

Shackleton’s Journey – Planning Overview
Written by Dan
Last updated March 8, 2024
The story of Ernest Shackleton’s incredible journey has captivated audiences for over a century. An endurance feat like no other, the famous Antarctic explorer faced impossible odds and unfathomable perils to survive his remarkable voyage – but with strong leadership, carefully crafted plans, and an unwavering determination, he ultimately gave future generations a heroic tale of resilience that still resonates today.
For teachers looking to introduce this extraordinary story in their classrooms, it can seem overwhelming to cover such an expansive topic effectively.
However, by breaking down the essential elements of Shackleton’s journey into manageable planning points, you, too, can traverse the icy terrain and deliver an inspiring lesson your students will never forget!
Related : For more, check out our article on Harry The Poisonous Centipede here.
Table of Contents
Shackleton’s Journey by William Grill
Shackleton’s journey is a beautiful and inspiring children’s book written and illustrated by William Grill. The book tells the story of Sir Ernest Shackleton and his crew as they set out on a dangerous expedition to cross Antarctica in 1914.
The journey began when Shackleton and his men sailed from England on the ship Endurance. They encountered many challenges, including treacherous weather conditions, thick ice, and hungry polar bears. Despite these obstacles, they persevered and continued on their journey.
However, disaster struck when the Endurance became trapped in ice for months. The crew was forced to abandon the ship and camp on an ice floe. They had limited supplies and were far from any civilization.
Despite these dire circumstances, Shackleton remained optimistic and determined to save his men. He led rescue missions over several months, braving freezing temperatures and dangerous terrain to reach safety.
All of Shackleton’s men survived thanks to his leadership and determination. The story of Shackleton’s Journey is a testament to the human spirit, showing that even in the face of extreme adversity, we can find hope and strength within ourselves.
Critical Themes In Shackleton’s Journey
Perseverance:.
This theme is evident throughout the story as Shackleton, and his crew face numerous challenges on their journey, including treacherous weather conditions, thick ice, and hunger. Despite these obstacles, they continue their mission, showing remarkable perseverance and determination.
Leadership:
Shackleton’s leadership skills are on full display in this story. He remains calm and focused even in the most challenging situations, inspiring his men to follow him and trust his decision-making abilities. His leadership ultimately leads to the successful rescue of his crew members.
The Endurance crew must work together to survive in harsh conditions with limited resources. They rely on each other for support and encouragement, demonstrating the importance of teamwork in achieving a common goal.
Even when faced with seemingly insurmountable challenges, Shackleton never loses hope that he will be able to save his men. His unwavering optimism inspires those around him to keep going despite the odds.
Resilience:
The crew demonstrates incredible resilience as they endure months of living on an ice floe with limited supplies and uncertain prospects for rescue. They find ways to adapt to their circumstances and persevere through difficult times.
Main Characters in Shackleton’s Journey
Here are the main characters in Shackleton’s Journey:
- Sir Ernest Shackleton – The expedition’s leader and the story’s protagonist.
- Frank Hurley – The photographer who documents the journey through photographs.
- Tom Crean – A skilled seaman who becomes one of Shackleton’s most trusted men.
- Frank Worsley – The captain of the Endurance, responsible for navigating the ship through treacherous waters.
- The crew of the Endurance – A group of 27 men from various countries who join Shackleton on his journey to cross Antarctica.
Teaching Opportunities
The story of Shackleton’s Journey can be an excellent tool for improving children’s writing skills in several ways:
- Vocabulary: The story is rich with descriptive language and technical terms related to sailing and exploration, which can help expand children’s vocabulary. Please encourage students to identify unfamiliar words and look up their meanings.
- Character development: The characters in the story are well-developed and complex, allowing students to analyze their motivations, actions, and relationships. Students can practice describing character traits and using evidence from the text to support their claims.
- Narrative structure: The story follows a clear narrative arc with a beginning, middle, and end. Students can study how the author builds tension and suspense throughout the story, using foreshadowing, imagery, and pacing techniques.
- Persuasive writing: Shackleton was known for his ability to inspire his crew members even in the most challenging circumstances. Students can analyze his leadership style and practice writing persuasive essays or speeches to motivate others toward a common goal.
- Research skills: The story of Shackleton’s Journey is based on actual events, providing an opportunity for students to conduct research on topics such as Antarctic exploration, sailing technology, or the history of polar expeditions. They can use this research to enhance their understanding of the story and incorporate factual information into their writing.
Key Vocabulary
Here are some key vocabulary words that children may encounter when reading Shackleton’s Journey, along with their definitions:
- Expedition – A journey or voyage taken for a specific purpose, often involving exploration or research.
- Antarctica – The southernmost continent on Earth, known for its extreme cold and ice-covered landscapes.
- Endurance – The name of the ship that Shackleton and his crew sailed on their expedition to Antarctica.
- Iceberg – A large piece of ice floating in the ocean, often dangerous to ships because it can be challenging to see.
- Navigation – The process of planning and directing the course of a ship or other vehicle.
- Arctic – The region around the North Pole, characterized by extreme cold and frozen landscapes.
- Sledging – Traveling over snow and ice using a sled pulled by dogs or humans.
- Blubber – A layer of fat beneath the skin of marine mammals, such as whales, used as a fuel source by Arctic explorers.
- Aurora Australis – Also known as the Southern Lights, a natural phenomenon where colourful lights appear in the sky over Antarctica due to solar activity.
By becoming familiar with these key vocabulary words, children will be better equipped to understand and appreciate Shackleton’s Journey story while expanding their language skills.
Lesson Plans
Lesson plan 1:.
Vocabulary Development Objective: Students can identify and define key vocabulary words from Shackleton’s Journey.
Materials Needed:
- Copies of Shackleton’s Journey or access to the text online
- Whiteboard or chart paper
- Introduce students to the concept of key vocabulary words, explaining that these are important words that they may frequently encounter in a particular text.
- Provide students with a list of key vocabulary words from Shackleton’s Journey (or have them create their own list as they read).
- Have students work in pairs or small groups to research the definitions of each word using dictionaries or online resources.
- As a class, discuss each word and its purpose, recording them on the whiteboard or chart paper.
- Please encourage students to use these words in writing and discussing the text.
Assessment:
Have students write short paragraphs using several key vocabulary words from Shackleton’s Journey, demonstrating their understanding of their meanings.
Lesson Plan 2:
Character Analysis Objective: Students will be able to analyze and describe characters from Shackleton’s Journey.
- Graphic organizers for character analysis (such as a character web or Venn diagram)
- Introduce students to character analysis, explaining that this involves studying a character’s traits, motivations, and relationships with other characters in a story.
- Please choose one or more characters from Shackleton’s Journey for students to analyze (such as Shackleton himself, Frank Worsley, or Tom Crean).
- Provide students with graphic organizers for character analysis and have them fill in details about each character based on evidence from the text.
- As a class, discuss each character and compare/contrast their traits and actions with those of other characters.
- Please encourage students to use what they’ve learned about these characters when writing about leadership, teamwork, or perseverance themes.
Have students write short essays describing one character from Shackleton’s Journey and how he contributed to the expedition’s success (or failure).
Lesson Plan 3:
Research Skills Objective: Students can research topics related to Antarctica exploration and incorporate this information into their writing.
- Computers with internet access
- Research prompts/questions related to Antarctica exploration
- Introduce students to some basic facts about Antarctica (location, climate, wildlife) and explain why it is an important area for scientific research.
- Provide students with research prompts/questions related to Antarctic explorers (Shackleton, Amundsen), sailing technology used during polar expeditions, or modern-day scientific research conducted in Antarctica.
- Have students work independently or in pairs/small groups using computers and online resources (such as National Geographic Kids) to research their chosen topic(s).
- Please encourage students to take notes on essential facts/details they discover during their investigation.
- Have students incorporate this information into their writing about Shackleton’s Journey – for example, by including historical context/background information at the beginning of an essay or incorporating scientific findings into a persuasive speech advocating for further exploration of Antarctica.
Have students present summaries of their research findings along with examples of how they incorporated this information into their writing about Shackleton’s Journey
Website Resources
Literacy Shed Plus: “Shackleton’s Journey” by William Grill This website offers a comprehensive set of resources for teaching Shackleton’s Journey, including lesson plans, activities, and worksheets. The resources are organized by key themes such as exploration, survival, and leadership. There are also links to relevant videos and websites for further research.
Link: https://www.literacyshedplus.com/en-us/resource/shackleton-s-journey-by-william-grill-en-gb
TES: 22-Lesson English Unit – Shackleton’s Journey by William Grill (Year 4/5/6) This resource provides a detailed unit plan for teaching Shackleton’s Journey throughout 22 lessons. The lessons are designed to cover a range of skills, including reading comprehension, writing, and speaking/listening. Each class includes learning objectives, activities, and assessment opportunities.
Link: https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/22-lesson-english-unit-shackleton-s-journey-by-william-grill-year-4-5-6-english-planning-12691208
Teachwire: KS2 Book Topic – Shackleton’s Journey This website offers a brief overview of Shackleton’s journey and some ideas for related activities and discussion topics. It includes suggestions for incorporating the book into cross-curricular studies such as history and geography.
Link: https://www.teachwire.net/news/ks2-book-topic-shackletons-journey/
Q: What age group is Shackleton’s Journey suitable for?
A: The book is generally recommended for children in grades 4-6 but can also be adapted for younger or older students.
Q: What critical themes in the book can be explored in the classroom?
A: Some key themes include exploration, leadership, perseverance, teamwork, and survival.
Q: Are there any films or videos that can supplement the book?
A: Yes! There are several documentaries about Shackleton’s expedition that can provide additional context and visuals. “Endurance” and “Shackleton” are two popular options.
Q: How can I incorporate writing into my lessons on Shackleton’s Journey?
A: There are many opportunities for writing throughout the book. For example, students could write journal entries from the perspective of one of the crew members, create persuasive speeches advocating for different courses of action during the journey, or write reflective essays on what they learned from reading about this historic expedition.
Q: Can Shackleton’s Journey be used to teach other subjects besides English/Language Arts?
A: Absolutely! The book relates to many other subjects, such as history (exploration and polar expeditions), geography (mapping and climate), science (biology and ecology), and even math (calculating distances and supplies needed).
Q: How long does teaching a unit on Shackleton’s Journey typically take?
A: This will depend on how much time you have available in your curriculum. Some teachers may focus only on certain aspects of the book over a few days or weeks, while others may plan a more extended unit lasting several months.
Q: Are any online resources available to help me plan my lessons on Shackleton’s Journey?
A: Yes! Several websites offer lesson plans, activities, videos, and other resources related to teaching this book. Examples include Literacy Shed Plus, TES, and Teachwire (links provided in this article).
Related Posts

About The Author
I'm Dan Higgins, one of the faces behind The Teaching Couple. With 15 years in the education sector and a decade as a teacher, I've witnessed the highs and lows of school life. Over the years, my passion for supporting fellow teachers and making school more bearable has grown. The Teaching Couple is my platform to share strategies, tips, and insights from my journey. Together, we can shape a better school experience for all.

Join our email list to receive the latest updates.
Add your form here

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Student blogs and videos
- Why Cambridge
Qualifications directory
- How to apply
- Fees and funding
- Frequently asked questions
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Visiting the University
- Term dates and calendars
- Video and audio
- Find an expert
- Publications
- International Cambridge
- Public engagement
- Giving to Cambridge
- For current students
- For business
- Colleges & departments
- Libraries & facilities
- Museums & collections
- Email & phone search
- Graduate Admissions
- Prospective Graduate Students
Studying at Cambridge

Department of Geography , University of Cambridge
document.addEventListener ('DOMContentLoaded', function () { const heading = document.querySelectorAll ('#content h1'); if (heading.length) { document.getElementById ('pagetitledynamic').innerHTML = heading[0].innerHTML; } });
- Scott Polar Research Institute
- Polar Archives
- Our collection
- Using the archive
- Adding to our collection
- Book a research visit
- Search the archive catalogue
- Publication / commercial use
- Access policy
- Exploration diaries
Shackleton items from the Archives
- Oral History project
- Courses by Title/Subject
- Courses by Department/Faculty/Institute
- Glossary of Awards
You are not currently logged in
Ernest Shackleton's Endurance diary, 1915
![shackleton's journey diary entry [Click for larger image in a new window]](https://www.spri.cam.ac.uk/archives/shackleton/images/p3291845.jpg)
© SPRI
More and larger images below
Expedition: Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition Author: Ernest Shackleton (1874 - 1922) Date of article: 1915 - 30/Dec/1915
Reference number: 1537/3/8; BJ
In August 1914 Ernest Shackleton and a crew of twenty seven set sail for the Antarctic in an attempt to cross the continent on foot. Disaster struck when Endurance was trapped fast in the pack ice, just eighty five miles from their destination. The ship was crushed like matchwood by the pressure, leaving the crew stranded on an ice floe. With three life boats and provisions salvaged from the sinking ship, Shackleton led the men to safety. The ordeal lasted 20 months. Shackleton kept this diary during the months spent marooned on the ice.
27 October 1915. The end came at last about 5pm - she was doomed, no ship built by human hands could have withstood the strain - I ordered all hands on to the floe and as the floe near us was cracking we started to sledge all the gear.
30 October 1915 Snowy high temps all wet Worsley self prospected, found way to fine safe old floe Broke camp 2. I lead pioneer party to break down pressure driftng and snowing hard: reach old floe 4 pm Too thick to see ahead camp dogs splendid 2 teams pull one boat keep Caird's photo dogs relay other sledges have 10 sledges 2 Boats. Weather clearing 6pm wind NE ship still above water and 26 _ All cheerful shoot seal good hoosh this floe really is strong _ Many look on this as _ it is better so Hurley splendid in fact all Wild same.
All photographs from this article
Larger image
![shackleton's journey diary entry [Click for larger image in a new window]](https://www.spri.cam.ac.uk/archives/shackleton/images/p3291778.jpg)
- About this site
- Site privacy & cookie policies
- Login with Raven
- Page last updated: 8th March 2024 by Webmaster
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- University A-Z
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Terms and conditions
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Spotlight on...
- About research at Cambridge
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
The Stunning Survival Story of Ernest Shackleton and His Endurance Crew
By: Kieran Mulvaney
Updated: May 2, 2024 | Original: October 21, 2020

All year, the ship had been trapped, ice pushing and pinching the hull, the wood howling in protest. Finally, on October 27, 1915, a new wave of pressure rippled across the ice, lifting the ship’s stern and tearing off its rudder and its keel. Freezing water began to rush in.
“She’s going, boys,” came the cry. “It’s time to get off.”
From the moment Ernest Shackleton and his crew aboard the British expedition ship, HMS Endurance had become immobilized in Antarctica's ice 10 months earlier, they had been preparing for this moment. Now, those on board removed their last remaining belongings from the ship and set up camp on the ice. Twenty-five days later, what remained of the wreck convulsed once more, and the Endurance disappeared beneath the ice.
Incredibly, all 27 men under Shackleton's command would survive the grueling Antarctic expedition, but their ship remained sunk and lost to history—until 106 years later.
On March 9, 2022, a team of scientists and adventurers announced they had finally located what remained of the Endurance at the bottom of Antarctica's Weddell Sea. The team made the discovery using submersibles and undersea drones and released stunning photos of the long-lost wooden ship where it had lodged in the seabed nearly 10,000 feet deep in clear and icy waters.
Endurance Is Locked in by Ice

Endurance had left South Georgia for Antarctica on December 5, 1914, carrying 27 men (plus one stowaway, who became the ship’s steward), 69 dogs, and a tomcat erroneously dubbed Mrs. Chippy. The goal of expedition leader Shackleton, who had twice fallen short—once agonizingly so—of reaching the South Pole, was to establish a base on Antarctica’s Weddell Sea coast.
From there a small party, including himself, would set out on the first crossing of the continent, ultimately arriving at the Ross Sea, south of New Zealand, where another group would be waiting for them, having laid depots of food and fuel along the way.
Two days after leaving South Georgia, Endurance entered the pack ice—the barrier of thick sea ice that stands guard around the Antarctic continent. For several weeks, the ship poked and prodded its way through leads in the ice, gingerly making its way south; but on January 18, a northerly gale pressed the pack hard against the land and pushed the floes tight against each other. Suddenly, there was no way forward, nor any way back. Endurance was beset—in the words of one of the crew, Thomas Orde-Lees, “frozen like an almond in the middle of a chocolate bar.”
They had been within a day’s sailing of their landing place; now the drift of the ice was slowly pushing them farther away with each passing day. There was nothing else to do but to establish a routine and wait out the winter.
Shackleton wrote Alexander Macklin, one of the ship’s surgeons, “did not rage at all, or show outwardly the slightest sign of disappointment; he told us simply and calmly that we must winter in the Pack; explained its dangers and possibilities; never lost his optimism and prepared for winter.”
In private, however, he revealed greater foreboding, quietly expressing to the ship’s captain, Frank Worsley, one winter’s night that, “The ship can’t live in this, Skipper … It may be a few months, and it may be only a question of weeks or even days … but what the ice gets, the ice keeps.”
Survival on an Ice Floe

In the time that passed between abandoning Endurance and watching the ice swallow it up completely, the crew salvaged as many provisions as they could, while sacrificing anything and everything that added weight or would consume valuable resources— including bibles, books, clothing, tools and keepsakes. Some of the younger dogs, too small to pull their weight, were shot, as was, to the chagrin of many, the unfortunate Mrs. Chippy.
The initial plan was to march across the ice toward land, but that was abandoned after the men managed just seven and a half miles in seven days. “There was no alternative,” wrote Shackleton, “but to camp once more on the floe and to possess our souls with what patience we could till conditions should appear more favorable for a renewal of the attempt to escape.” Slowly and steadily, the ice drifted farther to the north; and, on April 7, 1916, the snow-capped peaks of Clarence and Elephant Islands came into view, flooding them with hope.
“The floe has been a good friend to us,” wrote Shackleton in his diary, “but it is reaching the end of its journey, and is liable at any time now to break up.”
On April 9, it did just that, splitting beneath them with an almighty crack. Shackleton gave the order to break camp and launch the boats, and all at once, they were finally free of the ice that had alternately bedeviled and supported them.
Now they had a new foe to contend with: the open ocean. It threw freezing spray in their faces and tossed frigid water over them, and it batted the boats from side to side and brought brave men to the fetal position as they battled the elements and seasickness.
Through it all, Captain Worsley navigated through the spray and the squalls, until after six days at sea, Clarence and Elephant Islands appeared just 30 miles ahead. The men were exhausted. Worsley had by that stage not slept for 80 hours. And while some were crippled by seasickness, others were wracked with dysentery. Frank Wild, Shackleton’s second-in-command, wrote that “at least half the party were insane.” Yet they rowed resolutely toward their goal, and on April 15, they clambered ashore on Elephant Island.

Marooned on Elephant Island
It was the first time they had been on dry land since leaving South Georgia 497 days previously. But their ordeal was far from over. The likelihood of anybody coming across them was vanishingly small, and so after nine days of recuperation and preparation, Shackleton, Worsley and four others set out in one of the lifeboats, the James Caird, to seek help from a whaling station on South Georgia, more than 800 miles away.
For 16 days, they battled monstrous swells and angry winds, baling water out of the boat and beating ice off the sails. “The boat tossed interminably on the big waves under grey, threatening skies,” recorded Shackleton. “Every surge of the sea was an enemy to be watched and circumvented.” Even as they were within touching distance of their goal, the elements hurled their worst at them: “The wind simply shrieked as it tore the tops off the waves,” Shackleton wrote. “Down into valleys, up to tossing heights, straining until her seams opened, swung our little boat.”
The next day, the wind eased off and they made it ashore. Help was almost at hand; but this, too, was not the end. The storms had pushed the James Caird off course, and they had landed on the other side of the island from the whaling station. And so Shackleton, Worsley and Tom Crean set off to reach it by foot—climbing over mountains and sliding down glaciers, forging a path that no human being had ever forged before, until, after 36 hours of desperate hiking, they staggered into the station at Stromness.
'My Name Is Shackleton'
There was no conceivable circumstance under which three strangers could possibly appear from nowhere at the whaling station, and certainly not from the direction of the mountains. And yet here they were: their hair and beards stringy and matted, their faces blackened with soot from blubber stoves and creased from nearly two years of stress and privation.
And old Norwegian whaler recorded the scene when the three men stood before the station manager Thoralf Sørlle:
“Manager say: ‘Who the hell are you?’ And the terrible bearded man in the center of the three say very quietly: ‘My name is Shackleton.’ Me – I turn away and weep.”
Rescue Mission to Elephant Island

Once the other three members of the James Caird had been retrieved, attention turned to rescuing the 22 men remaining on Elephant Island. Yet, after all that had gone before, this final task in many ways proved to be the most trying and time-consuming of all. The first ship on which Shackleton set out ran dangerously low on fuel while trying to navigate the pack ice, and was forced to turn back to the Falkland Islands. The government of Uruguay proffered a vessel that came within 100 miles of Elephant Island before being beaten back by the ice.
Each morning on Elephant Island, Frank Wild, whom Shackleton had left in charge, issued the call for everyone to “Lash up and stow” their belongings. “The Boss may come today!” he declared daily. His companions grew increasingly dispirited and doubtful. “Eagerly on the lookout for the relief ship,” recorded Macklin on August 16, 1916. “Some of the party have quite given up hope of her coming.” Orde-Lees was clearly one of them. “There is no good in deceiving ourselves any longer,” he wrote.
But Shackleton procured a third ship, the Yelcho, from Chile; and finally, on August 30, 1916, the saga of the Endurance and its crew came to an end. The men on the island were settling down to a lunch of boiled seal’s backbone when they spied the Yelcho just off the coast. It had been 128 days since the James Caird had left; within an hour of the Yelcho appearing, all ashore had broken camp and left Elephant Island behind. Twenty months after setting out for the Antarctic, every one of the Endurance crew was alive and safe.

While Shackleton's crew miraculously made it back to England, his ship did not. For more than a century, the Endurance remained among history's most elusive shipwrecks. But in 2022, an international team of marine archaeologists, explorers and scientists located the Endurance at the bottom of the Weddell Sea, approximately four miles south of the position originally recorded when Endurance sank.
“We have made polar history with the discovery of Endurance, and successfully completed the world’s most challenging shipwreck search,” said John Shears , the leader of Endurance22, the expedition team that used submersibles and drones to locate the wooden ship.
Photos released from the Endurance22 expedition revealed the sunken, three-masted ship in mesmerizing detail, including an image of its stern where its name "ENDURANCE" was visible above a five-pointed star.
Shackleton's Early Death

Ernest Shackleton never did reach the South Pole or crossed Antarctica. He launched one more expedition to the Antarctic, but the Endurance veterans who rejoined him noticed he appeared weaker, more diffident, drained of the spirit that had kept them alive. On January 5, 1922, with the ship at South Georgia, he had a heart attack in his bunk and died. He was just 47.
With his death, Wild took the ship to Antarctica; but it proved unequal to the task, and after a month spent futilely attempting to penetrate the pack, he set a course for Elephant Island. From the safety of the deck, he and his comrades peered through binoculars at the beach where so many of them had lived in fear and hope.
“Once more I see the old faces & hear the old voices—old friends scattered everywhere,” wrote Macklin. “But to express all I feel is impossible.”
And with that, they turned north one last time and went home.
Alexander, Caroline, The Endurance: Shackleton’s Legendary Antarctic Expedition ( Alfred A. Knopf , 1998) Heacox, Kim, Shackleton: The Antarctic Challenge ( National Geographic Society, 1999) Huntford, Roland, Shackleton ( Hodder & Stoughton, 1985) Lansing, Alfred, Endurance: Shackleton’s Incredible Voyage ( Perseus Books , 1986) Shackleton, Ernest, South ( Macmillan , 1920) Worsley, F.A., Shackleton’s Boat Journey ( Hodder & Stoughton, 1940)

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Shackleton’s Journey: A Lovely Illustrated Chronicle of History’s Most Heroic Polar Expedition
By maria popova.

In August of 1914, legendary British explorer Ernest Shackleton led his brave crew of men and dogs on a journey to the end of the world — the enigmatic continent of Antarctica. That voyage — monumental both historically and scientifically — would become the last expedition of the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, which stretched from 1888 to 1914. From Flying Eye Books — the children’s book imprint of British indie press Nobrow, which gave us Freud’s comic biography , Blexbolex’s brilliant No Man’s Land and some gorgeous illustrated histories of aviation and the Space Race — comes Shackleton’s Journey ( public library ), a magnificent chronicle by emerging illustrator William Grill , whose affectionate and enchanting colored-pencil drawings bring to life the legendary explorer and his historic expedition.

As Grill tells us in the introduction, Shackleton was a rather extraordinary character:
Shackleton was the second of ten children. From a young age, Shackleton complained about teachers, but he had a keen interest in books, especially poetry — years later, on expeditions, he would read to his crew to lift their spirits. Always restless, the young Ernest left school at 16 to go to sea. After working his way up the ranks, he told his friends, “I think I can do something better, I want to make a name for myself.”
And make it he did. Reflecting on the inescapable allure of exploration, which carried him through his life of adventurous purpose, Shackleton once remarked:
I felt strangely drawn to the mysterious south. I vowed to myself that some day I would go to the region of ice and snow, and go on and on ’til I came to one of the poles of the Earth, the end of the axis on which this great round ball turns.

From the funding and recruitment of the famed expedition, to the pioneering engineering of the Endurance ship, to the taxonomy of crew members, dogs, and supplies, Grill traces Shackleton’s tumultuous journey from the moment the crew set sail to their misfortune-induced change of plans and soul-wrenching isolation “500 miles away from the nearest civilization” to their eventual escape from their icy prison and salvation ashore Elephant Island.

As a lover of dogs and visual lists , especially illustrated lists and dog-themed illustrations , I was especially taken with Grill’s visual inventories of equipment and dogs:

Despite the gargantuan challenges and life-threatening curveballs, Shackleton’s expedition drew to a heroic close without the loss of a single life. It is a story of unrelenting ambition to change the course of history, unflinching courage in the face of formidable setbacks, and above all optimism against all odds — the same optimism that emanates with incredible warmth from Grill’s tender illustrations.

Years later, Shackleton himself captured the spirit that carried them:
I chose life over death for myself and my friends… I believe it is in our nature to explore, to reach out into the unknown. The only true failure would be not to explore at all.
Shackleton’s Journey is an absolute treasure. Complement it with Rachel Sussman’s journey in Shackleton’s footsteps .
Images courtesy of Nobrow
— Published February 26, 2014 — https://www.themarginalian.org/2014/02/26/shackletons-journey-william-grill-nobrow/ —

www.themarginalian.org

PRINT ARTICLE
Email article, filed under, books children's books ernest shackleton history illustration nobrow william grill, view full site.
The Marginalian participates in the Bookshop.org and Amazon.com affiliate programs, designed to provide a means for sites to earn commissions by linking to books. In more human terms, this means that whenever you buy a book from a link here, I receive a small percentage of its price, which goes straight back into my own colossal biblioexpenses. Privacy policy . (TLDR: You're safe — there are no nefarious "third parties" lurking on my watch or shedding crumbs of the "cookies" the rest of the internet uses.)
Shackleton’s Endurance Expedition Centenary
Archives hub feature for october 2015.
Browse all descriptions relating to the Antarctic on the Archives Hub.
On the 27 th October 1915 Antarctic expedition ship Endurance was abandoned on the orders of Sir Ernest Shackleton. The ship had been stuck in the ice since 18 th January at the mercy of the currents of the Weddell Sea. The ship sank on 21 November leaving the men thousands of miles from home and Shackleton’s dream of being the first to cross the Antarctic continent via the South Pole in tatters.
The Endurance had sailed from England just as war was declared in August 1914, Shackleton had offered the ship and her crew to to the Admiralty but the response was that the expedition should proceed as planned. Sailing via Madeira and Buenos Aires the Endurance made her final port of call at the whaling stations of South Georgia.
Sir Ernest Shackleton, the expedition leader was no stranger to the Antarctic; he had been a member of Captain Scott’s first expedition in 1901-04 before leading his own expedition in 1907-09. That second expedition had seen him come to within 100 miles of the South Pole before making the difficult decision to turn back rather than risk the lives of his men further. In the intervening years the Norwegian Roald Amundsen had led the first team to reach the pole in 1911 and Captain Scott and his companions had perished on their own return journey in 1912.
Shackleton’s plan was to land a party of men, dogs and supplies on the Weddell Sea side of the continent and travel across uncharted territory to the South Pole. Here he would then follow Captain Scott’s journey before picking up the route he had taken back in 1908 to reach the Ross Sea. While he was making his attempt from a second party would lay depots of food and fuel across the Ross Ice Shelf towards the pole along that route for his crossing party to pick up.
When the Endurance was crushed in the ice of the Weddell Sea the expedition changed from one of exploration to one of survival. The men camped on the sea ice, from October 1915 through to April 1916. When the ice broke up around them they took to the three small lifeboats and spent a week at sea before reaching Elephant Island, their first dry land since leaving South Georgia. This uninhabited island was only a temporary salvation. With no means of contacting the outside world the expedition had to save themselves.
Sheltering under the upturned hulls of two of the boats the majority of the crew lived on the Island for five months. Meanwhile Shackleton and a five man crew sailed across the southern ocean in the third boat – the James Caird – to South Georgia. Shackleton, Worsley and Crean were then forced to undertake a 36 hour walk across the uncharted island to raise the alarm. The three walked into the Stromness whaling station on the 20 th May 1916. It took four attempts to rescue the men left behind on Elephant Island, all of whom were successfully rescued in August 1916.
Throughout the expedition Shackleton and his men kept up their diaries. These precious volumes were preserved when so much was abandoned with the ship. Writing in pencil, sometimes on scraps of paper sewn together, the diaries provide the personal account of what the men went through.
Miss Naomi Boneham Archives The Thomas H Manning Polar Archives Scott Polar Research Institute University of Cambridge
Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton collection on the Archives Hub: http://archiveshub.ac.uk/data/gb15-sirernesthenryshackleton
Browse other collections of the Scott Polar Research Institute, University of Cambridge on the Archives Hub .
All images copyright the Scott Polar Research Institute, University of Cambridge, and reproduced with the kind permission of the copyright holder .
- Child Protection & Safeguarding Policy
- A Happy Place to Learn and Play
- Our Vision and Values
- History of Our School
- Sports Funding
- Pupil Premium
- COVID-19 Catch-up Premium Spending – 2020
- Financial Information
- School Assessment
- Continuous Provision in Year 1 & 2
- Most recent Ofsted report
- School Policies
- Our Governors
- School Council
- St Michael’s Aldbourne PTA
- Christian Distinctiveness
- Spirituality
- Loved by God and those around us
- “The Boy in the Temple” Luke 2:41-52
- Collective Worship
- SIAMS Report
- Our Curriculum
- Special Educational Needs and Disabilities (SEN/D)
- Forest School
- Residential Trips & Visits
- Willows After School Club
- Aldbourne Pre-school
- Online Continuous Provision Showcase
- Forest School Level 3 Leader Course
- Continuous Provision Courses
- Acorn (Reception)
- Hazel (Year One)
- Birch (Year Two)
- Cherry (Year Three)
- Elder (Year Four)
- Rowan (Year Five)
- Oak (Year Six)
- St Michael’s Weekly Post and Letters
- Useful Contacts and Forms
- Useful Links
- Leave of Absence
- School Welcome Pack
- School Uniform
- Getting to School
- Breakfast Club
- Our School Day
- Eating in School
- Volunteering
- Parent View
- Emergency School Closure
- Online Safety
- Remote Education Provision
- Virtual Tour
- PTA Tickets
- Nativity 2020

- Child Protection & Safeguarding
- Most Recent Ofsted Report
- Respect, Honesty and Love
Key Stage 1
Key stage 2, communication, useful information, forms & links, prospective parents.
- Courses for Teachers
Shackleton’s Diary by Oak Class.

In English, we have been looking at ‘Shackleton’s Journey’ by William Grill. The children wrote three diary entries from Ernest Shackleton’s point of view, at different stages of his expedition to Antarctica.
Here are just a few examples, of their amazing writing.

In Art, we were looking at and creating ‘patterns’. A simple but very effective technique which resulted in some lovely patterns.

In Geography, we are looking at ‘latitude’ and how moving nearer to the Equator can affect climate.

And the list goes on!
We are super proud of how well ‘Oak Class’ are doing and the quality of your work. Keep it up! You are all amazing.
- Uncategorized , Year 6 , History
- Birch class explore food!
- Hazel Class: Super Science and more…

Recent Posts
- Platinum award for OPAL play!
- Sculptors in Hazel Class!
- Plasticine Animals- Cherry Class
- Rowan explore chemistry!
- Architecture in Birch Class!
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- February 2018
- September 2017
- Uncategorized
- St Michael's Post
- Religious Education
- School News
- Celebration Assemblies
- Fundraising
- Physical Education
- Design and Technology
St Michael’s C of E VA Primary School
Back Lane, Aldbourne, Wiltshire SN8 2BP 01672 540 434 [email protected]

© Copyright 2024 St Michael’s C of E (Aided) School, Aldbourne.

- Ernest Shackleton
- The Expedition
- Why Twitter?
- The Trailer
Diary entries

Diary page, Ernest Shackleton
“Everyone is keeping a diary now. There was so little incident from day to day in the ship that very few of us thought it worthwhile.”
— Thomas Orde-Lees

[images from SPRI ]
Share this:
About Ernest Shackleton
- Search for:
What is this?
From @eshackleton:, recent posts.
- Shackleton’s grave, Grytviken, South Georgia
- A wonderful evening
- All aboard the Quest
- The fate of the crew
- September 2016
- August 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- November 2012
- October 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- RSS - Posts
- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

Username or E-mail
Remember Me
Shackleton’s Journey
Home » Book Resources » Lower Key Stage 2 » Shackleton’s Journey

Shackleton's Journey by William Grill
In the last days of the Heroic Age of Exploration, Ernest Shackleton dreamed of crossing the frozen heart of Antarctica, a place of ferocious seas, uncharted mountains and bone-chilling cold. But when his ship, the Endurance became trapped in the deadly grip of the ice, Shackleton’s dreams were shattered. Stranded in a cold, white world, and thousands of miles from home, the men of the expedition set out on a desperate trek across the ice in search of rescue.
Shackleton’s Journey is the true story of how Shackleton and his crew managed to survive this epic adventure, and a testament to their great courage and endurance.

Main Focus: Alphabetical Order
This activity focuses on pages 7-8 of the book and alphabetical order.
In 1914, 99 dogs were sent from Canada to London. 69 of these dogs were then chosen for the expedition. They gave them all names; and some were named after famous people and members of the crew.
Some of the names were:
Wolf, Sooty, Paddy, Chips, Tim, Dismal, Bob, Martin, Hercules, Noel, Jamie, Alti, Jasper and Roy.
Your Year 3 / Year 4 class will put some of the names into alphabetical order.

Main Focus: Past and Present Tense
This activity focuses on pages 14-24 of the book and tense.
Your LKS2 class will identify verbs in the sentences that have been chosen from the Shackleton’s Journey book and identify whether they are past or present tense.

Main Focus: Vocabulary Extension - Pages 4-28
In this resource, your class will explore some of the challenging vocabulary from pages 4-28 of the book.
Your class will use the words bank to complete the sentences.
We have differentiated this a number of ways and your class can even do an extension activity of looking up definitions, synonyms, antonyms etc.
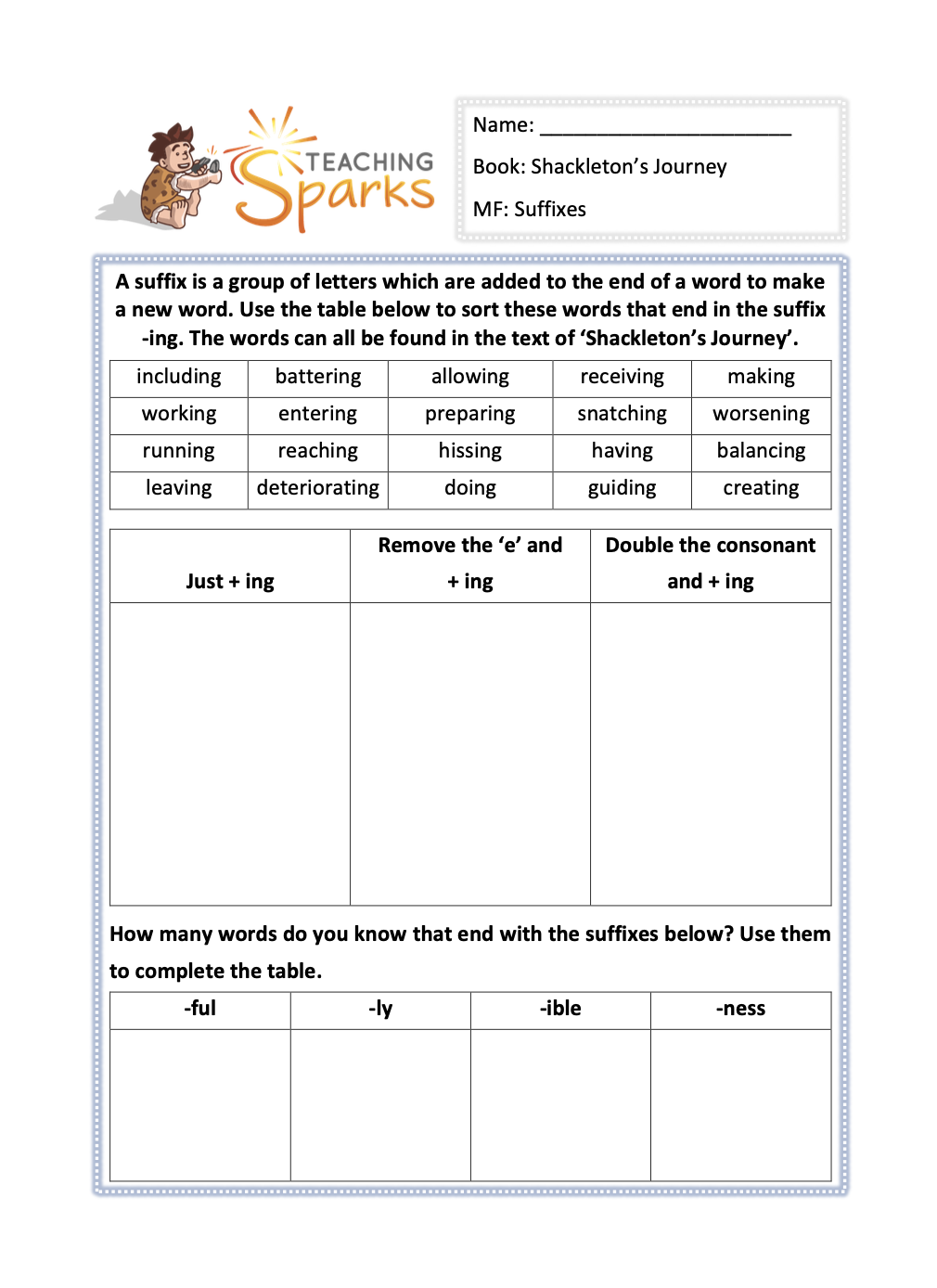
Main Focus: Suffixes
This resource focuses on suffixes: -ing, -ful, -ly, -ible & -ness
A suffix is a group of letters which are added to the end of a word to make a new word. Your class will use the table in the resource to sort the words that end in the suffix -ing.
The words can all be found in the text of ‘Shackleton’s Journey’.
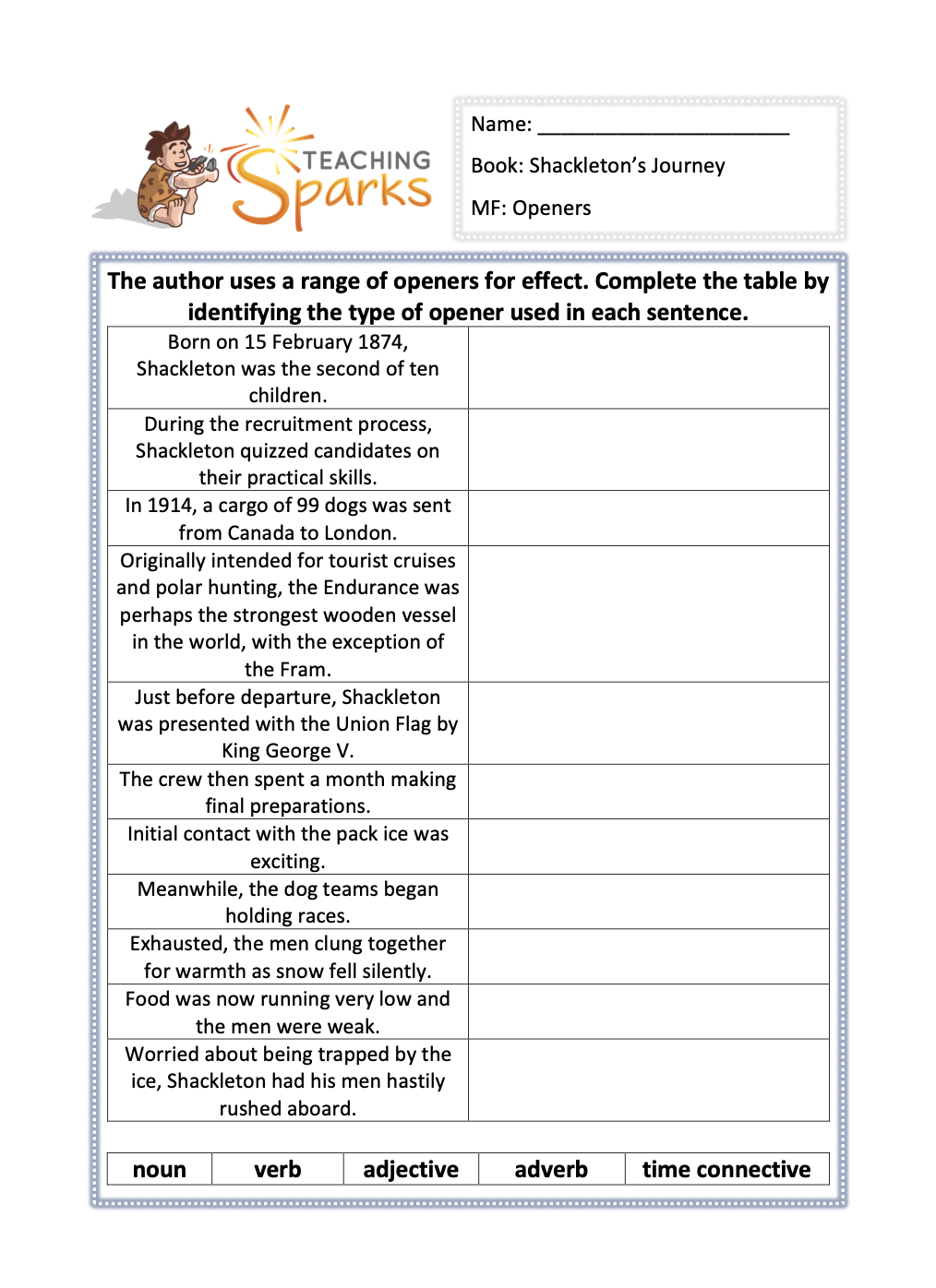
Main Focus: Sentence Openers
This LKS2 activity focuses on a range of sentence openers from the book.
Your class will begin to recognise the different openers used by the author by categorising them.
By recognising that there are different openers they can use, this will improve their literacy understanding and they can apply it to their independent writing.

Main Focus: Synonyms
Synonyms are words which have the same or similar meanings. We can use synonyms to make our writing more interesting.
In this whole class reading / guided reading activity, tour class will fill in the blanks in the resource with a synonym for the word in brackets.
Make sure to remind them to read the rest of the sentence carefully to check that their choice of synonym makes sense. The first one has been done for them.
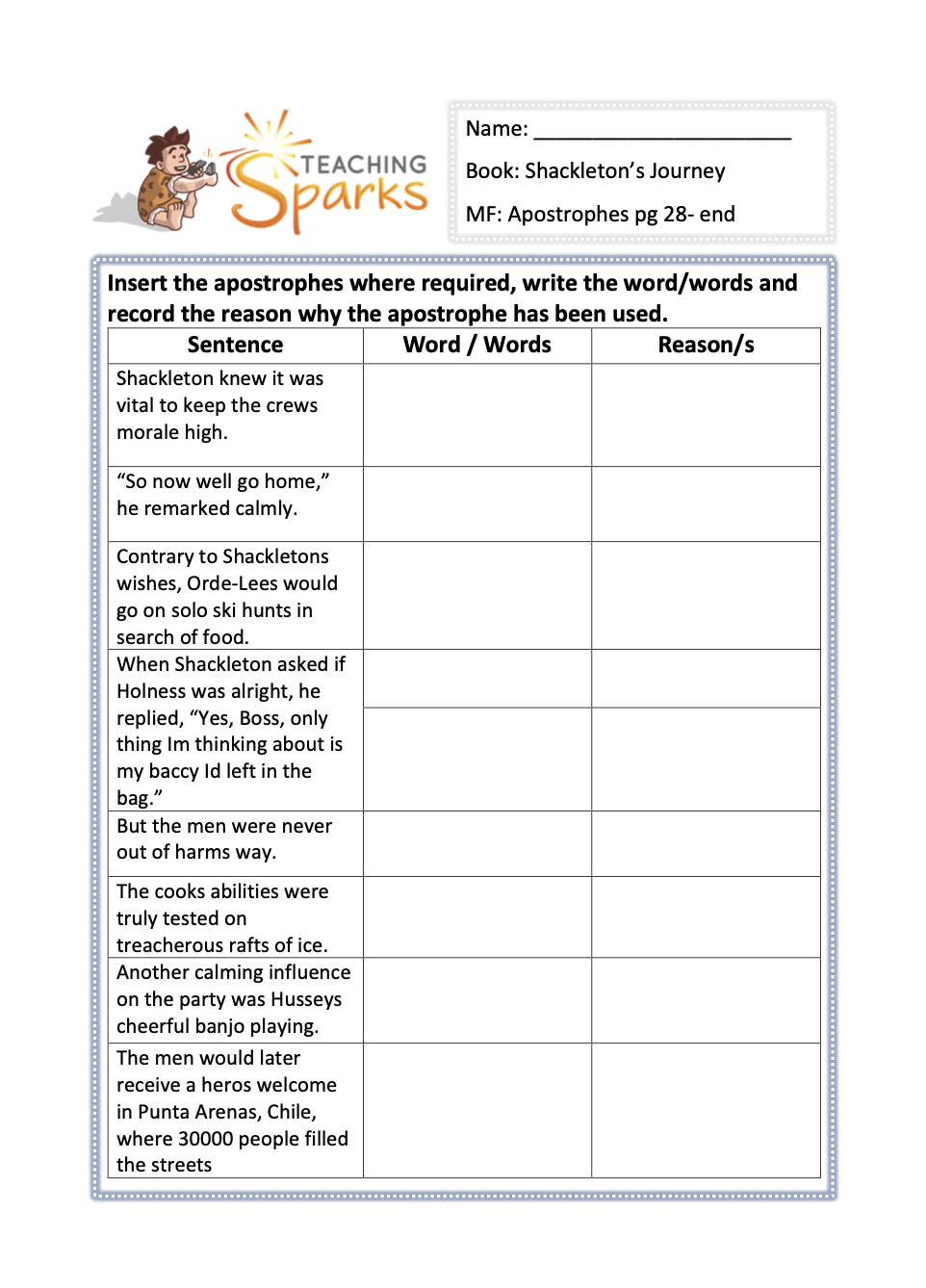
Main Focus: Apostrophes
This activity focuses on apostrophes and is from Page 28 of the book to the end.
This resource covers apostrophes for possession and contractions.

Main Focus: Spelling and Applying (including homophones)
This resource is linked to pages 51 and 52 of the book and spelling.
Your class are tasked to find all the spelling errors in the passage and then write the correct spelling of each word above.
We have also included homophones in this activity to help children identify words with different spelling and meanings, to help them put such words into the correct context.

Main Focus: Comprehension
This is a comprehension for the book Shackleton’s Journey and focuses on the whole book.
Your Year 3 / Year 4 class will be encouraged to use their knowledge of the story, their understanding and apply their knowledge to answer the questions.

Main Focus: Event Sequencing
In this activity, your class will sequence the main events from the story in chronological order to show their understanding.
Your Year 3 / Year 4 class will number each event from 1-14 to complete the story sequence.

Shackleton’s Diary
As part of year 9’s geography project at the Purbeck school in Wareham, Dorset last year, Kirsty Patterson, 14, imagined that she was Sir Ernest Shackleton during his famous Imperial Trans-Antarctic expedition (often known as the Endurance Expedition).

It was Mike’s idea to share Kirsty’s work with the Shackleton foundation and we are thrilled that he did. Click the pages below to view.
- The Foundation
- Impact Report 2016
- Impact Report 2019
- Impact Report 2022
- Sir Ernest Shackleton
- Centenary Expedition
- Shackleton Leaders
- Who we Fund
- Applying for Funding
- Leaders’ Forum
- Latest News
- Newsletters
Writing Root Back to List

Resource Preview
A writing root for shackleton's journey.
KS: Lower KS2
Year Group: Year 4
Author(s): William Grill
- Description
- Spelling Seed
- Home Learning Branch
This is a Home Learning Branch for Shackleton's Journey . These branches are designed to support home learners to access literature-based learning using a selection of books we love from Writing Roots. They include purposeful writing suggestions, links to the wider curriculum so that texts can be used across other subjects, key questions as well as spelling or phonics investigations.
A Spelling Seed is available for Shackleton's Journey.
Spelling Seed Overview:
This is a three-session spelling seed for the book Shackleton's Journey by William Grill. Below is the coverage from Appendix 1 of the National Curriculum 2014.
Spelling Seeds have been designed to complement Writing Roots by providing weekly, contextualised sequences of sessions for the teaching of spelling that include open-ended investigations and opportunities to practise and apply within meaningful and purposeful contexts, linked (where relevant) to other areas of the curriculum and a suggestion of how to extend the investigation into home learning.
There is a Spelling Seed session for every week of the associated Writing Root.
Word List Words
arrive, caught, imagine, island, medicine, accident(ally), calendar, earth, extreme, famous, sentence, mention
Spelling Rules and Patterns
More Prefixes: inter–, auto–, sub–
The suffix -ous
Home Learning Branch Overview:

A Spelling Seed for The Unforgotten Coat
KS: Upper KS2
Year Group: Year 6

A Writing Root for Jim, A Cautionary Tale
Year Group: Year 3

A Spelling Seed for The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe
- Primary Hub
- Art & Design
- Design & Technology
- Health & Wellbeing
- Secondary Hub
- Citizenship
- Primary CPD
- Secondary CPD
- Book Awards
- All Products
- Primary Products
- Secondary Products
- School Trips
- Trip Directory
- Trips by Subject
- Trips by Type
- Trips by Region
- Submit a Trip Venue
Trending stories

Top results

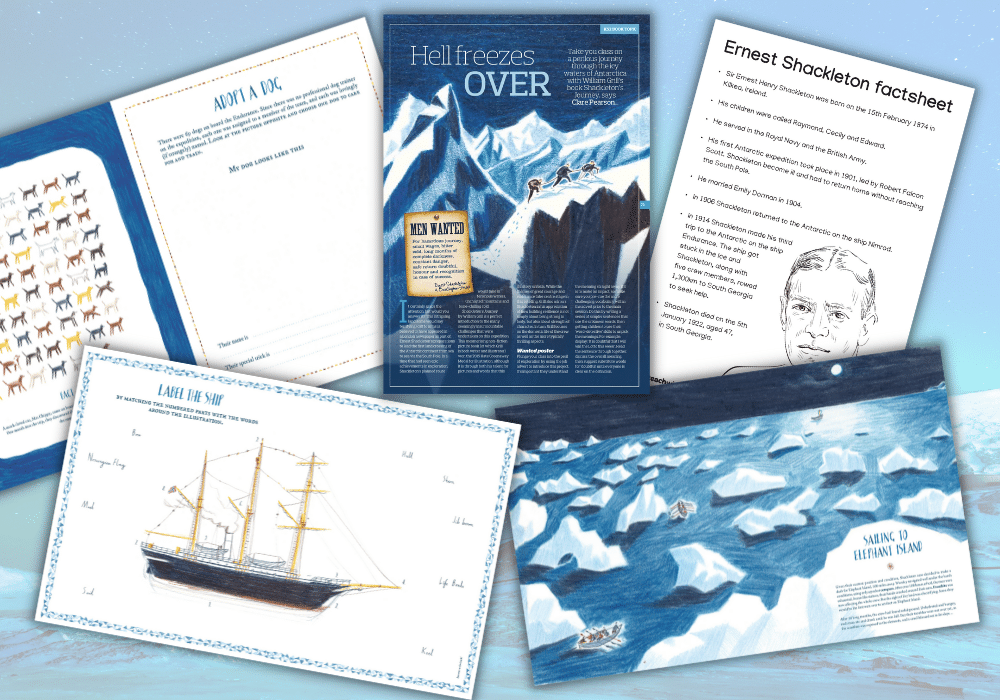
- Teaching Resources
- Ks2 Non Fiction Book Topic Shackletons Journey History Geography And Scienc
Shackleton’s Journey – KS2 book topic planning

Worksheets, activity ideas and extracts
Art & Design , Design & Technology , English , Geography , History , Science
Shackleton’s Journey is a mesmerising non-fiction picture book by William Grill that focuses on themes of courage and endurance, as well as going into detail about the lives of Shackleton’s crew and the thrilling elements of the expedition.
This download pack contains a three-page PDF featuring cross-curricular classroom activity ideas, including writing persuasive letters , model building, science experiments and learning about the rigours of Shackleton’s mission and the perils of the freezing climate.
This Shackleton’s Journey download contains:
- Three-page PDF featuring classroom activities
- Five worksheets to use in class
- PDF book extracts
- PDF of Ernest Shackleton facts
Ernest Shackleton facts
- Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton was born on the 15th February 1874 in Kilkea, Ireland.
- His children were called Raymond, Cecily and Edward.
- He served in the Royal Navy and the British Army.
- His first Antarctic expedition took place in 1901, led by Robert Falcon Scott. Shackleton become ill and had to return home without reaching the South Pole.
- He married Emily Dorman in 1904.
- In 1906 Shackleton returned to the Antarctic on the ship Nimrod.
- In 1914 Shackleton made his third trip to the Antarctic on the ship Endurance. The ship got stuck in the ice and Shackleton, along with five crew members, rowed 1,300km to South Georgia to seek help.
- Shackleton died on the 5th January 1922, aged 47, in South Georgia.
Clare Pearson is deputy headteacher at Summerbank Primary School in Stoke. Previously, Clare was the Primary Advisory English Teacher for Stoke-on-Trent.
Similar resources
- Brightstorm – KS2 cross-curricular activity ideas
- Alma Thomas lesson plan – Sunny KS1/KS2 art
- The One and Only Ivan – Explore emotions and empathy in KS2
- Roald Dahl art ideas – Make sculptures from recycled materials
- Mexico KS2 – Learn sculpture and folk art with alebrijes
Sign up to our newsletter
You'll also receive regular updates from Teachwire with free lesson plans, great new teaching ideas, offers and more. (You can unsubscribe at any time.)
Which sectors are you interested in?
Early Years
Thank you for signing up to our emails!
Explore teaching packs

Why join Teachwire?
Get what you need to become a better teacher with unlimited access to exclusive free classroom resources and expert CPD downloads.
Exclusive classroom resource downloads
Free worksheets and lesson plans
CPD downloads, written by experts
Resource packs to supercharge your planning
Special web-only magazine editions
Educational podcasts & resources
Access to free literacy webinars
Newsletters and offers
Create free account
By signing up you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Already have an account? Log in here
Thanks, you're almost there
To help us show you teaching resources, downloads and more you’ll love, complete your profile below.
Welcome to Teachwire!
Set up your account.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Commodi nulla quos inventore beatae tenetur.
I would like to receive regular updates from Teachwire with free lesson plans, great new teaching ideas, offers and more. (You can unsubscribe at any time.)
Log in to Teachwire
Not registered with Teachwire? Sign up for free
Reset Password
Remembered your password? Login here


COMMENTS
In the following excerpts from a previously unpublished first-hand account penned by Shackleton's ski and motor-sledge expert, Thomas Orde-Lees, relive the brutally cold and increasingly dangerous ...
Ernest Shackleton kept a diary for the 20 months that they were marooned there. Shackleton went on further expeditions, determined to cross Antarctica from sea to sea. His last mission was unsuccessful, and he died of a heart attack on the return journey. This was in South Georgia, in 1921. He was buried there.
The story of Ernest Shackleton's incredible journey has captivated audiences for over a century. An endurance feat like no other, the famous Antarctic explorer faced impossible odds and unfathomable perils to survive his remarkable voyage - but with strong leadership, carefully crafted plans, and an unwavering determination, he ultimately gave future generations a heroic tale of resilience ...
Expedition: Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition. Author: Ernest Shackleton (1874 - 1922) Date of article: 1915 - 30/Dec/1915. Reference number: 1537/3/8; BJ. In August 1914 Ernest Shackleton and a crew of twenty seven set sail for the Antarctic in an attempt to cross the continent on foot. Disaster struck when Endurance was trapped fast in the ...
The port side of the Endurance, pictured October 19, 1915, shortly before the ship was crushed by pack ice and sank. Endurance captain Frank Worsley and expedition leader Ernest Shackleton watch ...
ALEXANDRA SHACKLETON: And during the agonizing boat journey, Worsley wrote in his diary, "However bad things were, he somehow inspired us with the feeling that he could make things better ...
In August of 1914, legendary British explorer Ernest Shackleton led his brave crew of men and dogs on a journey to the end of the world — the enigmatic continent of Antarctica. That voyage — monumental both historically and scientifically — would become the last expedition of the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, which stretched from 1888 to 1914.
Original broadcast: March 26, 2002. Classroom Activity for the NOVA program Shackleton's Voyage of Endurance: In Weighty Decisions, students decide what to rescue from the sinking <i>Endurance</i ...
Shackleton's Journey is a uniquely visual non-fiction re-telling of Ernest Shackleton's epic expedition across the Antarctic. The text has a clear factual style as well as sparse but thought-provoking illustrations by William Grill which are highly engaging. This gives children an understanding of the period after the Victorians and the ...
In the intervening years the Norwegian Roald Amundsen had led the first team to reach the pole in 1911 and Captain Scott and his companions had perished on their own return journey in 1912. Shackleton's diary entry for the abandonment of Endurance in October 1915. SPRI MS 1537/3/8.
Norton) edition of Shackleton's Boat Journey, And yet, Shackleton, great explor - er though he was, could probably be regarded as unsuccessful on all his major journeys—if success ... Shackleton's diary entries for that final 36-hour trip across the glaciers at South Georgia grow ever
His diary is one of the more perceptive of those kept by the Endurance crew and much called upon by many accounts written about the expedition by others. Henry McNish - Carpenter (40) One of the oldest members of the expedition. ... Shackleton's Boat Journey: The narrative of Frank Worsley Book Shackleton biography by Roland Huntford Book The ...
Shackleton's Diary by Oak Class. In English, we have been looking at 'Shackleton's Journey' by William Grill. The children wrote three diary entries from Ernest Shackleton's point of view, at different stages of his expedition to Antarctica. Here are just a few examples, of their amazing writing. In Art, we were looking at and ...
In role, they were required to write CVs and attend job interviews with Ernest Shackleton and Frank Wild before writing goodbye letters and a series of diary entries recording the progress of the infamous expedition. Along the way, Year 6 have learnt a fantastic variety of techniques to enhance their writing.
About Ernest Shackleton. Polar Explorer. Leader of the Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition, 1914-1917. This entry was posted in Images, Other Voices, Shackleton. Bookmark the permalink . "Everyone is keeping a diary now. There was so little incident from day to day in the ship that very few of us thought it worthwhile."
This is Ernest Shackleton. He was an explorer and sailor. He was born in Ireland in 1874 and he joined the Merchant Navy at 16. He wanted to see places people had never been to before. He went on ...
Shackleton's Journey by William Grill. In the last days of the Heroic Age of Exploration, Ernest Shackleton dreamed of crossing the frozen heart of Antarctica, a place of ferocious seas, uncharted mountains and bone-chilling cold. But when his ship, the Endurance became trapped in the deadly grip of the ice, Shackleton's dreams were shattered.
Shackleton's Diary. As part of year 9's geography project at the Purbeck school in Wareham, Dorset last year, Kirsty Patterson, 14, imagined that she was Sir Ernest Shackleton during his famous Imperial Trans-Antarctic expedition (often known as the Endurance Expedition). With 19 separate entries covering the expedition's remarkable 1914 ...
Shackleton's Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition lasted from 1914 to 1917. It was meant to make the first land crossing of Antarctica, but Endurance became trapped and then lost in that cruel sea-ice.
I can identify and engage with the key themes in 'Shackleton's Journey'. 1 Slide deck. 1 Worksheet. 2 Quizzes. 1 Video. Free lessons and teaching resources about 'shackleton's journey': reading.
Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton CVO OBE FRGS FRSGS (15 February 1874 - 5 January 1922) was an Anglo-Irish Antarctic explorer who led three British expeditions to the Antarctic.He was one of the principal figures of the period known as the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration.. Born in Kilkea, County Kildare, Ireland, Shackleton and his Anglo-Irish family moved to Sydenham in suburban south London ...
Home Learning Branch. This is a Home Learning Branch for Shackleton's Journey. These branches are designed to support home learners to access literature-based learning using a selection of books we love from Writing Roots. They include purposeful writing suggestions, links to the wider curriculum so that texts can be used across other subjects ...
Shackleton's Journey is a mesmerising non-fiction picture book by William Grill that focuses on themes of courage and endurance, as well as going into detail about the lives of Shackleton's crew and the thrilling elements of the expedition.. This download pack contains a three-page PDF featuring cross-curricular classroom activity ideas, including writing persuasive letters, model building ...