsistent with mainstream tourism on which it relies; it is neither a theory nor a model and is not a niche form of tourism. Further, he argues that it has no distinctive method and is not only about people living in poverty.
Slow Tourism
The concept of slow tourism has emerged as a model of sustainable tourism development, and as such, it lacks an exact definition. The concept of slow tourism traces its origin back to some institutionalized social movements such as “slow food” and “slow cities” that began in Italy in the 1990s and spread rapidly around the world (Fullagar et al., 2012 ; Oh et al., 2016 , p. 205). Advocates of slow tourism tend to emphasize slowness in terms of speed, mobility, and modes of transportation that generate less environmental pollution. They propose niche marketing for alternative forms of tourism that focus on quality upgrading rather than merely increasing the quantity of visitors via the established mass-tourism infrastructure (Conway & Timms, 2010 ).
In the context of the Caribbean region, slow tourism has been promoted as more culturally sensitive and authentic, as compared to the dominant mass tourism development model that is based on all-inclusive beach resorts dependent on foreign investment (Conway & Timms, 2010 ). Recognizing its value as an alternative marketing strategy, Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) make the case for rebranding alternative tourism in the Caribbean as a means of revitalizing the sector for the changing demands of tourists in the 21st century . They suggest that slow tourism is the antithesis of mass tourism, which “relies on increasing the quantity of tourists who move through the system with little regard to either the quality of the tourists’ experience or the benefits that accrue to the localities the tourist visits” (Conway & Timms, 2010 , p. 332). The authors draw on cases from Barbados, the Grenadines, Jamaica, and Trinidad and Tobago to characterize models of slow tourism development in remote fishing villages and communities near nature preserves and sea turtle nesting sites.
Although there is a growing interest in the concept of slow tourism in the literature, there seems to be little agreement about the exact nature of slow tourism and whether it is a niche form of special interest tourism or whether it represents a more fundamental potential shift across the industry. Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) focus on the destination, advocating for slow tourism in terms of a promotional identity for an industry in need of rebranding. Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 77) discusses the implementation of slow tourism in terms of “encouraging visitors to make slower choices when planning and enjoying their holidays.” It is not clear whether slow tourism is a marketing strategy, a mindset, or a social movement, but the literature on slow tourism nearly always equates the term with sustainable tourism (Caffyn, 2012 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Oh et al., 2016 ). Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 80) suggests that slow tourism could offer a “win–win,” which she describes as “a more sustainable form of tourism; keeping more of the economic benefits within the local community and destination; and delivering a more meaningful and satisfying experience.” Research on slow tourism is nascent, and thus the contribution of slow tourism to sustainable development is not well understood.
Impacts of Tourism Development
The role of tourism in sustainable development can be examined through an understanding of the economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism. Tourism is a global phenomenon that involves travel, recreation, the consumption of food, overnight accommodations, entertainment, sightseeing, and other activities that simultaneously intersect the lives of local residents, businesses, and communities. The impacts of tourism involve benefits and costs to all groups, and some of these impacts cannot easily be measured. Nevertheless, they have been studied extensively in the literature, which provides some context for how these benefits and costs are distributed.
Economic Impacts of Tourism
The travel and tourism sector is one of the largest components of the global economy, and global tourism has increased exponentially since the end of the Second World War (UNWTO, 2020 ). The direct, indirect, and induced economic impact of global travel accounted for 8.9 trillion U.S. dollars in contribution to the global gross domestic product (GDP), or 10.3% of global GDP. The global travel and tourism sector supports approximately 330 million jobs, or 1 in 10 jobs around the world. From an economic perspective, tourism plays a significant role in sustainable development. In many developing countries, tourism has the potential to play a unique role in income generation and distribution relative to many other industries, in part because of its high multiplier effect and consumption of local goods and services. However, research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been fully realized (Liu, 2003 ).
Numerous studies have examined the impact of tourism expenditure on GDP, income, employment, and public sector revenue. Narayan ( 2004 ) used a computable general equilibrium model to estimate the economic impact of tourism growth on the economy of Fiji. Tourism is Fiji’s largest industry, with average annual growth of 10–12%; and as a middle-income country, tourism is critical to Fiji’s economic development. The findings indicate that an increase in tourism expenditures was associated with an increase in GDP, an improvement in the country’s balance of payments, and an increase in real consumption and national welfare. Evidence suggests that the benefits of tourism expansion outweigh any export effects caused by an appreciation of the exchange rate and an increase in domestic prices and wages.
Seetanah ( 2011 ) examined the potential contribution of tourism to economic growth and development using panel data of 19 island economies around the world from 1990 to 2007 and revealed that tourism development is an important factor in explaining economic performance in the selected island economies. The results have policy implications for improving economic growth by harnessing the contribution of the tourism sector. Pratt ( 2015 ) modeled the economic impact of tourism for seven small island developing states in the Pacific, the Caribbean, and the Indian Ocean. In most states, the transportation sector was found to have above-average linkages to other sectors of the economy. The results revealed some advantages of economies of scale for maximizing the economic contribution of tourism.
Apergis and Payne ( 2012 ) examined the causal relationship between tourism and economic growth for a panel of nine Caribbean countries. The panel of Caribbean countries includes Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Grenada, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, and Trinidad and Tobago. The authors use a panel error correction model to reveal bidirectional causality between tourism and economic growth in both the short run and the long run. The presence of bidirectional causality reiterates the importance of the tourism sector in the generation of foreign exchange income and in financing the production of goods and services within these countries. Likewise, stable political institutions and adequate government policies to ensure the appropriate investment in physical and human capital will enhance economic growth. In turn, stable economic growth will provide the resources needed to develop the tourism infrastructure for the success of the countries’ tourism sector. Thus, policy makers should be cognizant of the interdependent relationship between tourism and economic growth in the design and implementation of economic policy. The mixed nature of these results suggest that the relationship between tourism and economic growth depends largely on the social and economic context as well as the role of tourism in the economy.
The economic benefits and costs of tourism are frequently distributed unevenly. An analysis of the impact of wildlife conservation policies in Zambia on household welfare found that households located near national parks earn higher levels of income from wage employment and self-employment than other rural households in the country, but they were also more likely to suffer crop losses related to wildlife conflicts (Richardson et al., 2012 ). The findings suggest that tourism development and wildlife conservation can contribute to pro-poor development, but they may be sustainable only if human–wildlife conflicts are minimized or compensated.
Environmental Impacts of Tourism
The environmental impacts of tourism are significant, ranging from local effects to contributions to global environmental change (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Tourism is both dependent on water resources and a factor in global and local freshwater use. Tourists consume water for drinking, when showering and using the toilet, when participating in activities such as winter ski tourism (i.e., snowmaking), and when using swimming pools and spas. Fresh water is also needed to maintain hotel gardens and golf courses, and water use is embedded in tourism infrastructure development (e.g., accommodations, laundry, dining) and in food and fuel production. Direct water consumption in tourism is estimated to be approximately 350 liters (L) per guest night for accommodation; when indirect water use from food, energy, and transport are considered, total water use in tourism is estimated to be approximately 6,575 L per guest night, or 27,800 L per person per trip (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). In addition, tourism contributes to the pollution of oceans as well as lakes, rivers, and other freshwater systems (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling et al., 2011 ).
The clearing and conversion of land is central for tourism development, and in many cases, the land used for tourism includes roads, airports, railways, accommodations, trails, pedestrian walks, shopping areas, parking areas, campgrounds, vacation homes, golf courses, marinas, ski resorts, and indirect land use for food production, disposal of solid wastes, and the treatment of wastewater (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Global land use for accommodation is estimated to be approximately 42 m 2 per bed. Total global land use for tourism is estimated to be nearly 62,000 km 2 , or 11.7 m 2 per tourist; more than half of this estimate is represented by land use for traffic infrastructure.
Tourism and hospitality have direct and indirect links to nearly all aspects of food production, preparation, and consumption because of the quantities of food consumed in tourism contexts (Gössling et al., 2011 ). Food production has significant implications for sustainable development, given the growing global demand for food. The implications include land conversion, losses to biodiversity, changes in nutrient cycling, and contributions to greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change (Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Global food use for tourism is estimated to be approximately 39.4 megatons 1 (Mt), about 38% than the amount of food consumed at home. This equates to approximately 1,800 grams (g) of food consumed per tourist per day.
Although tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, (Gössling, 2000 ), assessments reveal that such pursuits have a significant carbon footprint, as tourism is significantly more carbon intensive than other potential areas of economic development (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Tourism is dependent on energy, and virtually all energy use in the tourism sector is derived from fossil fuels, which contribute to global greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change. Energy use for tourism has been estimated to be approximately 3,575 megajoules 2 (MJ) per trip, including energy for travel and accommodations (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). A previous estimate of global carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) emissions from tourism provided values of 1.12 gigatons 3 (Gt) of CO 2 , amounting to about 3% of global CO 2 -equivalent (CO 2 e) emissions (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). However, these analyses do not cover the supply chains underpinning tourism and do not therefore represent true carbon footprints. A more complete analysis of the emissions from energy consumption necessary to sustain the tourism sector would include food and beverages, infrastructure construction and maintenance, retail, and financial services. Between 2009 and 2013 , tourism’s global carbon footprint is estimated to have increased from 3.9 to 4.5 GtCO 2 e, four times more than previously estimated, accounting for about 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). The majority of this footprint is exerted by and within high-income countries. The rising global demand for tourism is outstripping efforts at decarbonization of tourism operations and as a result is accelerating global carbon emissions.
Social Impacts of Tourism
The social impacts of tourism have been widely studied, with an emphasis on residents’ perceptions in the host community (Sharpley, 2014 ). Case studies include research conducted in Australia (Faulkner & Tideswell, 1997 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Tovar & Lockwood, 2008 ), Belize (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ), China (Gu & Ryan, 2008 ), Fiji (King et al., 1993 ), Greece (Haralambopoulos & Pizam, 1996 ; Tsartas, 1992 ), Hungary (Rátz, 2000 ), Thailand (Huttasin, 2008 ), Turkey (Kuvan & Akan, 2005 ), the United Kingdom (Brunt & Courtney, 1999 ; Haley et al., 2005 ), and the United States (Andereck et al., 2005 ; Milman & Pizam, 1988 ), among others. The social impacts of tourism are difficult to measure, and most published studies are mainly concerned with the social impacts on the host communities rather than the impacts on the tourists themselves.
Studies of residents’ perceptions of tourism are typically conducted using household surveys. In most cases, residents recognize the economic dependence on tourism for income, and there is substantial evidence to suggest that working in or owning a business in tourism or a related industry is associated with more positive perceptions of tourism (Andereck et al., 2007 ). The perceived nature of negative effects is complex and often conveys a dislike of crowding, traffic congestion, and higher prices for basic needs (Deery et al., 2012 ). When the number of tourists far exceeds that of the resident population, negative attitudes toward tourism may manifest (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ). However, residents who recognize negative impacts may not necessarily oppose tourism development (King et al., 1993 ).
In some regions, little is known about the social and cultural impacts of tourism despite its dominance as an economic sector. Tourism is a rapidly growing sector in Cuba, and it is projected to grow at rates that exceed the average projected growth rates for the Caribbean and the world overall (Salinas et al., 2018 ). Still, even though there has been rapid tourism development in Cuba, there has been little research related to the environmental and sociocultural impacts of this tourism growth (Rutty & Richardson, 2019 ).
In some international tourism contexts, studies have found that residents are generally resentful toward tourism because it fuels inequality and exacerbates racist attitudes and discrimination (Cabezas, 2004 ; Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Mbaiwa, 2005 ). Other studies revealed similar narratives and recorded statements of exclusion and socioeconomic stratification (Sanchez & Adams, 2008 ). Local residents often must navigate the gaps in the racialized, gendered, and sexualized structures imposed by the global tourism industry and host-country governments (Cabezas, 2004 ).
However, during times of economic crisis, residents may develop a more permissive view as their perceptions of the costs of tourism development decrease (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). This increased positive attitude is not based on an increase in the perception of positive impacts of tourism, but rather on a decrease in the perception of the negative impacts.
There is a growing body of research on Indigenous and Aboriginal tourism that emphasizes justice issues such as human rights and self-empowerment, control, and participation of traditional owners in comanagement of destinations (Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Ryan & Huyton, 2000 ; Whyte, 2010 ).
Sustainability of Tourism
A process or system is said to be sustainable to the extent that it is robust, resilient, and adaptive (Anderies et al., 2013 ). By most measures, the global tourism system does not meet these criteria for sustainability. Tourism is not robust in that it cannot resist threats and perturbations, such as economic shocks, public health pandemics, war, and other disruptions. Tourism is not resilient in that it does not easily recover from failures, such as natural disasters or civil unrest. Furthermore, tourism is not adaptive in that it is often unable to change in response to external conditions. One example that underscores the failure to meet all three criteria is the dependence of tourism on fossil fuels for transportation and energy, which are key inputs for tourism development. This dependence itself is not sustainable (Wheeller, 2007 ), and thus the sustainability of tourism is questionable.
Liu ( 2003 ) notes that research related to the role of tourism in sustainable development has emphasized supply-side concepts such as sustaining tourism resources and ignored the demand side, which is particularly vulnerable to social and economic shocks. Tourism is vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include disaster vulnerability in coastal Thailand (Calgaro & Lloyd, 2008 ), bushfires in northeast Victoria in Australia (Cioccio & Michael, 2007 ), forest fires in British Columbia, Canada (Hystad & Keller, 2008 ); and outbreak of foot and mouth disease in the United Kingdom (Miller & Ritchie, 2003 ).
Like most other economic sectors, tourism is vulnerable to the impacts of earthquakes, particularly in areas where tourism infrastructure may not be resilient to such shocks. Numerous studies have examined the impacts of earthquake events on tourism, including studies of the aftermath of the 1997 earthquake in central Italy (Mazzocchi & Montini, 2001 ), the 1999 earthquake in Taiwan (Huan et al., 2004 ; Huang & Min, 2002 ), and the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in western Sichuan, China (Yang et al., 2011 ), among others.
Tourism is vulnerable to extreme weather events. Regional economic strength has been found to be associated with lower vulnerability to natural disasters. Kim and Marcoullier ( 2015 ) examined the vulnerability and resilience of 10 tourism-based regional economies that included U.S. national parks or protected seashores situated on the Gulf of Mexico or Atlantic Ocean coastline that were affected by several hurricanes over a 26-year period. Regions with stronger economic characteristics prior to natural disasters were found to have lower disaster losses than regions with weaker economies.
Tourism is extremely sensitive to oil spills, whatever their origin, and the volume of oil released need not be large to generate significant economic losses (Cirer-Costa, 2015 ). Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to the localized shock of an oil spill include research on the impacts of oil spills in Alaska (Coddington, 2015 ), Brazil (Ribeiro et al., 2020 ), Spain (Castanedo et al., 2009 ), affected regions in the United States along the Gulf of Mexico (Pennington-Gray et al., 2011 ; Ritchie et al., 2013 ), and the Republic of Korea (Cheong, 2012 ), among others. Future research on the vulnerability of tourist destinations to oil spills should also incorporate freshwater environments, such as lakes, rivers, and streams, where the rupture of oil pipelines is more frequent.
Significant attention has been paid to assessing the vulnerability of tourist destinations to acts of terrorism and the impacts of terrorist attacks on regional tourist economies (Liu & Pratt, 2017 ). Such studies include analyses of the impacts of terrorist attacks on three European countries, Greece, Italy, and Austria (Enders et al., 1992 ); the impact of the 2001 terrorist attacks on the United States (Goodrich, 2002 ); terrorism and tourism in Nepal (Bhattarai et al., 2005 ); vulnerability of tourism livelihoods in Bali (Baker & Coulter, 2007 ); the impact of terrorism on tourist preferences for destinations in the Mediterranean and the Canary Islands (Arana & León, 2008 ); the 2011 massacres in Olso and Utøya, Norway (Wolff & Larsen, 2014 ); terrorism and political violence in Tunisia (Lanouar & Goaied, 2019 ); and the impact of terrorism on European tourism (Corbet et al., 2019 ), among others. Pizam and Fleischer ( 2002 ) studied the impact of acts of terrorism on tourism demand in Israel between May 1991 and May 2001 , and they confirmed that the frequency of acts of terrorism had caused a larger decline in international tourist arrivals than the severity of these acts. Most of these are ex post studies, and future assessments of the underlying conditions of destinations could reveal a deeper understanding of the vulnerability of tourism to terrorism.
Tourism is vulnerable to economic crisis, both local economic shocks (Okumus & Karamustafa, 2005 ; Stylidis & Terzidou, 2014 ) and global economic crisis (Papatheodorou et al., 2010 ; Smeral, 2010 ). Okumus and Karamustafa ( 2005 ) evaluated the impact of the February 2001 economic crisis in Turkey on tourism, and they found that the tourism industry was poorly prepared for the economic crisis despite having suffered previous impacts related to the Gulf War in the early 1990s, terrorism in Turkey in the 1990s, the civil war in former Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, an internal economic crisis in 1994 , and two earthquakes in the northwest region of Turkey in 1999 . In a study of the attitudes and perceptions of citizens of Greece, Stylidis and Terzidou ( 2014 ) found that economic crisis is associated with increased support for tourism development, particularly out of self-interest. Economic crisis diminishes residents’ concern for environmental issues. In a study of the behavior of European tourists amid an economic crisis, Eugenio-Martin and Campos-Soria ( 2014 ) found that the probability of households cutting back on travel expenditures depends largely on the climate and economic conditions of tourists’ home countries, and households that do reduce travel spending engage in tourism closer to home.
Becken and Lennox ( 2012 ) studied the implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism in New Zealand, and they estimate that a doubling of oil prices is associated with a 1.7% decrease in real gross national disposable income and a 9% reduction in the real value of tourism exports. Chatziantoniou et al. ( 2013 ) investigated the relationship among oil price shocks, tourism variables, and economic indicators in four European Mediterranean countries and found that aggregate demand oil price shocks generated a lagged effect on tourism-generated income and economic growth. Kisswani et al. ( 2020 ) examined the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts and the sensitive susceptibility of tourism to oil price changes using nonlinear analysis. The findings document a long-run asymmetrical effect for most countries, after incorporating the structural breaks, suggesting that governments and tourism businesses and organizations should interpret oil price fluctuations cautiously.
Finally, the sustainability of tourism has been shown to be vulnerable to the outbreak of infectious diseases, including the impact of the Ebola virus on tourism in sub-Saharan Africa (Maphanga & Henama, 2019 ; Novelli et al., 2018 ) and in the United States (Cahyanto et al., 2016 ). The literature also includes studies of the impact of swine flu on tourism demand in Brunei (Haque & Haque, 2018 ), Mexico (Monterrubio, 2010 ), and the United Kingdom (Page et al., 2012 ), among others. In addition, rapid assessments of the impacts of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 have documented severe disruptions and cessations of tourism because of unprecedented global travel restrictions and widespread restrictions on public gatherings (Gössling et al., 2020 ; Qiu et al., 2020 ; Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Hotels, airlines, cruise lines, and car rentals have all experienced a significant decrease globally because of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the shock to the industry is significant enough to warrant concerns about the long-term outlook (Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Qiu et al. ( 2020 ) estimated the social costs of the pandemic to tourism in three cities in China (Hong Kong, Guangzhou, and Wuhan), and they found that most respondents were willing to pay for risk reduction and action in responding to the pandemic crisis; there was no significant difference between residents’ willingness to pay in the three cities. Some research has emphasized how lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic can prepare global tourism for an economic transformation that is needed to mitigate the impacts of climate change (Brouder, 2020 ; Prideaux et al., 2020 ).
It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, contested, and potentially paradoxical. This is due, in part, to the contested nature of sustainable development itself. Tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ), and many countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development has been viewed as an important sector for investment to enhance economic growth, poverty alleviation, and food security, and the sector provides an alternative opportunity to large-scale development projects and extractive industries that contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and cultural values. However, global evidence from research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been realized (Liu, 2003 ).
The role of tourism in sustainable development has been studied extensively and with a variety of perspectives, including the conceptualization of alternative or responsible forms of tourism and the examination of economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism development. The research has generally concluded that tourism development has contributed to sustainable development in some cases where it is demonstrated to have provided support for biodiversity conservation initiatives and livelihood development strategies. As an economic sector, tourism is considered to be labor intensive, providing opportunities for poor households to enhance their livelihood through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists.
Nature-based tourism approaches such as ecotourism and community-based tourism have been successful at attracting tourists to parks and protected areas, and their spending provides financial support for biodiversity conservation, livelihoods, and economic growth in developing countries. Nevertheless, studies of the impacts of tourism development have documented negative environmental impacts locally in terms of land use, food and water consumption, and congestion, and globally in terms of the contribution of tourism to climate change through the emission of greenhouse gases related to transportation and other tourist activities. Studies of the social impacts of tourism have documented experiences of discrimination based on ethnicity, gender, race, sex, and national identity.
The sustainability of tourism as an economic sector has been examined in terms of its vulnerability to civil conflict, economic shocks, natural disasters, and public health pandemics. Most studies conclude that tourism may have positive impacts for regional development and environmental conservation, but there is evidence that tourism inherently generates negative environmental impacts, primarily through pollutions stemming from transportation. The regional benefits of tourism development must be considered alongside the global impacts of increased transportation and tourism participation. Global tourism has also been shown to be vulnerable to economic crises, oil price shocks, and global outbreaks of infectious diseases. Given that tourism is dependent on energy, the movement of people, and the consumption of resources, virtually all tourism activities have significant economic, environmental, and sustainable impacts. As such, the role of tourism in sustainable development is highly questionable. Future research on the role of tourism in sustainable development should focus on reducing the negative impacts of tourism development, both regionally and globally.
Further Reading
- Bramwell, B. , & Lane, B. (1993). Sustainable tourism: An evolving global approach. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 1–5.
- Buckley, R. (2012). Sustainable tourism: Research and reality. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (2), 528–546.
- Butler, R. W. (1991). Tourism, environment, and sustainable development. Environmental Conservation , 18 (3), 201–209.
- Butler, R. W. (1999). Sustainable tourism: A state‐of‐the‐art review. Tourism Geographies , 1 (1), 7–25.
- Clarke, J. (1997). A framework of approaches to sustainable tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (3), 224–233.
- Fennell, D. A. (2020). Ecotourism (5th ed.). Routledge.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 (4), 283–302.
- Honey, M. (2008). Ecotourism and sustainable development: Who owns paradise? (2nd ed.). Island Press.
- Inskeep, E. (1991). Tourism planning: An integrated and sustainable development approach . Routledge.
- Jamal, T. , & Camargo, B. A. (2014). Sustainable tourism, justice and an ethic of care: Toward the just destination. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 22 (1), 11–30.
- Liburd, J. J. , & Edwards, D. (Eds.). (2010). Understanding the sustainable development of tourism . Oxford.
- Liu, Z. (2003). Sustainable tourism development: A critique. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 11 (6), 459–475.
- Sharpley, R. (2020). Tourism, sustainable development and the theoretical divide: 20 years on. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 28 (11), 1932–1946.
- Adams, W. M. (2009). Green development: Environment and sustainability in a developing world (3rd ed.). Routledge.
- Andereck, K. L. , Valentine, K. M. , Knopf, R. A. , & Vogt, C. A. (2005). Residents’ perceptions of community tourism impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 1056–1076.
- Andereck, K. , Valentine, K. , Vogt, C. , & Knopf, R. (2007). A cross-cultural analysis of tourism and quality of life perceptions. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 483–502.
- Anderies, J. M. , Folke, C. , Walker, B. , & Ostrom, E. (2013). Aligning key concepts for global change policy: Robustness, resilience, and sustainability . Ecology and Society , 18 (2), 8.
- Apergis, N. , & Payne, J. E. (2012). Tourism and growth in the Caribbean–evidence from a panel error correction model. Tourism Economics , 18 (2), 449–456.
- Arana, J. E. , & León, C. J. (2008). The impact of terrorism on tourism demand. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 (2), 299–315.
- Ashley, C. , & Roe, D. (2002). Making tourism work for the poor: Strategies and challenges in southern Africa. Development Southern Africa , 19 (1), 61–82.
- Ashley, C. , Roe, D. , & Goodwin, H. (2001). Pro-poor tourism strategies: Making tourism work for the poor: A review of experience (No. 1). Overseas Development Institute.
- Baker, K. , & Coulter, A. (2007). Terrorism and tourism: The vulnerability of beach vendors’ livelihoods in Bali. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (3), 249–266.
- Baral, N. , Stern, M. J. , & Bhattarai, R. (2008). Contingent valuation of ecotourism in Annapurna conservation area, Nepal: Implications for sustainable park finance and local development. Ecological Economics , 66 (2–3), 218–227.
- Becken, S. , & Lennox, J. (2012). Implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 133–142.
- Beckerman, W. (1994). “Sustainable development”: Is it a useful concept? Environmental Values , 3 (3), 191–209.
- Bhattarai, K. , Conway, D. , & Shrestha, N. (2005). Tourism, terrorism and turmoil in Nepal. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 669–688.
- Blewitt, J. (2015). Understanding sustainable development (2nd ed.). Routledge.
- Brouder, P. (2020). Reset redux: Possible evolutionary pathways towards the transformation of tourism in a COVID-19 world. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 484–490.
- Brunt, P. , & Courtney, P. (1999). Host perceptions of sociocultural impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 26 (3), 493–515.
- Buckley, R. (2011). Tourism and environment. Annual Review of Environment and Resources , 36 , 397–416.
- Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. Canadian Geographer/Le Géographe canadien , 24 (1), 5–12.
- Butler, R. , & Hinch, T. (Eds.). (2007). Tourism and indigenous peoples: Issues and implications . Routledge.
- Cabezas, A. L. (2004). Between love and money: Sex, tourism, and citizenship in Cuba and the Dominican Republic. Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society , 29 (4), 987–1015.
- Caffyn, A. (2012). Advocating and implementing slow tourism. Tourism Recreation Research , 37 (1), 77–80.
- Cahyanto, I. , Wiblishauser, M. , Pennington-Gray, L. , & Schroeder, A. (2016). The dynamics of travel avoidance: The case of Ebola in the US. Tourism Management Perspectives , 20 , 195–203.
- Calgaro, E. , & Lloyd, K. (2008). Sun, sea, sand and tsunami: Examining disaster vulnerability in the tourism community of Khao Lak, Thailand. Singapore Journal of Tropical Geography , 29 (3), 288–306.
- Castanedo, S. , Juanes, J. A. , Medina, R. , Puente, A. , Fernandez, F. , Olabarrieta, M. , & Pombo, C. (2009). Oil spill vulnerability assessment integrating physical, biological and socio-economical aspects: Application to the Cantabrian coast (Bay of Biscay, Spain). Journal of Environmental Management , 91 (1), 149–159.
- Cater, E. (1993). Ecotourism in the Third World: Problems for sustainable tourism development. Tourism Management , 14 (2), 85–90.
- Ceballos-Lascuráin, H. (1987, January). The future of “ecotourism.” Mexico Journal , 17 , 13–14.
- Chase, L. C. , Lee, D. R. , Schulze, W. D. , & Anderson, D. J. (1998). Ecotourism demand and differential pricing of national park access in Costa Rica. Land Economics , 74 (4), 466–482.
- Chatziantoniou, I. , Filis, G. , Eeckels, B. , & Apostolakis, A. (2013). Oil prices, tourism income and economic growth: A structural VAR approach for European Mediterranean countries. Tourism Management , 36 (C), 331–341.
- Cheong, S. M. (2012). Fishing and tourism impacts in the aftermath of the Hebei-Spirit oil spill. Journal of Coastal Research , 28 (6), 1648–1653.
- Chok, S. , Macbeth, J. , & Warren, C. (2007). Tourism as a tool for poverty alleviation: A critical analysis of “pro-poor tourism” and implications for sustainability. Current Issues in Tourism , 10 (2–3), 144–165.
- Cioccio, L. , & Michael, E. J. (2007). Hazard or disaster: Tourism management for the inevitable in Northeast Victoria. Tourism Management , 28 (1), 1–11.
- Cirer-Costa, J. C. (2015). Tourism and its hypersensitivity to oil spills. Marine Pollution Bulletin , 91 (1), 65–72.
- Coccossis, H. , & Nijkamp, P. (1995). Sustainable tourism development . Ashgate.
- Coddington, K. (2015). The “entrepreneurial spirit”: Exxon Valdez and nature tourism development in Seward, Alaska. Tourism Geographies , 17 (3), 482–497.
- Cohen, E. (1978). The impact of tourism on the physical environment. Annals of Tourism Research , 5 (2), 215–237.
- Conway, D. , & Timms, B. F. (2010). Re-branding alternative tourism in the Caribbean: The case for “slow tourism.” Tourism and Hospitality Research , 10 (4), 329–344.
- Corbet, S. , O’Connell, J. F. , Efthymiou, M. , Guiomard, C. , & Lucey, B. (2019). The impact of terrorism on European tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 75 , 1–17.
- Daly, H. E. (1990). Toward some operational principles of sustainable development. Ecological Economics , 2 (1), 1–6.
- Deery, M. , Jago, L. , & Fredline, L. (2012). Rethinking social impacts of tourism research: A new research agenda. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 64–73.
- Diedrich, A. , & Garcia-Buades, E. (2008). Local perceptions of tourism as indicators of destination decline. Tourism Management , 41 , 623–632.
- Durbarry, R. (2004). Tourism and economic growth: The case of Mauritius. Tourism Economics , 10 , 389–401.
- Elliott, S. M. , & Neirotti, L. D. (2008). Challenges of tourism in a dynamic island destination: The case of Cuba. Tourism Geographies , 10 (4), 375–402.
- Enders, W. , Sandler, T. , & Parise, G. F. (1992). An econometric analysis of the impact of terrorism on tourism. Kyklos , 45 (4), 531–554.
- Eugenio-Martin, J. L. , & Campos-Soria, J. A. (2014). Economic crisis and tourism expenditure cutback decision. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 53–73.
- Farrell, B. , & McLellan, R. (1987). Tourism and physical environment research. Annals of Tourism Research , 14 (1), 1–16.
- Faulkner, B. , & Tideswell, C. (1997). A framework for monitoring community impacts of tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (1), 3–28.
- Fennell, D. A. , & Eagles, P. F. (1990). Ecotourism in Costa Rica: A conceptual framework. Journal of Park and Recreation Administration , 8 (1), 23–34.
- Fullagar, S. , Markwell, K. , & Wilson, E. (Eds.). (2012). Slow tourism: Experiences and mobilities . Channel View.
- Garau-Vadell, J. B. , Gutierrez-Taño, D. , & Diaz-Armas, R. (2018). Economic crisis and residents’ perception of the impacts of tourism in mass tourism destinations. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management , 7 , 68–75.
- Garrod, B. , & Fyall, A. (1998). Beyond the rhetoric of sustainable tourism? Tourism Management , 19 (3), 199–212.
- Ghimire, K. B. (Ed.). (2013). The native tourist: Mass tourism within developing countries . Routledge.
- Goodrich, J. N. (2002). September 11, 2001 attack on America: A record of the immediate impacts and reactions in the USA travel and tourism industry. Tourism Management , 23 (6), 573–580.
- Gössling, S. (1999). Ecotourism: A means to safeguard biodiversity and ecosystem functions? Ecological Economics , 29 , 303–320.
- Gössling, S. (2000). Tourism–sustainable development option? Environmental Conservation , 27 (3), 223–224.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 , 283–302.
- Gössling, S. , & Peeters, P. (2015). Assessing tourism’s global environmental impact 1900–2050. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 23 (5), 639–659.
- Gössling, S. , Peeters, P. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J.‑P. , Dubois, G. , Lehman, L. V. , & Scott, D. (2011). Tourism and water use: Supply, demand and security, and international review. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 16–28.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , & Hall, C. M. (2020). Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 29 (1), 1–20.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J. P. , & Dubois, G. (2012). Consumer behaviour and demand response of tourists to climate change. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (1), 36–58.
- Gray, N. J. , & Campbell, L. M. (2007). A decommodified experience? Exploring aesthetic, economic and ethical values for volunteer ecotourism in Costa Rica. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 463–482.
- Grober, U. (2007). Deep roots—a conceptual history of “sustainable development” (Nachhaltigkeit) . Wissenschaftszentrum Berlin für Sozialforschung.
- Gu, H. , & Ryan, C. (2008). Place attachment, identity and community impacts of tourism—the case of a Beijing hutong. Tourism Management , 29 (4), 637–647.
- Gursoy, D. , Chi, C. G. , & Dyer, P. (2010). Locals’ attitudes toward mass and alternative tourism: The case of Sunshine Coast, Australia. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (3), 381–394.
- Haley, A. J. , Snaith, T. , & Miller, G. (2005). The social impacts of tourism a case study of Bath, UK. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 647–668.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (2009). Understanding and managing tourism impacts: An integrated approach . Routledge.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (Eds.). (1998). Sustainable tourism: A geographical perspective . Longman.
- Haque, T. H. , & Haque, M. O. (2018). The swine flu and its impacts on tourism in Brunei. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management , 36 , 92–101.
- Haralambopoulos, N. , & Pizam, A. (1996). Perceived impacts of tourism: The case of Samos. Annals of Tourism Research , 23 (3), 503–526.
- Harrison, D. (2008). Pro-poor tourism: A critique. Third World Quarterly , 29 (5), 851–868.
- Hearne, R. R. , & Salinas, Z. M. (2002). The use of choice experiments in the analysis of tourist preferences for ecotourism development in Costa Rica. Journal of Environmental Management , 65 (2), 153–163.
- Hetzer, N. D. (1965). Environment, tourism, culture. Links , 1 (2), 1–3.
- Höhler, S. (2015). Spaceship earth in the environmental age, 1960–1990 . Routledge.
- Honey, M. , & Gilpin, R. (2009). Tourism in the developing world: Promoting peace and reducing poverty . United States Institute for Peace.
- Huan, T. C. , Beaman, J. , & Shelby, L. (2004). No-escape natural disaster: Mitigating impacts on tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 31 (2), 255–273.
- Huang, J. H. , & Min, J. C. (2002). Earthquake devastation and recovery in tourism: The Taiwan case. Tourism Management , 23 (2), 145–154.
- Hunter, C. (1995). On the need to re-conceptualise sustainable tourism development. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 3 (3), 155–165.
- Hunter, C. , & Green, H. (1995). Tourism and the environment. A sustainable relationship? Routledge.
- Huttasin, N. (2008). Perceived social impacts of tourism by residents in the OTOP tourism village, Thailand. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 13 (2), 175–191.
- Hystad, P. W. , & Keller, P. C. (2008). Towards a destination tourism disaster management framework: Long-term lessons from a forest fire disaster. Tourism Management , 29 (1), 151–162.
- Katircioglu, S. (2009). Tourism, trade and growth: The case of Cyprus. Applied Economics , 41 (21), 2741–2750.
- Katircioglu, S. (2010). Testing the tourism-led growth hypothesis for Singapore: An empirical investigation from bounds test to cointegration and Granger causality tests. Tourism Economics , 16 (4), 1095–1101.
- Khan, M. M. (1997). Tourism development and dependency theory: Mass tourism vs. ecotourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 24 (4), 988–991.
- Kim, H. , & Marcouiller, D. W. (2015). Considering disaster vulnerability and resiliency: The case of hurricane effects on tourism-based economies. The Annals of Regional Science , 54 (3), 945–971.
- King, B. , Pizam, A. , & Milman, A. (1993). Social impacts of tourism: Host perceptions. Annals of Tourism Research , 20 (4), 650–665.
- Kisswani, K. M. , Zaitouni, M. , & Moufakkir, O. (2020). An examination of the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts. Current Issues in Tourism , 23 (4), 500–522.
- Kuvan, Y. , & Akan, P. (2005). Residents’ attitudes toward general and forest-related impacts of tourism: The case of Belek, Antalya. Tourism Management , 26 (5), 691–706.
- Lai, P. H. , & Nepal, S. K. (2006). Local perspectives of ecotourism development in Tawushan Nature Reserve, Taiwan. Tourism Management , 27 (6), 1117–1129.
- Lanouar, C. , & Goaied, M. (2019). Tourism, terrorism and political violence in Tunisia: Evidence from Markov-switching models. Tourism Management , 70 , 404–418.
- Lee, C. C. , & Chang, C. P. (2008). Tourism development and economic growth: A closer look at panels. Tourism Management , 29 , 180–192.
- Lenzen, M. , Sun, Y. Y. , Faturay, F. , Ting, Y. P. , Geschke, A. , & Malik, A. (2018). The carbon footprint of global tourism. Nature Climate Change , 8 (6), 522–528.
- Lian Chan, J. K. , & Baum, T. (2007). Ecotourists’ perception of ecotourism experience in lower Kinabatangan, Sabah, Malaysia. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 574–590.
- Liu, A. , & Pratt, S. (2017). Tourism’s vulnerability and resilience to terrorism. Tourism Management , 60 , 404–417.
- Manyara, G. , & Jones, E. (2007). Community-based tourism enterprises development in Kenya: An exploration of their potential as avenues of poverty reduction. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (6), 628–644.
- Maphanga, P. M. , & Henama, U. S. (2019). The tourism impact of Ebola in Africa: Lessons on crisis management. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure , 8 (3), 1–13.
- Mathieson, A. , & Wall, G. (1982). Tourism, economic, physical and social impacts . Longman.
- May, V. (1991). Tourism, environment and development—values, sustainability and stewardship. Tourism Management , 12 (2), 112–124.
- Mazzocchi, M. , & Montini, A. (2001). Earthquake effects on tourism in central Italy. Annals of Tourism Research , 28 (4), 1031–1046.
- Mbaiwa, J. E. (2005). The socio-cultural impacts of tourism development in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. Journal of Tourism and Cultural Change , 2 (3), 163–185.
- McKercher, B. (1993a). Some fundamental truths about tourism: Understanding tourism’s social and environmental impacts, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 6–16.
- McKercher, B. (1993b). The unrecognized threat to tourism: Can tourism survive “sustainability”? Tourism Management , 14 (2), 131–136.
- Meadows, D. H. , Meadows, D. L. , Randers, J. , & Behrens, W. W. (1972). The limits to growth . Universe Books.
- Miller, G. A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2003). A farming crisis or a tourism disaster? An analysis of the foot and mouth disease in the UK. Current Issues in Tourism , 6 (2), 150–171.
- Milman, A. , & Pizam, A. (1988). Social impacts of tourism on central Florida. Annals of Tourism Research , 15 (2), 191–204.
- Monterrubio, J. C. (2010). Short-term economic impacts of influenza A (H1N1) and government reaction on the Mexican tourism industry: An analysis of the media. International Journal of Tourism Policy , 3 (1), 1–15.
- Narayan, P. K. (2004). Economic impact of tourism on Fiji’s economy: Empirical evidence from the computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Economics , 10 (4), 419–433.
- Nash, D. , & Butler, R. (1990). Towards sustainable tourism. Tourism Management , 11 (3), 263–264.
- Novelli, M. , Burgess, L. G. , Jones, A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2018). “No Ebola . . . still doomed”—the Ebola-induced tourism crisis. Annals of Tourism Research , 70 , 76–87.
- Oh, C. (2005). The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tourism Management , 26 , 39–44.
- Oh, H. , Assaf, A. G. , & Baloglu, S. (2016). Motivations and goals of slow tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 55 (2), 205–219.
- Okumus, F. , & Karamustafa, K. (2005). Impact of an economic crisis evidence from Turkey. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 942–961.
- Page, S. , Song, H. , & Wu, D. C. (2012). Assessing the impacts of the global economic crisis and swine flu on inbound tourism demand in the United Kingdom. Journal of Travel Research , 51 (2), 142–153.
- Papatheodorou, A. , Rosselló, J. , & Xiao, H. (2010). Global economic crisis and tourism: Consequences and perspectives. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 39–45.
- Peeters, P. (2012). A clear path towards sustainable mass tourism? Rejoinder to the paper “Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence” by David B. Weaver. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1038–1041.
- Pennington-Gray, L. , London, B. , Cahyanto, I. , & Klages, W. (2011). Expanding the tourism crisis management planning framework to include social media: Lessons from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill 2010. International Journal of Tourism Anthropology , 1 (3–4), 239–253.
- Pizam, A. , & Fleischer, A. (2002). Severity versus frequency of acts of terrorism: Which has a larger impact on tourism demand? Journal of Travel Research , 40 (3), 337–339.
- Pratt, S. (2015). The economic impact of tourism in SIDS. Annals of Tourism Research , 52 , 148–160.
- Prideaux, B. , Thompson, M. , & Pabel, A. (2020). Lessons from COVID-19 can prepare global tourism for the economic transformation needed to combat climate change. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 667–678.
- Qiu, R. T. , Park, J. , Li, S. , & Song, H. (2020). Social costs of tourism during the COVID-19 pandemic . Annals of Tourism Research , 84 , 102994.
- Rátz, T. (2000). Residents’ perceptions of the socio-cultural impacts of tourism at Lake Balaton, Hungary. Tourism and Sustainable Community Development , 7 , 36.
- Ribeiro, L. C. D. S. , Souza, K. B. D. , Domingues, E. P. , & Magalhães, A. S. (2020). Blue water turns black: Economic impact of oil spill on tourism and fishing in Brazilian Northeast . Current Issues in Tourism , 1–6.
- Richardson, R. B. , Fernandez, A. , Tschirley, D. , & Tembo, G. (2012). Wildlife conservation in Zambia: Impacts on rural household welfare. World Development , 40 (5), 1068–1081.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Loomis, J. B. (2004). Adaptive recreation planning and climate change: A contingent visitation approach. Ecological Economics , 50 (1), 83–99.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Witkowski, K. (2010). Economic vulnerability to climate change for tourism-dependent nations. Tourism Analysis , 15 (3), 315–330.
- Ritchie, B. W. , Crotts, J. C. , Zehrer, A. , & Volsky, G. T. (2013). Understanding the effects of a tourism crisis: The impact of the BP oil spill on regional lodging demand. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (1), 12–25.
- Rogerson, C. M. (2011). Urban tourism and regional tourists: Shopping in Johannesburg, South Africa. Tijdschrift voor economische en sociale geografie , 102 (3), 316–330.
- Rutty, M. , & Richardson, R. (2019). Tourism research in Cuba: Gaps in knowledge and challenges for sustainable tourism. Sustainability , 11 (12), 3340–3346.
- Ryan, C. , & Huyton, J. (2000). Who is interested in Aboriginal tourism in the Northern Territory, Australia? A cluster analysis. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 53–88.
- Salinas, E. , Mundet, L. , & Salinas, E. (2018). Historical evolution and spatial development of tourism in Cuba, 1919–2017: What is next? Tourism Planning & Development , 15 (3), 216–238.
- Sanchez, P. M. , & Adams, K. M. (2008). The Janus-faced character of tourism in Cuba. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 , 27–46.
- Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , & Gössling, S. (2012). Tourism and climate change: Impacts, adaptation and mitigation . Routledge.
- Seetanah, B. (2011). Assessing the dynamic economic impact of tourism for island economies. Annals of Tourism Research , 38 (1), 291–308.
- Sharma, A. , & Nicolau, J. L. (2020). An open market valuation of the effects of COVID-19 on the travel and tourism industry . Annals of Tourism Research , 83 , 102990.
- Sharpley, R. (2000). Tourism and sustainable development: Exploring the theoretical divide. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 1–19.
- Sharpley, R. (2014). Host perceptions of tourism: A review of the research. Tourism Management , 42 , 37–49.
- Smeral, E. (2010). Impacts of the world recession and economic crisis on tourism: Forecasts and potential risks. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 31–38.
- Southgate, C. R. (2006). Ecotourism in Kenya: The vulnerability of communities. Journal of Ecotourism , 5 (1–2), 80–96.
- Spenceley, A. (Ed.). (2012). Responsible tourism: Critical issues for conservation and development . Routledge.
- Stabler, M. (Ed.). (1997). Tourism and sustainability: Principles to practice . Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International.
- Stronza, A. (2007). The economic promise of ecotourism for conservation. Journal of Ecotourism , 6 (3), 210–230.
- Stylidis, D. , & Terzidou, M. (2014). Tourism and the economic crisis in Kavala, Greece. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 210–226.
- Suntikul, W. , Bauer, T. , & Song, H. (2009). Pro-poor tourism development in Viengxay, Laos: Current state and future prospects. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 14 (2), 153–168.
- Swarbrooke, J. (1999). Sustainable tourism management . CABI.
- Tovar, C. , & Lockwood, M. (2008). Social impacts of tourism: An Australian regional case study. International Journal of Tourism Research , 10 (4), 365–378.
- Tsartas, P. (1992). Socioeconomic impacts of tourism on two Greek isles. Annals of Tourism Research , 19 (3), 516–533.
- Turner, L. , & Ash, J. (1975). The golden hordes: International tourism and the pleasure periphery . Constable.
- United Nations . (2015). Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development . Division for Sustainable Development Goals.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2002). Tourism and poverty alleviation . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2020). UNWTO world tourism barometer . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- Viner, D. (2006). Tourism and its interactions with climate change. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 14 (4), 317–322.
- Vitousek, P. M. , Mooney, H. A. , Lubchenco, J. , & Melillo, J. M. (1997). Human domination of Earth’s ecosystems. Science , 277 (5325), 494–499.
- World Commission on Environment and Development . (1987). Our common future . Oxford University Press.
- Weaver, D. (2007). Towards sustainable mass tourism: Paradigm shift or paradigm nudge? Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 65–69.
- Weaver, D. B. (2012). Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1030–1037.
- Weaver, D. B. (2014). Asymmetrical dialectics of sustainable tourism: Toward enlightened mass tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (2), 131–140.
- Wheeller, B. (2007). Sustainable mass tourism: More smudge than nudge the canard continues. Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 73–75.
- Whitford, M. , & Ruhanen, L. (2016). Indigenous tourism research, past and present: Where to from here? Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 24 (8–9), 1080–1099.
- Whyte, K. P. (2010). An environmental justice framework for indigenous tourism. Environmental Philosophy , 7 (2), 75–92.
- Wolff, K. , & Larsen, S. (2014). Can terrorism make us feel safer? Risk perceptions and worries before and after the July 22nd attacks. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 200–209.
- Yang, W. , Wang, D. , & Chen, G. (2011). Reconstruction strategies after the Wenchuan earthquake in Sichuan, China. Tourism Management , 32 (4), 949–956.
- Young, G. (1973). Tourism—blessing or blight? Penguin.
- Zapata, M. J. , Hall, C. M. , Lindo, P. , & Vanderschaeghe, M. (2011). Can community-based tourism contribute to development and poverty alleviation? Lessons from Nicaragua. Current Issues in Tourism , 14 (8), 725–749.
1. One megatonne (Mt) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) metric tons.
2. One megajoule (MJ) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) joules, or approximately the kinetic energy of a 1-megagram (tonne) vehicle moving at 161 km/h.
3. One gigatonne (Gt) is equal to 1 billion (10 9 ) metric tons.
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Environmental Science. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 20 April 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|81.177.182.136]
- 81.177.182.136
Character limit 500 /500

- Get Connected
- globalEDGE Blog
The Importance of Tourism on Economies and Businesses
Published: 3/26/2019 12:21:08 PM

Image Source
Tourism is vital for the success of many economies around the world. There are several benefits of tourism on host destinations. Tourism boosts the revenue of the economy, creates thousands of jobs, develops the infrastructures of a country, and plants a sense of cultural exchange between foreigners and citizens.
The number of jobs created by tourism in many different areas is significant. These jobs are not only a part of the tourism sector but may also include the agricultural sector, communication sector, health sector, and the educational sector. Many tourists travel to experience the hosting destination’s culture, different traditions, and gastronomy. This is very profitable to local restaurants, shopping centers, and stores. Melbourne, Australia ’s population is greatly affected by tourism. It has a population of around 4 million people and around 22,000 citizens are employed by the tourism sector only.
Governments that rely on tourism for a big percentage of their revenue invest a lot in the infrastructure of the country . They want more and more tourists to visit their country which means that safe and advanced facilities are necessary. This leads to new roads and highways, developed parks, improved public spaces, new airports, and possibly better schools and hospitals. Safe and innovative infrastructures allow for a smooth flow of goods and services. Moreover, local people experience an opportunity for economic and educational growth.
Tourism creates a cultural exchange between tourists and local citizens. Exhibitions, conferences, and events usually attract foreigners. Organizing authorities usually gain profits from registration fees, gift sales, exhibition spaces, and sales of media copyright. Furthermore, foreign tourists bring diversity and cultural enrichment to the hosting country.
Tourism is a great opportunity for foreigners to learn about a new culture, but it also creates many opportunities for local citizens . It allows young entrepreneurs to establish new products and services that would not be sustainable on the local population of residents alone. Moreover, residents experience the benefits that come with tourism occurring in their own country.
To learn about the countries earning the most from international tourist arrivals, click on the link below!
Countries Earning the Most from International Tourism
Share this article

Unveiling the Scope of the Travel and Tourism Industry: A Global Perspective

How to Build a Successful Career in Travel and Tourism Industry

Career In Cultural Tourism 2023 – Job Profile, Salary & Courses

- career in travel industry
- Learn And Travel
- Travel and Tourism
- Travel Courses
- Travel Education
- Travel Inspiration
- Travel Passion
- Travel Smart

The scope of the travel and tourism industry is vast and ever-evolving. It encompasses a wide range of activities, services, and destinations that cater to the diverse needs and preferences of travelers. From leisure tourism and adventure travel to business trips and educational excursions, the industry offers something for everyone. It includes transportation services such as airlines, trains, and cruises, as well as accommodation options like hotels, resorts, and vacation rentals. Attractions and entertainment venues, such as museums, theme parks, and cultural sites, also fall within its scope. Additionally, travel agencies, tour operators, and online booking platforms globalization, the scope of the travel and tourism industry continues to expand, contribute to the industry’s extensive reach. With increasing connectivity and embracing emerging trends such as sustainable tourism, experiential travel, and digital innovations. As an essential catalyst for economic growth, job creation, and cultural enrichment, this industry holds immense potential for both individuals and societies, fostering understanding, appreciation, and exploration of our diverse world.

Let’s explore the scope of the travel and tourism industry from a global perspective:
1. International Travel:
The industry facilitates international travel, enabling people to explore different countries and cultures. International tourism involves activities such as leisure vacations, business travel, educational trips, and visiting friends and relatives. It contributes to cross-cultural understanding, global cooperation, and exchange of ideas.
2. Domestic Tourism:
Domestic tourism refers to travel within one’s own country. It includes activities such as visiting tourist attractions, national parks, heritage sites, and participating in local events and festivals. Domestic tourism promotes regional development, supports local businesses, and encourages the preservation of cultural and natural heritage.
3. Economic Impact:
The travel and tourism industry is a major economic driver worldwide. It generates revenue through various sectors, including transportation, accommodation, food and beverage services, entertainment, and attractions. The industry creates jobs directly and indirectly, supporting diverse sectors such as aviation, hotel management, tour operations, and more.
4. Hospitality and Accommodation:
The hospitality sector is a vital component of the travel and tourism industry, playing an essential role in providing services and amenities to travelers. It includes a range of establishments such as hotels, resorts, guesthouses, bed and breakfasts, and homestays. These accommodations offer lodging facilities, dining options, and additional amenities to meet the diverse needs and preferences of travelers.
5. Transportation:
Transportation is an integral component of the travel and tourism industry. It includes air travel, road transport, railways, cruises, and other modes of transportation. Airlines, airports, car rental companies, and public transportation systems contribute to the seamless movement of tourists within and between destinations.
6. Sustainable Tourism:
The concept of sustainable tourism has gained prominence in recent years. It focuses on minimizing negative impacts on the environment, culture, and society while maximizing the benefits of tourism. Sustainable practices include promoting responsible travel, conserving natural resources, supporting local communities, and raising awareness about environmental issues.
7. Travel Agencies and Tour Operators:
Travel agencies and tour operators facilitate trip planning, booking, and coordination of travel services. They provide assistance in selecting destinations, organizing itineraries, arranging transportation, accommodations, and tours. These intermediaries play a vital role in promoting tourism and offering customized experiences to travelers.
8. Government Initiatives and Policies:
Governments across the world recognize the importance of the travel and tourism industry and implement policies to promote its growth. They invest in infrastructure development, marketing campaigns, visa facilitation, and safety regulations to attract tourists and create a conducive environment for the industry.
9. Challenges and Opportunities:
The travel and tourism industry faces various challenges, including geopolitical uncertainties, natural disasters, public health crises, and changing consumer preferences. However, it also presents numerous opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and sustainable development. Emerging trends such as ecotourism, adventure tourism, wellness travel, and digital nomadism are reshaping the industry’s landscape.
10. Technological advancements:
Technological advancements have had a transformative impact on the travel and tourism industry. The introduction of online booking platforms, mobile applications, virtual reality experiences, and digital marketing strategies has revolutionized the way travelers plan and enjoy their trips. These technological innovations have provided convenience and efficiency to both businesses and travelers alike. Furthermore, ongoing technological advancements are expected to further shape the future of the industry. In conclusion, the travel and tourism industry holds immense global significance with its wide-ranging scope. It encompasses diverse activities, including international and domestic travel, hospitality services, transportation, and more. The industry plays a substantial role in driving economies, fostering cultural exchange, and contributing to the overall well-being of societies around the world.
Gaurav Gera
Related posts.

Build A Successful Career in Hotel Management- Jobs and Courses for Hotel Management in India

What is the MICE Industry- Components, Job Opportunities, and Required Skills For the MICE Industry

Build a Career in Adventure Tourism- Skills, Jobs, and Salary in Adventure Tourism
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Components of tourism: Structure of the tourism industry
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
The travel and tourism industry is argued by many as being the largest industry in the world. It is, therefore, no surprise that the structure of the tourism industry is quite complex, involving many components of tourism.
With many different types of tourism and types of businesses operating within the tourism industry, from private companies to charities and NGOs, the structure of the tourism industry is made up of many different segments and components.
In this article I will provide you with an overview of the structure of the tourism industry, outlining the types of organisations and stakeholders in tourism that are involved.
Structure of the tourism industry
Components of tourism, international organisations, national tourist boards, regional tourist boards, tourist information centres, travel by air, travel by road, travel by train, travel by water, hotels chains, hostels and budget accommodation, holiday parks and campsites, accommodation innovations, world travel market, football world cup, glastonbury, holi festival, day of the dead, natural attractions, built attractions, tour operators, travel agents, ancillary services, components of tourism | structure of the tourism industry, structure of the tourism industry | components of tourism: further reading.
The importance of tourism is demonstrated when you can see how big the industry is!
The structure of the industry is made up of several components of tourism and involves many different stakeholders. These components are all interrelated in one way of another. The components of tourism make up the entire tourism system.

There are several integral components of tourism. Without these components, the tourism industry would struggle to function. I have explained what this means below, but before you read on, take a look at this short video that I made (and if you like what you see, don’t forget to subscribe to my YouTube channel)!
This was demonstrated, for example, during the Coronavirus pandemic, which halted air travel around the world. Travel services are a vital component of tourism and without these services being operational, the tourism industry struggled to survive!
There are six major components of tourism, each with their own sub-components. These are: tourist boards, travel services, accommodation services, conferences and events, attractions and tourism services.

Below, I will explain what each of the components offer to the tourism industry and provide some relevant examples.
Components of tourism: Tourist boards
A tourist board is an essential component of tourism and an integral part of the structure of the tourism industry.
A tourism board is responsible for the promotion of tourism in a particular area. This could be a city, a region, a country or a group of countries.
A tourism board is usually Government funded and is usually a public travel and tourism organisation (although this is not always the case).
A tourism board is also often referred to as a Destination Marketing Organisation (DMO).
Most tourist boards focus on promoting tourism in a particular area, city or country. There are, however, some organisations which aim to promote tourism across more than one country.
Whilst these organisation often have many functions other than tourism, they will also play a role in the promotion of tourism in particular parts of the world. This could include the European Union , the ASEAN network or organisations such as the United Nations.
A national tourist board is a national organisation whose aim is to promote tourism across the country.
There are usually several management bodies that are involved with a national tourist board. They are essential stakeholders who determine many aspects of tourism in the country, such as budgets, taxation and regulations.
Said management bodies include the parliament, the tourist board, an auditing committee and the Prime Minister, President or Head of State.
The national tourist board is funded from tourist taxes, membership fees, Government funding and other sources.
Examples of national tourist boards (often most commonly referred to by their ‘campaign title’ as opposed to the Government title) include Visit Britain , Incredible India and Amazing Thailand .
A regional tourist board is a tourist board that focusses on a particular region of a country. They are often a sub-division of a country’s national tourist board.
Regional tourism boards are often funded and operated in the same way as national tourist boards.
Examples of successful regional tourism boards include: Visit Cornwall in the UK, Kerala Tourism in India, Visite Montreal in Canada and Cape Town Tourism in South Africa.
A tourist information centre is the place where tourists can go for advice and help with regards to all matters related to tourism in the area.
In the tourist information centre (TIC) you will find staff who are knowledgeable about the local area. There will often be a range of printed and digital information for you, including leaflets, maps, coupons and guidebooks. Sometimes there will be virtual tourism facilities.
Tourist information centres have been an important component of tourism throughout the history of travel and tourism , however, they are coming under increasing pressure as a result of information that is available online. This has resulted in fewer people visiting TICs in person.
Most major tourist areas will have a tourist information centre. These are usually centrally located.
Tourist information centres are funded by the local Government.
Other posts that you might be interested in: – What is tourism? A definition of tourism – The history of tourism – Stakeholders in tourism – Dark tourism explained – What is ABTA and how does it work? – The economic impacts of tourism
Components of tourism:Transport services
The relationship between transport and tourism is strong.
According to the most commonly accepted definitions of tourism, a person must travel away from their home environment for at least one night in order to be a tourist (although I would argue that this definition needs updating given that it doesn’t account for novel forms of tourism such as a staycation or virtual tourism ).
Based on this fact, therefore, transport is an integral component of tourism. Without transport, people cannot reach their intended destination.
There are a range of different transport types. The most common and popular methods of transport that make up the structure of the tourism industry, however, are: air, road, train and water .

Travel by air has grown exponentially in the past few decades. With the introduction of low cost airlines and deregulation, the competitive market has been a tourist’s paradise.
New routes opening up has introduced tourists to areas that they may never have been able to reach before and low prices have resulted in more of us taking more trips abroad using air travel as our means of transportation.
Travel by air is an essential component of tourism and this was demonstrated during the Coronavirus epidemic. During this time most air traffic was halted, which had a devastating impact of the tourism industry world-wide.
Travel by road is also a core component of tourism, particularly for domestic tourism .
Travel by road is more popular in some countries than others. This largely depends on accessibility options (i.e. what is accessible by road), distances required and road conditions.
In destinations where travel by road is popular, there are often many car hire or rental companies.
Travel by train is very popular in destinations that have good rail networks in infrastructure.
In some parts of the world, such as China and Japan, there are world-class high-speed railways that can be more efficient than flying.
In other parts of the world, the rail journey is part of the tourism experience. A good example of this is the Siberian Railway.
In Europe you can buy an affordable interrail pass , which allows you to travel throughout Europe using the rail system.

Travel by water is also an important component of tourism.
The structure of the tourism industry includes cruises, ferries and leisure boats, among other types of travel by water.
Travel by water can vary considerably in price and can include anything from a round the world cruise to a short long tail ride in Thailand .
Components of tourism: Accommodation services
Accommodation services make up an important part of the structure of the tourism industry.
Whilst accommodation services were traditionally focussed mainly around the hotel industry, nowadays accommodation options for tourists are much more varied. This adds an additional layer of complexity to the structure of the tourism industry.
There are many hotel chains that operate throughout the tourism industry and that are a key component of tourism.
Multinational corporations have expanded throughout the tourism industry with key players being hotel chains such as Marriott, Radisson, Hilton, Travel Lodge and Holiday Inn.
However, hotel chains such as these have come under increased scrutiny as a result of the economic leakage in tourism that they cause.
Hostels and budget accommodation options are popular with budget travellers and backpackers.
There are a range of hostels found throughout the world. These are particularly popular in destinations where accommodation is expensive, such as London, New York and Singapore.
The Youth Hostel Association (YHA) and Hostelling International are popular hostel providers that are found across the UK and overseas.
Billy Butlin changed the face of the British holiday market with the introduction of his seaside holiday parks back in 1936.
Since this time, other similar chains have expanded throughout the UK and the rest of the world.
Camping is also an important component of tourism. There are camp sites situated throughout the world ranging from safari camps to glamping (glamorous camping).
Homestays have become an increasingly prominent component of tourism.
Whilst bed and breakfast accommodation has been around for a very long time, nowadays there are many more options that are grounded on the concept of a homestay.
The sharing economy has seen the growth and introduction of many types of accommodations into the travel and tourism sector that did not exist before.
The most popular of these is Airbnb, where people rent out a room or an entire property to tourists. You can read more about how Airbnb works here .
In recent years consumers have been demanding new and unusual experiences more than ever. In response to this, we have seen many accommodation innovations emerge throughout the world.
From staying in an ice hotel in Finland, to sleeping in a hammock in Borneo to a night in a haunted castle in Wales, there are many different types of accommodation options that can make your holiday a little bit more exciting!
Components of tourism: Conferences and events
Conferences and events make up a significant part of the structure of the tourism industry.
Conferences, which often come under business tourism , come in all shapes and sizes around the world.
From a small academic gathering to a large-scale summit involving national leaders from around the world, conferences are an important component of tourism.
Likewise, the event sector is also a significant part of the tourism industry.
There are millions of events that take place around the world each year that vary in size and function. Many of these form an integral part of the tourism industry.
Examples of major conferences and events around the world
There are many major conferences and events that take place around the world every year. Here are a few of my favourites:
The World Travel Market (WTM) is held in London each November. This is a large event that is held at the Excel venue.
WTM provides travel industry experts with the opportunity to showcase their work, learn more about the industry and to network.
ITB is the world’s leading international travel trade show. It is held in Berlin each year.
Similar to the WTM, this large-scale event enables industry professionals to network and undertake continuous professional development.
The vast majority of people are familiar with the Football World Cup.
The Football World Cup is held every four years in a different location.
The Football World Cup attracts millions of tourists from all over the world. The event also acts as a stimuli for tourism as the nation will often use the opportunity of hosting the event as a chance to market tourism in the area to those who are tuning in from their TVs from around the world.
Sports tourism , which includes events such as the Football World Cup, contributes significantly to the overall tourism industry.
Glastonbury is a popular British music festival. It takes place each summer in Somerset.
Glastonbury is a five-day festival of contemporary performing arts. In addition to music, the festival hosts dance, comedy, theatre, circus, cabaret, and other arts to entertain visitors.
Glastonbury attracts many domestic tourists as well as international tourists.
San Fermin is a festival that is held in Pamplona, Spain each July.
San Fermin, also known as the ‘Running of the Bulls’ is a historically-rooted festival that lasts five days. It involves dancing, eating and drinking, games and the famous bull races and fights.
San Fermin has been subject to a lot of controversy in recent years, with many people protesting that it is a cruel form of animal tourism .

Holi Festival is known as the ‘festival of spring’, the ‘festival of colours’ or the ‘festival of love’.
Holi Festival is celebrated in India each year during the month of March.
Holi Festival is famous for the way in which coloured paints are used and often thrown onto people’s faces and clothes.
This is a Hindu festival that signifies the victory of good over evil.
The Day of the Dead festival, locally referred to as ‘Dia de los Muertos’, is a festival that is celebrated in November each year in Mexico.
This day is a celebration of the deceased, whereby it is believed that the alive and the dead are reunited. On this day many people will create offerings for the deceased.
Many people choose to dress up as skeletons and in halloween-type outfits and they celebrate with food, drink and music.
Components of tourism: Attractions
An essential component of the tourism industry are the tourist attractions.
There are a multitude of different tourist attractions around the world.
Some are built, some are natural. Some are paid, some are free. Some are famous, others are not. Some are large and some are small.
Natural attractions are just as it says on the tin – natural. In other words, they are attractions that have not been made by man.
Natural attractions are found all over the world and vary in size and scope. There is even a definitive list of the seven natural wonders of the world .
I have visited many natural attractions around the world, here is a list of some of my favourites:
- Drakansburg Mountains, South Africa
- Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania
- Mount Toubkal, Morocco
- Sahara Desert, Morocco
- Red Sea, Egypt
- Dead Sea, Israel
- Sierra Nevada, Spain
- Chicken Island, Thailand
- Niagara Falls, USA
- Rocky Mountains, Canada
- Pammukale Thermal Pools, Turkey
- Iceland (the island is filled with wonderful natural attractions!)
- Amazon Rainforest , Ecuador
- Cenotes, Mexico
- Iguazu Falls, Brazil
- The Great Barrier Reef, Australia
- Ha Long Bay, Vietnam
- Waterways of Kerela, India
- Mount Hallasan, South Korea
Built attractions also make up an important part of the structure of the tourism industry.
There are many built attractions throughout the world. Some attractions are built for the purpose of tourism, such as theme parks or museums. Other attractions are built for other purposes but then become tourist attractions, such as the Empire State Building or the Sydney Opera House.
I have visited many built attractions throughout the world. Here are some of my favourites:
- Robin Island, South Africa
- The Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
- La Sagrada Familia, Spain
- The Eiffel Tower, France
- The United States Capitol Building, USA
- Statue of Liberty, New York
- Petronas Towers, Malaysia
- Marina Sands Bay Hotel, Singapore
- Angkor Wat, Cambodia
- Taj Mahal, India
- Sydney Harbour Bridge, Australia
- Houses of Parliament, UK
- Sheikh Zayed Mosque, UAE
Components of tourism: Tourism services
Tourism services are an essential component of tourism. Without many tourism services, the tourism industry would fail to adequately function.
Below I will explain the three major tourism services that make up the structure of the tourism industry.
A tour operator is the individual or organisation who puts together a trip.
Typically, a tour operator would package together essential elements including accommodation, transport and transfer. They would then sell this package to the tourists.
However, tour operators are becoming fewer in recent years. Consumers are now far more Internet savvy and are more capable of researching the individual elements of their holiday and booking this independently. This is known as dynamic packaging .
Traditionally, a travel agent would sell the product that the tour operator has produced i.e. the package holiday.
While travel agents have and continue to sell individual holiday components, they have historically been most commonly used by tourists who wish to book a package holiday.
In today’s society, there is far less scope for travel agents than there used to be. A few years ago it would be easy to finish school and to get a job in a travel agent selling holidays. Now, however, people are more likely to set up their own travel agent business online or to be employed by an online retailer.
Many high street stores have now closed as there is little demand these days for holidays to be booked in this way. Instead, many people are selling holidays and travel services via their blogs or websites.
The travel agent does still exist, but he has changed the way he looks.
Ancillary services are another core component of tourism.
Ancillary basically means ‘extra’ or ‘additional’. An ancillary service in the context of tourism, therefore, is any product or service that is additional to the core elements of accommodation, transport and transfer.
Here are some examples of ancillary products:
- Attraction tickets
- Meal tickets
- Extra luggage
- Currency exchange
- Airport parking
As you can see, the tourism industry is large and complex, but understanding the different components of tourism isn’t too difficult.
All of the components of tourism are interconnected in one way or another and many rely on one another to be successful.
Want to learn more about the structure of tourism? I have listed some recommended texts below.
- An Introduction to Tourism : a comprehensive and authoritative introduction to all facets of tourism including: the history of tourism; factors influencing the tourism industry; tourism in developing countries; sustainable tourism; forecasting future trends.
- The Business of Tourism Management : an introduction to key aspects of tourism, and to the practice of managing a tourism business.
- Tourism Management: An Introduction : gives its reader a strong understanding of the dimensions of tourism, the industries of which it is comprised, the issues that affect its success, and the management of its impact on destination economies, environments and communities.
Liked this article? Click to share!
Travel, Tourism & Hospitality
Global tourism industry - statistics & facts
What are the leading global tourism destinations, digitalization of the global tourism industry, how important is sustainable tourism, key insights.
Detailed statistics
Total contribution of travel and tourism to GDP worldwide 2019-2033
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 1950-2023
Global leisure travel spend 2019-2022
Editor’s Picks Current statistics on this topic
Current statistics on this topic.
Leading global travel markets by travel and tourism contribution to GDP 2019-2022
Travel and tourism employment worldwide 2019-2033
Related topics
Recommended.
- Hotel industry worldwide
- Travel agency industry
- Sustainable tourism worldwide
- Travel and tourism in the U.S.
- Travel and tourism in Europe
Recommended statistics
- Basic Statistic Total contribution of travel and tourism to GDP worldwide 2019-2033
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism: share of global GDP 2019-2033
- Basic Statistic Leading global travel markets by travel and tourism contribution to GDP 2019-2022
- Basic Statistic Global leisure travel spend 2019-2022
- Premium Statistic Global business travel spending 2001-2022
- Premium Statistic Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 1950-2023
- Basic Statistic Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 2005-2023, by region
- Basic Statistic Travel and tourism employment worldwide 2019-2033
Total contribution of travel and tourism to gross domestic product (GDP) worldwide in 2019 and 2022, with a forecast for 2023 and 2033 (in trillion U.S. dollars)
Travel and tourism: share of global GDP 2019-2033
Share of travel and tourism's total contribution to GDP worldwide in 2019 and 2022, with a forecast for 2023 and 2033
Total contribution of travel and tourism to GDP in leading travel markets worldwide in 2019 and 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Leisure tourism spending worldwide from 2019 to 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Global business travel spending 2001-2022
Expenditure of business tourists worldwide from 2001 to 2022 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide from 1950 to 2023 (in millions)
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide 2005-2023, by region
Number of international tourist arrivals worldwide from 2005 to 2023, by region (in millions)
Number of travel and tourism jobs worldwide from 2019 to 2022, with a forecast for 2023 and 2033 (in millions)
- Premium Statistic Global hotel and resort industry market size worldwide 2013-2023
- Premium Statistic Most valuable hotel brands worldwide 2023, by brand value
- Basic Statistic Leading hotel companies worldwide 2023, by number of properties
- Premium Statistic Hotel openings worldwide 2021-2024
- Premium Statistic Hotel room openings worldwide 2021-2024
- Premium Statistic Countries with the most hotel construction projects in the pipeline worldwide 2022
Global hotel and resort industry market size worldwide 2013-2023
Market size of the hotel and resort industry worldwide from 2013 to 2022, with a forecast for 2023 (in trillion U.S. dollars)
Most valuable hotel brands worldwide 2023, by brand value
Leading hotel brands based on brand value worldwide in 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Leading hotel companies worldwide 2023, by number of properties
Leading hotel companies worldwide as of June 2023, by number of properties
Hotel openings worldwide 2021-2024
Number of hotels opened worldwide from 2021 to 2022, with a forecast for 2023 and 2024
Hotel room openings worldwide 2021-2024
Number of hotel rooms opened worldwide from 2021 to 2022, with a forecast for 2023 and 2024
Countries with the most hotel construction projects in the pipeline worldwide 2022
Countries with the highest number of hotel construction projects in the pipeline worldwide as of Q4 2022
- Premium Statistic Airports with the most international air passenger traffic worldwide 2022
- Premium Statistic Market value of selected airlines worldwide 2023
- Premium Statistic Global passenger rail users forecast 2017-2027
- Premium Statistic Daily ridership of bus rapid transit systems worldwide by region 2023
- Premium Statistic Number of users of car rentals worldwide 2019-2028
- Premium Statistic Number of users in selected countries in the Car Rentals market in 2023
- Premium Statistic Carbon footprint of international tourism transport worldwide 2005-2030, by type
Airports with the most international air passenger traffic worldwide 2022
Leading airports for international air passenger traffic in 2022 (in million international passengers)
Market value of selected airlines worldwide 2023
Market value of selected airlines worldwide as of May 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Global passenger rail users forecast 2017-2027
Worldwide number of passenger rail users from 2017 to 2022, with a forecast through 2027 (in billion users)
Daily ridership of bus rapid transit systems worldwide by region 2023
Number of daily passengers using bus rapid transit (BRT) systems as of April 2023, by region
Number of users of car rentals worldwide 2019-2028
Number of users of car rentals worldwide from 2019 to 2028 (in millions)
Number of users in selected countries in the Car Rentals market in 2023
Number of users in selected countries in the Car Rentals market in 2023 (in million)
Carbon footprint of international tourism transport worldwide 2005-2030, by type
Transport-related emissions from international tourist arrivals worldwide in 2005 and 2016, with a forecast for 2030, by mode of transport (in million metric tons of carbon dioxide)
Attractions
- Premium Statistic Market size of museums, historical sites, zoos, and parks worldwide 2022-2027
- Premium Statistic Leading museums by highest attendance worldwide 2019-2022
- Basic Statistic Most visited amusement and theme parks worldwide 2019-2022
- Basic Statistic Monuments on the UNESCO world heritage list 2023, by type
- Basic Statistic Selected countries with the most Michelin-starred restaurants worldwide 2023
Market size of museums, historical sites, zoos, and parks worldwide 2022-2027
Size of the museums, historical sites, zoos, and parks market worldwide in 2022, with a forecast for 2023 and 2027 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Leading museums by highest attendance worldwide 2019-2022
Most visited museums worldwide from 2019 to 2022 (in millions)
Most visited amusement and theme parks worldwide 2019-2022
Leading amusement and theme parks worldwide from 2019 to 2022, by attendance (in millions)
Monuments on the UNESCO world heritage list 2023, by type
Number of monuments on the UNESCO world heritage list as of September 2023, by type
Selected countries with the most Michelin-starred restaurants worldwide 2023
Number of Michelin-starred restaurants in selected countries and territories worldwide as of July 2023
Online travel market
- Premium Statistic Online travel market size worldwide 2017-2028
- Premium Statistic Estimated desktop vs. mobile revenue of leading OTAs worldwide 2023
- Premium Statistic Number of aggregated downloads of leading online travel agency apps worldwide 2023
- Basic Statistic Market cap of leading online travel companies worldwide 2023
- Premium Statistic Forecast EV/Revenue ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
- Premium Statistic Forecast EV/EBITDA ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
Online travel market size worldwide 2017-2028
Online travel market size worldwide from 2017 to 2023, with a forecast until 2028 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Estimated desktop vs. mobile revenue of leading OTAs worldwide 2023
Estimated desktop vs. mobile revenue of leading online travel agencies (OTAs) worldwide in 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Number of aggregated downloads of leading online travel agency apps worldwide 2023
Number of aggregated downloads of selected leading online travel agency apps worldwide in 2023 (in millions)
Market cap of leading online travel companies worldwide 2023
Market cap of leading online travel companies worldwide as of September 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
Forecast EV/Revenue ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
Forecast enterprise value to revenue (EV/Revenue) ratio in the online travel market worldwide in 2024, by segment
Forecast EV/EBITDA ratio in the online travel market 2024, by segment
Forecast enterprise value to EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) ratio in the online travel market worldwide in 2024, by segment
Selected trends
- Premium Statistic Global travelers who believe in the importance of green travel 2023
- Premium Statistic Sustainable initiatives travelers would adopt worldwide 2022, by region
- Premium Statistic Airbnb revenue worldwide 2017-2023
- Premium Statistic Airbnb nights and experiences booked worldwide 2017-2023
- Premium Statistic Technologies global hotels plan to implement in the next three years 2022
- Premium Statistic Hotel technologies global consumers think would improve their future stay 2022
Global travelers who believe in the importance of green travel 2023
Share of travelers that believe sustainable travel is important worldwide in 2023
Sustainable initiatives travelers would adopt worldwide 2022, by region
Main sustainable initiatives travelers are willing to adopt worldwide in 2022, by region
Airbnb revenue worldwide 2017-2023
Revenue of Airbnb worldwide from 2017 to 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Airbnb nights and experiences booked worldwide 2017-2023
Nights and experiences booked with Airbnb from 2017 to 2023 (in millions)
Technologies global hotels plan to implement in the next three years 2022
Technologies hotels are most likely to implement in the next three years worldwide as of 2022
Hotel technologies global consumers think would improve their future stay 2022
Must-have hotel technologies to create a more amazing stay in the future among travelers worldwide as of 2022
- Premium Statistic Travel and tourism revenue worldwide 2019-2028, by segment
- Premium Statistic Distribution of sales channels in the travel and tourism market worldwide 2018-2028
- Premium Statistic Inbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
- Premium Statistic Outbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
Travel and tourism revenue worldwide 2019-2028, by segment
Revenue of the global travel and tourism market from 2019 to 2028, by segment (in billion U.S. dollars)
Distribution of sales channels in the travel and tourism market worldwide 2018-2028
Revenue share of sales channels of the travel and tourism market worldwide from 2018 to 2028
Inbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
Inbound tourism visitor growth worldwide from 2020 to 2022, with a forecast until 2025, by region
Outbound tourism visitor growth worldwide 2020-2025, by region
Outbound tourism visitor growth worldwide from 2020 to 2022, with a forecast until 2025, by region
Further reports Get the best reports to understand your industry
Get the best reports to understand your industry.
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)

What Is the Purpose of Tourism?
By Michael Ferguson
Tourism is a vital industry that has been rapidly growing over the past few decades. It refers to the activities of individuals traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for leisure, business, or other purposes.
The tourism industry is a major contributor to the global economy and plays a significant role in the development of many countries. In this article, we will explore the purpose of tourism in detail.
Exploring New Places and Experiences
One of the primary purposes of tourism is to explore new places and experiences. People often travel to different parts of the world to escape their daily routine, try new activities, learn about different cultures, and gain new perspectives on life. Tourism provides an opportunity for people to discover new destinations, try new foods, engage in adventure activities like hiking or skiing, and experience local traditions.
Relaxation and Recreation
Another significant purpose of tourism is relaxation and recreation. Many people plan vacations specifically to unwind from their stressful lives.
They may seek out peaceful locations like beaches or mountains where they can relax, read a book, or take part in wellness activities like yoga or meditation. Other travelers may engage in recreational activities like golfing or fishing as a way to relax.
Economic Development
Tourism can also be an essential driver of economic development for many countries. The revenue generated from tourism can support local businesses and infrastructure development projects. When people travel to a destination, they spend money on transportation, accommodation, food, souvenirs, and other goods and services that contribute to local economies.
Cultural Exchange
Tourism also plays an important role in facilitating cultural exchange between different nations. Travelers who visit foreign countries have an opportunity to learn about their customs, traditions, and ways of life. This exchange contributes towards mutual respect for different cultures while promoting intercultural understanding.
Education and Learning
Tourism provides an opportunity for people to learn about history, art, and architecture. Many travelers visit museums, galleries, and historical landmarks to gain knowledge about significant events and cultures. This purpose of tourism is particularly relevant for students who may travel to different countries as part of their educational curriculum.
8 Related Question Answers Found
What is the main meaning of tourism, what is the meaning of tourism, what do we mean by tourism, what are the basic nature of tourism, what is meant by tourism, what are the nature of tourism, what is the nature of tourism, what does tourism mean, backpacking - budget travel - business travel - cruise ship - vacation - tourism - resort - cruise - road trip - destination wedding - tourist destination - best places, london - madrid - paris - prague - dubai - barcelona - rome.
© 2024 LuxuryTraveldiva
ColorWhistle
Digital Web Design Agency India

Explore our Market-Fit Services
We ensure to establish websites with the latest trends as we believe that, products whose value satisfies the needs of the market and its potential customers can be efficiently successful.
Quick Links
- About Us – ColorWhistle
- Engagement Models
- Testimonials
- Case Studies
- Agency Services
- Web Development
- Web App Development
- Digital Marketing
- Travel Website Development Services Company
- Real Estate Website Development Services Company
- Education Website Development Services Company
- Healthcare Website Development Services Company
- Hotel and Restaurant Website Development Services

Category: Travel
Date: August 18, 2023
Everything You Need to Know About Travel & Tourism Industry
The travel and tourism industry is one of the biggest and fastest-growing industries in the world. We are still witnessing the continued interest of many people preferring to spend their spare time on travel.
This has given an enormous opportunity for travel and tourism-related business like travel agencies and tour operators to cater to the needs of this emerging demand.
In an effort to help people who want to enter the travel business, we have written this comprehensive introduction blog about the travel and tourism industry. We also regularly share informative resources for people in the travel industry . Do check out our blog section on a regular basis to read information-rich resources.
Let’s dive in.
What is the Difference Between Travel & Tourism Industry?
The terms travel and tourism are often used side by side and are closely linked. However, there are differences between the two. In this blog, we will find out more about the difference between both travel and tourism and the activities that set them apart.
- What is tourism industry? – Tourism is the act of traveling to a different location for either business or pleasure for more than one consecutive year
- What is travel industry? – Travel refers to moving from one location to another. It can be long-distance, short-distance, overseas or domestic travel and can cover a wide variety of different travel purposes.
It is completely understandable that many find it hard to figure out the distinction between both the terms because there seems to be a significant overlap. Many of the businesses and service providers seem to carter for both travel and tourism.
Despite the progressive and adaptive nature of the industry where the changes are evident via new introduction of tourism forms , there is no attempt to develop a commonly accepted definition of travel and tourism.
While we have attempted to define the concept of travel and tourism from a generic perspective, the practical application of the meanings we outlined can be difficult when used for specific types.
We would say that academics and practitioners from the industry have to come up with appropriate definitions so that it will represent the travel and tourism industry that operates today.
Evolution of the Travel & Tourism Industry
Here is a graphic we prepared that highlights the evolution of the travel and tourism industry .
What Are the Sectors and Components Within the Travel and Tourism Industry?
In this section, we will explain the various sectors and components that are present in the travel and tourism industry.
Sectors Within the Travel and Tourism Industry
1. transportation, airline industry.

The transport (accessibility) system is one of the main key parts of the travel and tourism industry. It is considered as a link between tourist generating and tourism destination regions. Some of the major airlines in the world are,
- Emirates Airline
- Jet Airways
- Malaysia Airlines
- Air France KLM
- Southwest Airlines

People give a lot of importance to comfort while traveling. That is why there is a huge rise in companies that provide a variety of vehicles according to requirement and comfort of the clients. Some of the famous car rental companies are,
- Budget Rent a Car
Water transport

Waterways are important to the transportation of people and goods throughout the world. It has played a vital role in drawing different parts of the world closer and is essential to foreign trade. The different types of water transport are,
- Tug boats, Rigs
Bus & coach

Buses and coaches are one of the most important forms of passenger transport around the world. They have been shaping sustainable mobility for more than a century. Here are some of the luxury busses in the world,
- Marchi Mobile EleMMent Palazzo
- Featherlite Vantare Platinum Plus
- Prevost H3-45 VIP
- Foretravel IH-45 Luxury Motor Coach
- Country Coach Prevost

Railways have helped mankind in many ways – in both voyages of commerce and discovery. They are still the most popular form of transport and given the environmental benefits , they will be with us for many years to come. Here are some of the most famous trains in the world,
- Trans-Siberian Express
- Orient Express
- Flying Scotsman
- Golden Arrow
- Maharajas’ Express

This type of transportation has developed in recent years and is going to be quite influential in the years to come. The most famous company offering commercial space tourism is Virgin Galactic .
2. Accommodation

Hotels are one of the most popular forms of accommodations for tourists or anyone who is looking for a place to stay overnight or on a short-term basis. They provide guests with private rooms, bathroom and other facilities. Some of the popular hotels in the world are
- Emirates Palace
- Rancho Valencia Resort & Spa
- The Westin Excelsior
- Burj Al Arab Hotel
Shared accommodations

Shared accommodations are commonly defined as two or more people living in accommodation together. Usually, each person will have their own bed and will share certain common areas such as kitchens and bathrooms. This is a budget-friendly option for tourists. Some of the most popular shared accommodation service providers are,
- OneFineStay

Camping or temporary shelter is an outdoor accommodation which is in the form of a tent. Travelers who camp will also prefer to stay at a commercial campsite which has additional facilities. Some of the popular camping sites in the world are,
- Mount Cook National Park, New Zealand
- Devon, England
- Loch Lomond & The Trossachs, Scotland
- The Alps, France
- Hossa National Park, Finland

Bed and breakfast (B&B)

Bed-and-breakfast are cozy accommodations that are inviting, intimate environment where innkeepers are often present to look after every guest. In some cases, the owner of the B&B may live in the building too. Some of the most popular B&B’s in the world are,
- Le Quartier Sonang — Amsterdam
- Bed and Breakfast by the Beach — Bournemouth, England
- Arbor Guest House — Napa Valley, California
- Glendon Guest House — Derbyshire, England.
- Cliffside Inn Bed And Breakfast — Newport, R.I.

Cruise is a combined form of transportation and accommodation. People who go on cruise travel will have their own cabin where they can rest and relax. A major part of the passenger’s time is spent on the cruise ship. Some of the most popular cruise destinations in the world are,
- Avignon, France
- Glacier Bay, Alaska
- Vienna, Austria
Timeshare accommodation

Timesharing is shared ownership of a vacation property. A management company handles the construction of a property and sells shares where buyers can spend a specific amount of time on the property usually 1 week per year. Famous timeshare resorts in the world are,
- The Ritz Carlton Club
- The Disney Vacation Club
- The Marriott Vacation Club
- The Hilton Grand Vacations Club
- The Hyatt Residence Club
3. Food & Beverage
Restaurants.

The restaurant and dining business is equally important as the scenery, accommodations, and destination areas because tourists want to engage in local culture when they go on a holiday. If you have any plans to create a restaurant website we have written a detailed blog about the essential elements a restaurant website must-have . Here are some of the famous restaurants in the world,
- Osteria Francescana
- El Celler de Can Roca
- Eleven Madison Park
Bars & cafés

Bars & Cafés give a relaxed environment for travelers to eat and drink. Bars tend to focus on selling alcoholic drinks and soft drinks whereas cafés sell hot drinks and snacks. We have also written a detailed blog that has an amazing list of bakery & cafés website design inspiration , do check it out. Some of the world-famous bars & cafés are,
- The Broken Shaker
- Bell in Hand Tavern
- El Floridita
- Sant’Eustachio il Caffe
- La Cafeotheque

Nightclubs are commercial establishments that will stay open until late at night. These places combine music, dance and alcohol sales. Some of the world-famous nightclubs are,
- Green Valley
4. Entertainment

Casinos are similar to indoor amusement parks, but it is for adults. It has many games of chance such as slot machines, blackjack, roulette, craps, keno and baccarat provides billions of dollars in revenue for casinos. Some of the world-famous casinos are,
- WinStar World Casino
- Venetian Macau
- City of Dreams

Shopping plays a vital role in the travel and tourism industry as it caters the basic necessities and it is also a form of entertainment. Many people specifically travel to experience shopping in those destinations. Some of the world-famous shopping destinations are,
- New York City

Museums have objects and materials of cultural, religious and historical importance in one place. They are presented to the public for education and enjoyment. Some of the world-famous museums are,
- Zeitz Museum of Contemporary Art
- National Gallery of Canada
- Tate Modern
- The Metropolitan Museum Of Art
- Mauritshuis
Theme parks

A theme park has various attractions, such as rides, games and events for entertainment. They will also have shops, restaurants and other entertainment outlets. Such types of parks can be enjoyed by adults, teenagers and children. Some of the famous theme parks in the world are,
- Universal Studios
- Pleasure Beach
- Alton Towers
Components of Travel Services
Travel agency.
A travel agency sells or arranges transportation, accommodations, tours and trips for travelers. Some of the functions of a travel agency are to recommend a particular service that will be suitable for the traveler, provide assistance in procuring travel documents, process travel arrangements and give assistance in case of refunds or cancellations.
Online travel agency (OTA)
An OTA is a travel website that specializes in providing travel services to customers including flights, hotels, car rentals, cruises, activities, and packages. These websites have in-built booking systems that allow users to instantly book.
Some of the popular examples of OTAs are Expedia, Priceline and Orbitz. We have also written a detailed blog about what is an online travel agency and the benefits of partnering with them. If you are planning to create an OTA website, you can take inspiration from these 100+ travel websites .
Tour operators
A tour operator will combine tour products and travel services together to offer packaged holidays to the customers. Usually, a packaged tour will have a combination of air travel, accommodation and entertainment. The tour operator will provide organized activities for customers.
Destination marketing organizations (DMO)
DMO’s represent destinations and help to promote a particular destination as an attractive one by creating a long-term travel and tourism strategy.
Through this, they try to strengthen the economic position of that place which in turn will improve the employment opportunity for the people in that region. At ColorWhistle, we can help any type of travel and tourism provider to improve online visibility . All you have to do is, just get in touch with us to learn how we can help.
Drive Conversions and Boost your Business with Expert Travel Website Development.
How can colorwhistle’s digital solutions help travel and tourism businesses.
One thing that is common in this blog is that when we were researching to find the famous travel-related product or service provider in the world, each one of the big players had amazing websites. Those websites were the gateway through which those players showed their expertise to the world.
That is where ColorWhiste can help. We will help you to present your capability to the online world. If you are Solopreneur looking to enter the travel arena or growing or established travel business, we understand that improving your current state of affairs will always be on your mind.
Our amazing team at ColorWhistle can offer professional assistance. We have a powerhouse of multi-talented people experienced in web development and digital marketing .
If it is redesigning your existing website or creating a new one, we can polish your online image in no time. Get in touch with us today and let’s talk business!
In quest of the Perfect Travel Tech Solutions Buddy?
Be unrestricted to click the other trendy writes under this title that suits your needs the best!
- Best Tour Operators USA
- Online Travel Marketing Techniques
- Travel Insurance Agency Technology
- Best Tour Operators Europe
- Travel Tourism Trends
- Travel Marketing Campaigns
- Medical Tourism Business
Related Posts

Exploring the World Through AI and VR in the Travel Industry

How AI-based Travel Booking Applications Can be Developed?

Latest Marketing Trends for Travel Businesses in This New Year
About the Author - Anjana
Anjana is a full-time Copywriter at ColorWhistle managing content-related projects. She writes about website technologies, digital marketing, and industries such as travel. Plus, she has an unhealthy addiction towards online marketing, watching crime shows, and chocolates.
View Our Services
Have an idea? Request a quote
Share This Blog
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Ready to get started?
Let’s craft your next digital story

Sure thing, leave us your details and one of our representatives will be happy to call you back!
Eg: John Doe
Eg: United States
Eg: [email protected]
More the details, speeder the process :)
What is purpose of tourism?
Exploring the Essence of Tourism
Tourism is a multifaceted industry that caters to diverse interests and preferences. It allows people to unwind, learn, and grow by experiencing different cultures, landscapes, and cuisines. The purpose of tourism is not just limited to leisure and relaxation; it encompasses various aspects that contribute to personal and societal growth. In this article, we will delve deeper into the different purposes of tourism and how they enrich our lives.
Experiencing Different Cultures
Traveling to new places exposes us to different cultures and traditions, allowing us to experience the world from a fresh perspective. We learn about the history, language, customs, and beliefs of the people we encounter, which in turn broadens our understanding and appreciation of the world. This cultural exchange also fosters tolerance and empathy, as we become more open to embracing the differences that make each culture unique.
Personal Growth and Self-Discovery
Travel can be a transformative experience that fosters personal growth and self-discovery. It pushes us out of our comfort zones and challenges us to adapt to unfamiliar environments. By navigating new situations, we develop problem-solving skills, resilience, and a greater sense of independence. Moreover, immersing ourselves in different cultures leads to introspection, helping us better understand our values, beliefs, and aspirations.
Escaping the Mundane
One of the most obvious purposes of tourism is to provide an escape from the monotony of daily life. Traveling to new destinations allows us to break free from our routines and experience new adventures. Whether it's exploring a bustling city, relaxing on a tropical beach, or trekking through a dense jungle, these experiences can rejuvenate us and provide a much-needed break from the stresses of everyday life.
Creating Lasting Memories
Traveling, especially with friends and family, creates lasting memories that we cherish for a lifetime. These shared experiences strengthen our bonds with our loved ones and provide us with stories to reminisce about for years to come. Moreover, capturing these moments through photographs and videos allows us to preserve these memories and share them with future generations.
Supporting Local Economies
Tourism plays a vital role in supporting local economies, as it generates income and creates employment opportunities. When we travel, we contribute to the local economy by spending on accommodation, food, transportation, and various attractions. This financial boost helps improve infrastructure, fund public services, and ultimately improve the quality of life for local residents.
Promoting Environmental Conservation
Eco-tourism, which focuses on responsible travel to natural areas, plays a crucial role in promoting environmental conservation. By visiting protected areas and supporting eco-friendly initiatives, we contribute to the preservation of ecosystems and wildlife. Furthermore, our experiences in nature can inspire us to become more environmentally conscious and take action to protect our planet for future generations.
Enhancing International Relations
Tourism helps build bridges between nations by fostering cultural exchange and understanding. When we visit other countries, we have the opportunity to form friendships and connections with people from different backgrounds. These interactions contribute to breaking down stereotypes and promoting goodwill, ultimately fostering a more peaceful and interconnected world.
In conclusion, the purpose of tourism is multifaceted and extends beyond leisure and relaxation. Travelling allows us to experience different cultures, promotes personal growth, and helps us escape the mundane. Additionally, it creates lasting memories, supports local economies, promotes environmental conservation, and enhances international relations. As we continue to explore the world, let us embrace the many benefits that tourism has to offer and strive to be responsible travelers.
Write a comment
- Travel and Tourism
- Travel & Tourism in India
- Career Advice in Tourism
- Travel/Immigration Advice for Tourists in the USA
- Hospitality Management in Tourism
- Travel and Tourism Information
- Education & Careers
- international tourism
- inbound tourism
- immigration
- hospitality
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer

share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
About UN Tourism
UN Tourism’s leadership vision acknowledges the most pressing challenges facing tourism and identifies the sector’s ability to overcome them and to drive wider positive change, including the opportunities responsible tourism offers for the advancement of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
UN Tourism members have endorsed the Management Vision of the Secretary-General which seeks to position tourism as a policy priority, lead in knowledge creation, enhance the Organization’s capacity through building new and stronger partnerships , and offer better value for existing Members while also expanding membership.
To realize the Management Vision, UN Tourism’s work is based around five distinct pillars:
- making tourism smarter through celebrating innovation and leading the digital transformation of the sector;
- making tourism more competitive at every level through promoting investment and promoting entrepreneurship;
- creating more and better jobs and providing relevant training;
- building resilience and promoting safe and seamless travel; and
- harnessing tourism’s unique potential to protect cultural and natural heritage and to support communities both economically and socially.
As the leading international organization in the field of tourism, UN Tourism promotes tourism as a driver of economic growth, inclusive development and environmental sustainability and offers leadership and support to the sector in advancing knowledge and tourism policies worldwide.
UN Tourism encourages the implementation of the Global Code of Ethics for Tourism , to maximize tourism’s socio-economic contribution while minimizing its possible negative impacts, and is committed to promoting tourism as an instrument in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) , geared towards reducing poverty and fostering sustainable development worldwide.
UN Tourism generates market knowledge, promotes competitive and sustainable tourism policies and instruments, fosters tourism education and training, and works to make tourism an effective tool for development through technical assistance projects in over 100 countries around the world.
UN Tourism’s membership includes 160 Member States, 6 Associate Members and over 500 Affiliate Members representing the private sector, educational institutions, tourism associations and local tourism authorities.
Basic Documents
Our management.

The management team works towards a comprehensive vision for development of the tourism sector. This includes positioning tourism as a policy priority, establishing thought leadership in knowledge and policy creation, increasing resources and strengthening UN Tourism’s capacity through meaningful partnerships.
Governing Bodies

The bodies of the World Tourism Organization are the:
- General Assembly
- Regional Commissions
- Executive Council
- Secretariat
Member States

An intergovernmental organization, UN Tourism has 160 Member States, 6 Associate Members, 2 Observers
Working With the Private Sector

Bringing together over 500 companies, educational and research institutions, destinations and NGOs, the UN Tourism Affiliate Members provides a space for members to engage in dialogue, share information and take further action.
UN Tourism Liaison Office in Geneva

As part of the UN Tourism Geneva Liaison Office (GVLO) scope of work to represent UN Tourism to the UN System and Diplomatic Missions in Geneva and in building strategic partnerships for increased capacity, GVLO has participated in numerous United Nations System led activities.
UN Tourism Tourism Ambassadors

UN Tourism’s Ambassadors for Sustainable Tourism are drawn from the worlds of sport, entertainment, business, gastronomy and more.
Sustainable tourism
Related sdgs, promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable ....

Description
Publications.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States (SIDS) and coastal least developed countries (LDCs) (see also: The Potential of the Blue Economy report as well as the Community of Ocean Action on sustainable blue economy).
The World Tourism Organization defines sustainable tourism as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities".
Based on General assembly resolution 70/193, 2017 was declared as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development.
In the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development SDG target 8.9, aims to “by 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism is also highlighted in SDG target 12.b. which aims to “develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”.
Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “by 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries” as comprised in SDG target 14.7.
In the Rio+20 outcome document The Future We want, sustainable tourism is defined by paragraph 130 as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities by supporting their local economies and the human and natural environment as a whole. ” In paragraph 130, Member States also “call for enhanced support for sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building in developing countries in order to contribute to the achievement of sustainable development”.
In paragraph 131, Member States “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small- and medium-sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”. In this regard, Member States also “underline the importance of establishing, where necessary, appropriate guidelines and regulations in accordance with national priorities and legislation for promoting and supporting sustainable tourism”.
In 2002, the World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg called for the promotion of sustainable tourism development, including non-consumptive and eco-tourism, in Chapter IV, paragraph 43 of the Johannesburg Plan of Implementation.
At the Johannesburg Summit, the launch of the “Sustainable Tourism – Eliminating Poverty (ST-EP) initiative was announced. The initiative was inaugurated by the World Tourism Organization, in collaboration with UNCTAD, in order to develop sustainable tourism as a force for poverty alleviation.
The UN Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD) last reviewed the issue of sustainable tourism in 2001, when it was acting as the Preparatory Committee for the Johannesburg Summit.
The importance of sustainable tourism was also mentioned in Agenda 21.
For more information and documents on this topic, please visit this link
UNWTO Annual Report 2015
2015 was a landmark year for the global community. In September, the 70th Session of the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a universal agenda for planet and people. Among the 17 SDGs and 169 associated targets, tourism is explicitly featured in Goa...
UNWTO Annual Report 2016
In December 2015, the United Nations General Assembly declared 2017 as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development. This is a unique opportunity to devote a year to activities that promote the transformational power of tourism to help us reach a better future. This important cele...
Emerging Issues for Small Island Developing States
The 2012 UNEP Foresight Process on Emerging Global Environmental Issues primarily identified emerging environmental issues and possible solutions on a global scale and perspective. In 2013, UNEP carried out a similar exercise to identify priority emerging environmental issues that are of concern to ...
Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
This Agenda is a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. It also seeks to strengthen universal peace in larger freedom, We recognize that eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for su...
15 Years of the UNWTO World Tourism Network on Child Protection: A Compilation of Good Practices
Although it is widely recognized that tourism is not the cause of child exploitation, it can aggravate the problem when parts of its infrastructure, such as transport networks and accommodation facilities, are exploited by child abusers for nefarious ends. Additionally, many other factors that contr...
Towards Measuring the Economic Value of Wildlife Watching Tourism in Africa
Set against the backdrop of the ongoing poaching crisis driven by a dramatic increase in the illicit trade in wildlife products, this briefing paper intends to support the ongoing efforts of African governments and the broader international community in the fight against poaching. Specifically, this...
Status and Trends of Caribbean Coral Reefs: 1970-2012
Previous Caribbean assessments lumped data together into a single database regardless of geographic location, reef environment, depth, oceanographic conditions, etc. Data from shallow lagoons and back reef environments were combined with data from deep fore-reef environments and atolls. Geographic c...
Natural Resources Forum: Special Issue Tourism
The journal considers papers on all topics relevant to sustainable development. In addition, it dedicates series, issues and special sections to specific themes that are relevant to the current discussions of the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD)....
Thailand: Supporting Sustainable Development in Thailand: A Geographic Clusters Approach
Market forces and government policies, including the Tenth National Development Plan (2007-2012), are moving Thailand toward a more geographically specialized economy. There is a growing consensus that Thailand’s comparative and competitive advantages lie in amenity services that have high reliance...
Road Map on Building a Green Economy for Sustainable Development in Carriacou and Petite Martinique, Grenada
This publication is the product of an international study led by the Division for Sustainable Development (DSD) of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) in cooperation with the Ministry of Carriacou and Petite Martinique Affairs and the Ministry of Environment, Foreig...
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal (NRF)
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal, seeks to address gaps in current knowledge and stimulate relevant policy discussions, leading to the implementation of the sustainable development agenda and the achievement of the Sustainable...
UN Ocean Conference 2025
Our Ocean, Our Future, Our Responsibility “The ocean is fundamental to life on our planet and to our future. The ocean is an important source of the planet’s biodiversity and plays a vital role in the climate system and water cycle. The ocean provides a range of ecosystem services, supplies us with
UN Ocean Conference 2022
The UN Ocean Conference 2022, co-hosted by the Governments of Kenya and Portugal, came at a critical time as the world was strengthening its efforts to mobilize, create and drive solutions to realize the 17 Sustainable Development Goals by 2030.
58th Session of the Commission for Social Development – CSocD58
22nd general assembly of the united nations world tourism organization, world tourism day 2017 official celebration.
This year’s World Tourism Day, held on 27 September, will be focused on Sustainable Tourism – a Tool for Development. Celebrated in line with the 2017 International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, the Day will be dedicated to exploring the contribution of tourism to the Sustainable Deve
World Tourism Day 2016 Official Celebration
Accessible Tourism for all is about the creation of environments that can cater for the needs of all of us, whether we are traveling or staying at home. May that be due to a disability, even temporary, families with small children, or the ageing population, at some point in our lives, sooner or late
4th Global Summit on City Tourism
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and the Regional Council for Tourism of Marrakesh with support of the Government of Morroco are organizing the 4th Global Summit on City Tourism in Marrakesh, Morroco (9-10 December 2015). International experts in city tourism, representatives of city DMOs, of
2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and Ulsan Metropolitan City with support of the Government of the Republic of Korea are organizing the 2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference, in Ulsan, Republic of Korea (14 - 16 October 2015). Under the title “Paving the Way for a Bright Future for Mounta
21st General Assembly of the United Nations World Tourism Organization
Unwto regional conference enhancing brand africa - fostering tourism development.
Tourism is one of the Africa’s most promising sectors in terms of development, and represents a major opportunity to foster inclusive development, increase the region’s participation in the global economy and generate revenues for investment in other activities, including environmental preservation.
- January 2017 International Year of Tourism In the context of the universal 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the International Year aims to support a change in policies, business practices and consumer behavior towards a more sustainable tourism sector that can contribute to the SDGs.
- January 2015 Targets 8.9, 12 b,14.7 The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development commits Member States, through Sustainable Development Goal Target 8.9 to “devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism, as a driver for jobs creation and the promotion of local culture and products, is also highlighted in Sustainable Development Goal target 12.b. Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “increase [by 2030] the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries”, through Sustainable Development Goals Target 14.7.
- January 2012 Future We Want (Para 130-131) Sustainable tourism is defined as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities” as well as to “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small and medium sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”.
- January 2009 Roadmap for Recovery UNWTO announced in March 2009 the elaboration of a Roadmap for Recovery to be finalized by UNWTO’s General Assembly, based on seven action points. The Roadmap includes a set of 15 recommendations based on three interlocking action areas: resilience, stimulus, green economy aimed at supporting the tourism sector and the global economy.
- January 2008 Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria The Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria represent the minimum requirements any tourism business should observe in order to ensure preservation and respect of the natural and cultural resources and make sure at the same time that tourism potential as tool for poverty alleviation is enforced. The Criteria are 41 and distributed into four different categories: 1) sustainability management, 2) social and economic 3) cultural 4) environmental.
- January 2003 WTO becomes a UN specialized body By Resolution 453 (XV), the Assembly agreed on the transformation of the WTO into a United Nations specialized body. Such transformation was later ratified by the United Nations General Assembly with the adoption of Resolution A/RES/58/232.
- January 2003 1st Int. Conf. on Climate Change and Tourism The conference was organized in order to gather tourism authorities, organizations, businesses and scientists to discuss on the impact that climate change can have on the tourist sector. The event took place from 9 till 11 April 2003 in Djerba, Tunisia.
- January 2002 World Ecotourism Summit Held in May 2002, in Quebec City, Canada, the Summit represented the most important event in the framework of the International Year of Ecosystem. The Summit identified as main themes: ecotourism policy and planning, regulation of ecotourism, product development, marketing and promotion of ecotourism and monitoring costs and benefits of ecotourism.
- January 1985 Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code At the World Tourism Organization Sixth Assembly held in Sofia in 1985, the Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code were adopted, setting out the rights and duties of tourists and host populations and formulating policies and action for implementation by states and the tourist industry.
- January 1982 Acapulco Document Adopted in 1982, the Acapulco Document acknowledges the new dimension and role of tourism as a positive instrument towards the improvement of the quality of life for all peoples, as well as a significant force for peace and international understanding. The Acapulco Document also urges Member States to elaborate their policies, plans and programmes on tourism, in accordance with their national priorities and within the framework of the programme of work of the World Tourism Organization.
What next for travel and tourism? Here's what the experts say

In many countries, more than 80% of travel and tourism spending actually comes from the domestic market. Image: Unsplash/Surface
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Julie Masiga

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Travel and Tourism is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, travel and tourism.
- In 2020 alone, the travel and tourism sector lost $4.5 trillion and 62 million jobs globally.
- But as the world recovers from the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, travel and tourism can bounce back as an inclusive, sustainable, and resilient sector.
- Two experts highlight some of the key transformations in the sector going forward during the World Economic Forum's Our World in Transformation series.
The Travel & Tourism sector was one of the hardest hit by the COVID-19 pandemic, leaving not only companies but also tourism-driven economies severely affected by shutdowns, travel restrictions and the disappearance of international travel.
In 2020 alone, the sector lost $4.5 trillion and 62 million jobs, impacting the living standards and well-being of communities across the globe. Moreover, the halt in international travel gave both leisure and business travellers the chance to consider the impact of their choices on the climate and environment.
Amid shifting demand dynamics and future opportunities and risks, a more inclusive, sustainable and resilient travel and tourism sector can be - and needs to be - built.
The World Economic Forum's Travel & Tourism Development Index 2021 finds that embedding inclusivity, sustainability and resilience into the travel and tourism sector as it recovers, will ensure it can continue to be a driver of global connectivity, peace and economic and social progress.
We spoke to Sandra Carvao , Chief of Market Intelligence and Competitiveness at the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), and Liz Ortiguera , CEO of the Pacific Asia Travel Association in Thailand (PATA), and asked them to highlight some of the key areas of risk and opportunity in the sector during an episode of the World Economic Forum's Our World in Transformation series.
Have you read?
Travel & tourism development index 2021: rebuilding for a sustainable and resilient future, towards resilience and sustainability: travel and tourism development recovery, how can we really achieve sustainability in the travel sector, what are some of the top global trends you're witnessing currently in the travel and tourism sector.
Liz Ortiguera: Given the extended lockdown that we had on travel with the pandemic, vacation for friends and relatives (VFR) is now a high priority for people who haven’t been in touch for a long time thanks to the pandemic. So, people are reconnecting. And that kind of links to the second trend, which is multi-purpose or blended travel. Never before, particularly now that we can connect digitally through Zoom, has the ability to work from anywhere enabled travellers to cover multiple purposes, like visits with friends and multiple business trips. So, we'll find that the duration of travel and the length of stay is longer. And third is the continued high focus on safety and wellness which is top of mind for travellers due to the pandemic. All travel is wellness-related now.
Sandra Carvao: I think there is a bigger concern with sustainability, which is very welcome in our industry. Consumers, particularly the younger generation, are much more aware of the impact they have, not only on the environment but also socially and on the communities they live in. We've also seen an increase in expenditure per trip, so I think people are very eager to go outside, and they're staying longer. And on the other side, I think there are some challenges: we’re seeing a rise in late bookings because restrictions can change at short notice and that’s having an impact on the decisions of travellers. This is putting pressure on the industry in terms of planning and anticipating fluctuations in demand.
Social media surveys have shown that travellers who have immersive experiences are more likely to post about them, which is good for the industry.
What is community-based tourism and why is it important?
Sandra Carvao: One of the positive impacts of the pandemic is that people are looking for local experiences and are spending more time with communities. So, the concept of community-based tourism is obviously one that puts the community at the core of every development, ensuring that it's engaged and empowered and that it benefits. At the UNWTO, we worked with the G20 and the Saudi presidency back in 2020 and produced a framework for tourism development in communities, which states that communities need to be part of the planning and management of tourism activities. We need to go beyond traditional definitions of community to a point where the industry leans on partnerships between the public and private sectors and communities.
Liz Ortiguera: In July 2022, PATA is hosting a destination-marketing forum and one of the key themes is community-based tourism. The purpose is really to put the community and authenticity-in-culture activities at the heart of the travel experience. There are benefits for all stakeholders. One is that travellers can have an authentic experience. They're not in overcrowded, touristic locations and they experience something new and unique within the community. These experiences are designed in partnership with communities who get the benefit of financial inclusion, and if activities are designed properly, the reinforcement of their cultural heritage. Governments also engage in economic development more broadly across countries. Another interesting trend is creative tourism, which means you create an experience for tourists to participate in, like a dance lesson, or a cooking lesson. Social media surveys have shown that travellers who have these kinds of immersive experiences are more likely to post about them online and that's good for the industry.
It is important to emphasize that virtual experiences, while they are a fun tool, can never replace visiting a destination.
How is technology and innovation helping to leverage cultural resources?
Sandra Carvao: One interesting trend we’re seeing is that more and more people are booking trips directly, so communities need to be supported to digitize their systems. Education and upskilling of communities are important so that they can leverage digital platforms to market themselves. From the tourists’ perspective, it is important to emphasize that virtual experiences, while they are a fun tool, can never replace visiting a destination.
Liz Ortiguera: People have been living virtually for more than two years. Amazing innovations have emerged, such as virtual reality and augmented reality, and all kinds of applications and tools. But the important thing is the experience. The destination. Real-world experiences need to remain front and centre. Technology tools should be viewed as enablers and not the core experience. And when it comes to staff, technology can really democratize education. There’s an opportunity to mobilize a mobile-first approach for those who are on the frontlines, or out in the field, and can’t easily access computers, but need to get real-time information.

How is the sector dealing with labour shortages and re-employment of the workforce?
Liz Ortiguera: Labour shortages are much more dynamic in North America and in Europe. But it’s having a knock-on effect on Asia. If, for example, their air carriers are limited by staff and they have to cancel flights, which we're very much seeing out of Europe, seating capacity then becomes a limiting factor in the recovery of Asia Pacific. That's the main constraint right now. And compounding that is the rising price of fuel. But people in the Asia Pacific are keen to get reemployed.
Sandra Carvao: Labour shortages are a priority for the sector in countries around the world. Many workers left the sector during the pandemic and the uncertainty that surrounded the measures taken to contain it left many people unsure of whether the sector would recover. It is time to address things like conditions, scheduling, and work/life balance, all things which have been top of mind for workers during the pandemic. As the sector recovers, we need time to bring new hires on board and to train them to take over where those who switched jobs left off.
Are we seeing a growing trend towards domestic tourism?
Sandra Carvao: We’re talking about 9 billion people travelling within their own countries. And in many countries, for example in Germany, more than 80% of the tourism spending actually comes from the domestic market, similarly in countries like Spain and even smaller economies. Whenever it's possible to travel again, domestic markets tend to be more resilient. They kick off first mostly due to perceptions of safety and security issues. As the world economy recovers from the pandemic, there is a good opportunity for nations to rethink their strategy, look at the domestic market in a different way, and leverage different products for domestic tourists.

When it comes to sustainable tourism, how quickly could we mainstream eco-friendly modes of transportation?
Sandra Carvao: Transport is one of the key contributors to energy impacts and tourism. But it's also important that we look at the whole value chain. The UNWTO together with the One Planet Sustainable Tourism Programme just launched the Glasgow Declaration, which includes green commitments from destinations and companies. We’re seeing a strong movement in the airline industry to reduce emissions. But I think, obviously, technological developments will be very important. But it's also very important to look at market shifts. And we can't forget small islands and developing states that rely on long-haul air travel. It’s important to make sure that we invest in making the problem much less impactful.
Liz Ortiguera: 'Travel and tourism' is such a broad encompassing term that it’s not fair to call it an industry: it is actually a sector of many industries. The pandemic taught us how broad the impact of the sector is in terms of sustainability. There's a big movement in terms of destination resilience, which is the foundation for achieving sustainability in the journey to net-zero. We now have standards to mitigate that impact including meetings-and-events (MIE) standards and standards for tour operators. There are multiple areas within our industry where progress is being made. And I'm really encouraged by the fact that there is such a focus not just within the sector but also among consumers.
This interview was first done at the World Economic Forum's studios in Geneva as part of 'Our World in Transformation' - a live interactive event series for our digital members. To watch all the episodes and join future sessions, please subscribe here .
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Travel and Tourism .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

How Japan is attracting digital nomads to shape local economies and innovation
Naoko Tochibayashi and Naoko Kutty
March 28, 2024

Turning tourism into development: Mitigating risks and leveraging heritage assets
Abeer Al Akel and Maimunah Mohd Sharif
February 15, 2024

Buses are key to fuelling Indian women's economic success. Here's why
Priya Singh
February 8, 2024

These are the world’s most powerful passports to have in 2024
Thea de Gallier
January 31, 2024

These are the world’s 9 most powerful passports in 2024

South Korea is launching a special visa for K-pop lovers
Retrospect, Inspire, and Learn
What is the role of tour operators in the tourism industry.

As a person working in the tourism field, I can confidentially say that the tourism industry has emerged as one of the most promising industries, with millions of people travelling across the country and internationally. There are numerous factors associated with a person’s need to travel, which may vary from business, leisure, medical purpose, or visiting a relative and friends. Taking care of your travel arrangements can be a cumbersome task, especially when you are exposed to a large number of online portals and offline agents boasting of exclusive packages and discounts. Here is where a tour operator comes to your rescue. He/she caters to all your travel needs, from taking care of documentation, money exchanges, hotel bookings, transportation, etc., to providing a seamless experience and a memorable time with your loved ones. During a discussion with Mr. Manoj Tulsani, CEO of Rayna Tours, we came up with some crucial points on the importance of travel and tourism.
Importance of Travel and Tourism
1) economic growth.
Tourism sparks economic growth in a region, thus helping local tourism recover. Countries where tourists visit the most get an influx of wealth from visitors coming in and spending on food, hotels, transport, activities, etc.
2) Gaining a New Perspective
This is something that I have personally experienced. When travelling, people expose themselves to various cultures, customs, religions, and lifestyles. Venturing into a new place can teach you more than any movie or book can.
3) Protecting the Environment
Many tour companies are becoming more conscious of the environmental implications of tourism by developing more socially responsible and environmentally friendly vacation packages.
By booking a tour, travelers can experience a foreign land and make sure that they visit the best spots. Here I have mentioned the role and functions of tour operators that aim to provide travelers with an ultimate travel experience.
Roles of a Tour Operator

While a tour operator’s role can vary depending upon their position and employer, these professionals are generally responsible for the following:
1) Creating Tour Packages
No one knows the travel destinations better than the tour operators. They are experts responsible for developing tour packages for individual customers or groups of travelers. They work with customers to understand their interests, thereby recommending a variety of attractions, modes of transportation, and accommodation options to help customers choose the tour package as per their requirements.
2) Prepare Travel Arrangements
Tour operators help arrange travel plans for customers so that they can easily reach their destinations. For e.g., they can book their train or flight tickets to help customers fly between cities or reserve a rental car so that customers can visit tourist attractions. All of your trip plans, including visa processing, hotel reservations, airport transfers, and travel insurance, are handled by them.
3) Budgeting the Tour Operations
Tour operators work with customers to help them prepare a budget for their tour. They develop different itineraries with varying prices and guide and advise their clients on attractions and accommodations within their preferred budgets.
4) Negotiating Rates
Tour operators negotiate rates with vendors, such as transportation companies and hotels and get the best deals for their clients. People travelling in large groups can benefit from this.
5) Providing Customer Support
A tour operator offers customer service to assist clients in preparing for their excursions. For instance, they may answer customer questions about a destination, provide information about currency exchange rates, or notify them about any changes in their itinerary.
6) Researching Travel Options
Tour operators research various travel options and provide recommendations to their clients about where to visit, stay, and eat during their tours. They gather the latest information about changing travel trends and provide their clients with the current information.
7) Providing a Safe and Enjoyable Tour
If you’re travelling somewhere for the first time, you probably want to know beforehand how safe it is for visitors. The help of tour operators is offered here, and they provide you with all the information you need. You’ll be able to keep away from any locations that might endanger your life. Tour guides ensure that you have a pleasurable and memorable experience with your family and friends in addition to attending to your safety concerns.
8) Providing Sustainable Tourism
Tour operators have a social responsibility to provide sustainable tour packages to reduce their negative impact while building a greener tourism industry. This includes focusing on creating benefits for local communities, protecting the environment through conservation projects, and giving priority to animal welfare.
Some More Responsibilities of a Tour Operator
- Use operations management skills
- Use sales and marketing skills
- Manage human resources
- Develop products
- Use financial management skills
- Directing visa application process
- Collaborating with the security staff, marketers, and venue operating teams
- Shipping requisite equipment to pertinent locations
- Remaining accessible to stakeholders
- Managing allotted finances
- Completing client-requested errands (within reasons)
Thus, I can conclude that tour operators play an important role in the success of the tourism industry. They contribute to the positive experiences that travelers across the world endure with their knowledge and expertise, allowing people to travel stress-free at a relatively reasonable price. Tourists can count on them to make their dream vacations a reality.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
C-Suite Concerns and Priorities for 2024
On the Bloomberg Businessweek podcast , BCG’s Global Chair Rich Lesser discusses the top priorities for CEOs today. He explains that their views on risk flipped over the past year: previously, fears of recession weighed the heaviest on CEOs’ minds; but now, geopolitics is their top concern. While C-suite executives have adapted to the many challenges posed by geopolitical conflicts, this was not always the norm. “We’ve almost come to expect this level of uncertainty and disruption and risk,” Lesser says.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
tourism, the act and process of spending time away from home in pursuit of recreation, relaxation, and pleasure, while making use of the commercial provision of services.As such, tourism is a product of modern social arrangements, beginning in western Europe in the 17th century, although it has antecedents in Classical antiquity.. Tourism is distinguished from exploration in that tourists ...
The tourism industry requires many facilities/ infrastructure to meet the needs of the tourist. This often means that many developments in an area as a result of tourism will be available for use by the locals also. Local people often gained new roads, new sewage systems, new playgrounds, bus services etc as a result of tourism. ...
The contribution of tourism to economic well-being depends on the quality and the revenues of the tourism offer. UN Tourism assists destinations in their sustainable positioning in ever more complex national and international markets. As the UN agency dedicated to tourism, UN Tourism points out that particularly developing countries ...
Tourism Industry: Everything You Need to Know About Tourism. What is the tourism industry? What is a tourist? What are the benefits of tourism?
Tourism Industry Definition and Significance In order to fully understand the tourism industry, we must start with the basics. What exactly is the tourism industry and what is its significance on a global scale. ... These events often take place in purpose-built convention centers, hotels with conference facilities, and event venues tailored ...
While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as "the ...
While tourism is the all-encompassing umbrella term for the activities and industry that create the tourist experience, the UNWTO (2020) defines travel as the activity of moving between different locations often for any purpose but more so for leisure and recreation (Hall & Page, 2006). On the other hand, hospitality can be defined as "the ...
1 Introduction. This chapter describes the main sectors within the travel, tourism and hospitality industries. It provides a good overview of the vertical and horizontal inter-relationships between different sectors. Firstly, this chapter describes the nature of tourism and the individuals' inherent motivations to travel.
About Us. The World Tourism Organization (UN Tourism) is the United Nations agency responsible for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism. As the leading international organization in the field of tourism, UN Tourism promotes tourism as a driver of economic growth, inclusive development and environmental ...
1.1 Introduction. This chapter describes the main sectors within the travel, tourism and hospitality industries. It provides a good overview of the vertical and horizontal inter-relationships between different sectors. Firstly, this chapter describes the nature of tourism and the individuals inherent motivations to travel.
Background. Tourism is one of the world's largest industries, and it has linkages with many of the prime sectors of the global economy (Fennell, 2020).As a global economic sector, tourism represents one of the largest generators of wealth, and it is an important agent of economic growth and development (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018).Tourism is a critical industry in many local and national ...
Tourism is vital for the success of many economies around the world. There are several benefits of tourism on host destinations. Tourism boosts the revenue of the economy, creates thousands of jobs, develops the infrastructures of a country, and plants a sense of cultural exchange between foreigners and citizens.
The scope of the travel and tourism industry is vast and ever-evolving. It encompasses a wide range of activities, services, and destinations that cater to the diverse needs and preferences of travelers. From leisure tourism and adventure travel to business trips and educational excursions, the industry offers something for everyone. ...
These are: tourist boards, travel services, accommodation services, conferences and events, attractions and tourism services. There are many components of tourism that make up the industry. Below, I will explain what each of the components offer to the tourism industry and provide some relevant examples.
In its broadest sense, tourism is defined as when people travel and stay in places outside of their usual environment for less than one consecutive year for leisure, business, health, or other ...
The tourism industry is a major contributor to the global economy and plays a significant role in the development of many countries. In this article, we will explore the purpose of tourism in detail. Exploring New Places and Experiences. One of the primary purposes of tourism is to explore new places and experiences.
An OTA is a travel website that specializes in providing travel services to customers including flights, hotels, car rentals, cruises, activities, and packages. These websites have in-built booking systems that allow users to instantly book. Some of the popular examples of OTAs are Expedia, Priceline and Orbitz.
Tourism is a multifaceted industry that caters to diverse interests and preferences. It allows people to unwind, learn, and grow by experiencing different cultures, landscapes, and cuisines. The purpose of tourism is not just limited to leisure and relaxation; it encompasses various aspects that contribute to personal and societal growth.
About UN Tourism. UN Tourism's leadership vision acknowledges the most pressing challenges facing tourism and identifies the sector's ability to overcome them and to drive wider positive change, including the opportunities responsible tourism offers for the advancement of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).. UN Tourism members have endorsed the Management Vision of the Secretary ...
Learn more about the travel and tourism industries, their differences, and the sectors within those industries.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States ...
In 2020 alone, the travel and tourism sector lost $4.5 trillion and 62 million jobs globally. But as the world recovers from the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, travel and tourism can bounce back as an inclusive, sustainable, and resilient sector. Two experts highlight some of the key transformations in the sector going forward during the ...
The implementation of smart technologies in the tourism industry has become a new trend. This is aimed at enriching tourists' experiences and improving their satisfaction. The purpose of the present paper is to enhance tourists' experiences and to increase tourists' satisfaction using smart technologies and to identify experts' perspectives regarding the use of these technologies.
Some More Responsibilities of a Tour Operator. Use operations management skills. Use sales and marketing skills. Manage human resources. Develop products. Use financial management skills. Directing visa application process. Collaborating with the security staff, marketers, and venue operating teams.
The industry has suffered an unprecedented shock. BCG collaborates with travel and tourism providers as they navigate this turbulence and build resilience for the future. Visit Page. Within Travel and Tourism ... Excavating purpose is among the rewarding journeys companies can take. BCG BrightHouse helps organizations embrace purpose to achieve ...
The purpose of the article is to theoretically study the global automotive industry as an object of tourist interest. The methodology is based on scientific and special research methods. The used methods were analysis, synthesis, systematization, classification, generalization of economic and methodological literature as well as and scientific publications.