- Disclosures
- Insights & Reports
Owned by 186 member countries and consistently rated AAA/Aaa. IFC aims to achieve our mission of promoting development by providing debt and equity to the private sector, through a range of benchmark and bespoke products.
- Governments
- Apply for Financing
- IFC Careers
- General Inquiries

A Ticket to Recovery: Reinventing Africa’s Tourism Industry

- COVID-19 triggered an unprecedented crisis in Africa’s tourism industry.
- Still, a growing middle class and young population bode well for travel businesses.
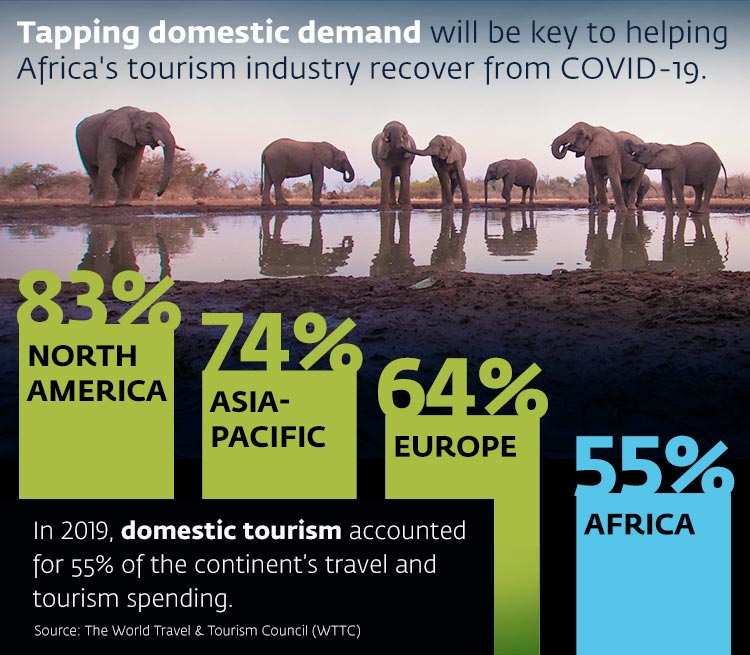
- Tapping domestic tourism demand will be key to rejuvenating the sector.
By Olivier Monnier
Months into the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, Kenya’s normally manicured beaches were carpeted three-feet deep in parts with thick layers of seaweed.
The Indian Ocean had seemingly taken advantage of the shuttered hotels and absence of tourists to reclaim the white sands in normally bustling Diani, Watamu, Malindi, and other favoured places along Kenya’s coastline.
The story was similar across much of Africa: pandemic-induced lockdowns and grounded flights devastated the continent’s tourism industry, forcing many operators to the brink of bankruptcy—or to cease operations.
During the height of the pandemic in West Africa, the Azalaï Hotel Group took the difficult decision to close completely. The Group has since reopened most of its hotels in the region, but more than half its rooms remain empty.
"I think 2021 is going to be another tough year for the sector," said Mossadeck Bally, founder and Chief Executive Officer of the hotel group. "The vaccination rollout will give travellers some confidence, but I don’t think people will travel much this year. The recovery will really start in 2022."
Unprecedented Crisis
Over the past 20 years, tourism has become vital to African economies. In 2019, the industry accounted for about seven percent of Africa’s GDP and contributed $169 billion to its economy—about the size of Côte d’Ivoire’s and Kenya’s combined GDP.
“The impact has been very strong,” said Bally, who refused a salary himself for more than a year. “Our industry was devastated because all of a sudden, we’ve been asked to just stop operating. We are a front-line sector so we are suffering first before it reaches the other industries.”
Aside from its Grand Hotel in Bamako, Mali’s capital, Azalai’s locations have resumed operations but with fewer staff, pay cuts of up to 40 percent and a hiring freeze, Bally said. Occupancy rates range from five percent in Guinea Bissau to 40 percent in Côte d’Ivoire, still well below normal levels.
Dependence on Foreign Travelers
Africa’s tourism sector has persevered largely without the financial relief provided by governments in wealthier, more developed regions, with the continent’s smaller businesses in the sector most affected.
The crisis has also exposed Africa’s dependence on foreign travelers. This is especially true for countries in Eastern and Southern Africa, which have developed significant leisure and safari-oriented facilities that appeal to European, American, Asian, and other visitors.

In December 2020, an IFC and Dalberg Advisors survey of selected tourism companies in Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia revealed that the companies would lose two thirds of their revenue from international tourism receipts in the 2020-2021 season.
Some experts believe that Africa might take longer to recover than other regions due in part to a lack of domestic and intraregional demand and the sector’s weaker supply chain.
According to the WTTC, domestic tourism accounted for 55 percent of travel and tourism spending in Africa in 2019, below the contribution of local tourism in North America (83 percent), Europe (64 percent) and Asia-Pacific (74 percent). Domestic tourism accounted for 73 percent of the total global tourism spending in 2017 .
“Much of the world has had the advantage of relying on captive domestic and regional audiences. But in Africa, domestic tourism has been overlooked for a long time,” said Hermione Nevill, an IFC Senior Tourism Specialist in Johannesburg. “The sector needs to be oriented towards more diversified markets so that there is greater resilience in future.”
But all is not lost for Africa’s hard-pressed tourism sector—and some countries have already acted to entice domestic tourists.

Reinventing the Industry
While Africa’s domestic tourism industry is growing—by 2050, Nigeria will have the world’s third largest population, for example—it remains largely untapped and burdened by challenges.
Connectivity is an issue. Traveling around the continent can be complicated and expensive, in part because countries restrict their markets to protect their state-owned air carriers. Although 44 African countries adopted the Yamoussoukro decision to liberalize the aviation market in 1999, implementation has fallen short.
There’s also a need for more and better infrastructure beyond capital cities, which are now generally well served with hotels and other amenities, said Olivier Baric, Africa Aviation Director at Egis, a French multinational company involved in infrastructure and transport.
Tourism experts believe domestic tourists could be enticed if operators invest in the economy and mid-scale market, develop smaller, more authentic, and greener resorts, and introduce more products aimed at middle-class African families and millennials, while marketing more directly to these groups.
Finally, there is the question—and problem—of ownership. The long-term strength and sustainability of Africa’s tourism industry will in part depend on the number of Africans building businesses and supporting and encouraging others on the continent to do so.
Despite the many challenges ahead, Azalai’s Bally says he sees the crisis as an opportunity—but one that can only be grasped through hard work and with fresh thinking:
“I am not worried, but I am perfectly aware that we have to reinvent ourselves to deal with the new situation,” he added. “Those who can reinvent themselves will survive.”
An aerial view of Zaina Lodge, a luxury safari hotel in northern Ghana. Photo: Courtesy of Zaina Lodge.
South Africa, which welcomed 10 million international tourists in 2019, made local tourism in 2020 a focus of its recovery plan . Rwanda, with advisory support from IFC, is developing a recovery strategy that includes developing local and regional markets. Meanwhile in Kenya, entry fees to all game parks and reserves have been cut for one year to attract more local tourists.
“Where we've seen some resilience is when there's domestic travel,” Wayne Godwin, senior vice-president of JLL Hotels & Hospitality Group for Sub-Saharan Africa, said at a virtual IFC event on the future of the tourism sector in Africa and the Middle-East.
Young Travellers and Free Trade
Africa’s growing middle class, its soaring population of young travellers hungry for adventure, and the recently launched African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), the world’s largest free trade area by the number of participating countries, are among the pillars seen supporting the future growth of domestic and regional tourism in the continent.
“The free-trade agreement is an absolute game changer for travel,” Godwin said. “If 97 percent of commodities and goods are tariff-free, that's going to do a lot for regional trade. And when there's regional trade, travel will follow. It just will happen.”
With its abundant wildlife and varied landscapes, Kenya is a leader in Africa in promoting local tourism.
The country’s beaches have been busy again following COVID’s initial shock, though another month-long lockdown announced for parts of the country in April 2021 frayed nerves among the country’s tourism operators.
Even before COVID-19, Kenya enjoyed a 55 percent rise in bed night occupancies by domestic tourists between 2014 to 2018, according to official data . The growth has been credited to digital campaigns, growing disposable income among Kenyans, and efforts to promote affordable alternatives to five-star resorts.
“International bookings are a higher value in terms of revenue but the domestic market is more resilient,” said Muthuri Kinyamu, cofounder of Kenyan tour operator Turnup.Travel . “Clients take multiple trips with you, and they come back.”
Kinyamu’s company has held up well during the pandemic, even adding staff. It benefited from a strong digital presence, developed new packages and partnered with low-cost airline Jambojet, a unit of Kenya Airways, to create content to reassure travelers and boost domestic bookings, Kinyamu said.
“Of course, our growth trajectory has been hampered by COVID-19 but when we look at our 2020 numbers, the revenues have evened out,” Kinyamu said. “With the restrictions, we had to adapt but we never had to lay off our staff as our business has diverse sources of incomes.”
Across the continent in West Africa, Zaina Lodge , a luxury safari hotel in Ghana, enjoyed its second-best month ever in December 2020—thanks to the power of domestic tourism.
“We established ourselves as a local brand from day one,” said company cofounder Andy Murphy. “The long-term growth in the continent is going to have to come from domestic tourism. If you're a business in tourism in Africa, you need to seriously think about how you build a domestic client base to match or even exceed your international base,” he said.
Published in May 2021

No spam. We promise.

Unlocking Opportunities for Travel & Tourism Growth in Africa
Create an account for free or login to download
Report details
The report studies the historical trends of the Travel & Tourism sector in Africa and provides a forecast for the next decade. It also identifies the key opportunities and challenges that, if addressed, could propel the region’s sector to achieve even higher growth. This hypothesis is supported by a forecast scenario analysis based on the introduction of a policy package. Additionally, the report highlights various countries within Africa that are performing well and provides case studies of best practices in the sector.
Some of the key themes discussed are:
- Economic impact of Travel & Tourism in Africa
- Environmental impact of Travel & Tourism in Africa
- Social impact of Travel & Tourism in Africa
- Connectivity and infrastructure in Africa
- Perceptions of Travel & Tourism in Africa
See the Executive Summary here (for free)
In collaboration with

Supported by

Non-Members
Related products.

Water Roadmap for Travel & Tourism
.jpg)
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI) Technology: Guide for Travel & Tourism Leaders

Global Retail Tourism Trends and Insights: Full Report
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
African Destinations Meet to Plan Growth and Sustainable Future for Tourism
Recovery and resilience were the central themes as the members of the World Tourism Organization’s Regional Commission for Africa (CAF) met for the 63rd time today. Reflecting the extraordinary circumstances, the meeting was held virtually, bringing together Ministers of Tourism from across the region with representatives of the African Union, the West African Monetary Union and from the private sector, to plot a united course towards a stronger and better tourism sector .
Held as the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) leads the global restart of tourism, the meeting enjoyed the virtual presence of 140 participants from 30 countries , including 24 Ministers of Tourism. They were joined by representatives of 10 international organizations and by members of the UNWTO Affiliate Members network.
Priorities to unlock Africa’s tourism potential
As well as addressing the immediate challenge posed by COVID-19, discussions also focused on the key areas of UNWTO’s Agenda for Africa , a roadmap designed to guide the sector in sustainable growth up to 2030. These priorities include enhancing Africa’s tourism Infrastructure, boosting air connectivity, easing visa facilitation, ensuring the safety and security of tourists, investing in the development of human capital development, and improving the image of Africa to the rest of the world.
UNWTO Secretary-General Zurab Pololikashvili said: “Africa’s tourism potential is undeniable, as is the potential of tourism to drive inclusive development across the continent. The steady easing of travel restrictions, first within nations and then across international borders, will allow the many social and economic benefits of tourism to return. If tourism’s restart is managed in a responsible and coordinated manner, harnessing the power of innovation and entrepreneurship, then it can transform millions of lives and help protect and preserve Africa’s rich cultural and natural heritage.”
If tourism’s restart is managed in a responsible and coordinated manner, harnessing the power of innovation and entrepreneurship, then it can transform millions of lives and help protect and preserve Africa’s rich cultural and natural heritage
Realigning the Agenda for Africa
Joining Mr Pololikashvili for the 63rd meeting of the CAF was the group’s current chairman Roland Chitotela, who also serves as Minister of Tourism and Arts, Zambia, and the African Union was represented by its Commissioner for Infrastructure and Energy, Dr. Amani Abou-Zeid. All participants welcomed the latest initiatives designed at growing African tourism announced by the Secretary-General, including the Brand Africa marketing competition and a fresh emphasis on showcasing African gastronomy and using this as a new market for sustainable tourism and job creation.
In the run-up to the meeting, UNWTO’s Member States took part in an online survey through which they were invited to share their thoughts on how the UNWTO Agenda for Africa can be utilized to accelerate recovery from the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and build resilience for the future. Participants expressed a strong desire to see the top five key areas of the Agenda for Africa prioritized in order to support swift and sustainable recovery. These priorities are: unlocking growth through investment and through effective public-private partnerships; promoting innovation and technology; visa facilitation and enhanced connectivity; advocating for Brand Africa, and fostering greater resilience, including through enhanced safety and security for tourists.
Related Links
- Download the news release
- Survey: UNWTO Agenda for Africa Tourism for Inclusive Growth
- Global Guidelines to Restart Tourism
- UNWTO: Gastronomy and Tourism
- UNWTO: Innovation and Digital Transformation
- UNWTO: Africa Newsletter
Category tags
Related content, unwto members meet to rethink agenda for african tourism, african tourism united to transform sector for growth a..., africa’s tourism leaders identify investments as key to....
Africa’s tourism potential
Subscribe to africa in focus, trends, drivers, opportunities, and strategies, landry signé landry signé senior fellow - global economy and development , africa growth initiative @landrysigne.
December 3, 2018
The tourism industry is playing an increasingly important role in the global economy, contributing 5 percent of gross domestic product (GDP), 30 percent of service exports, and 235 million jobs. Indeed, each year, approximately 1 billion people travel internationally. By 2030, consumer spending on tourism, hospitality, and recreation in Africa is projected to reach about $261.77 billion, $137.87 billion more than in 2015. From 1998 to 2015, service exports, including of “industries without smokestacks” such as tourism, have grown about six times faster than merchandise exports in Africa.
Given these trends, the travel and tourism industry has significant potential in Africa, notably due to the continent’s richness in natural resources and its potential to further develop cultural heritage, e.g., music. However, except in a few countries, such as Mauritius and Seychelles, where the tourism sector’s share of the economy is particularly large, tourism in Africa is still at an early stage of development and strongly connected with more general and longstanding development challenges, including infrastructure and security.
Aware of the potential for tourism, most countries in the region have already drafted strategic plans to develop the sector as an economic opportunity and development catalyst. For example, Gambia, Kenya, South Africa, and Tanzania are all putting significant efforts into advancing travel and tourism development. Botswana, Mauritius, Rwanda, and South Africa are working particularly hard to improve their business environment for tourism investment.
The African Union and sub-regional communities have also put tourism at the top of their agendas. For example, the African Union has endorsed the continent’s Tourism Action Plan (TAP) developed by the New Partnership for Africa’s Development (NEPAD), renamed African Union Development Agency (AUDA). The TAP recognizes tourism development among priority sector strategies of AUDA across Africa and aims to make Africa the destination of the 21st century. The 15 members of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) have introduced a visa policy that enables free movement of people across member states, offering a larger market to international travelers.
While improvements have been achieved in various areas, especially at the local level, much more needs to be done by both the public and the private sectors to fully tap Africa’s potential in the tourism industry. This report starts with an overview of tourism development in Africa and explores some of the key constraints that have prevented this sector from maturing. It identifies important stakeholders and potential opportunities for its future development. It also provides illustrative examples of countries representative of different trajectories of tourism development. Finally, with attention to current major policy reforms, the report draws conclusions about the future of the tourism sector in Africa.
The report aims to offer business leaders an overview of Africa’s biggest opportunities and risks in the tourism sector, discussing trends, drivers, perspectives, and strategies for effective investment. It also provides policymakers with some solutions related to the areas that need to be improved to attract private investors, accelerate tourism development, and contribute to growth and poverty alleviation, facilitating the fulfillment of the Sustainable Development Goals and the African Union’s Agenda 2063.
Related Content
Mariama Sow
July 20, 2017
January 11, 2018
Brahima Sangafowa Coulibaly
May 3, 2018
Emerging Markets & Developing Economies
West Africa
Global Economy and Development
Sub-Saharan Africa West Africa
Africa Growth Initiative
Joseph Asunka, Landry Signé
May 15, 2024
Margaret McMillan, Harun Onder
May 14, 2024
Anwar Aridi, Jeong-Dong Lee
May 1, 2024

Abbas Africa

Tourism in Africa: Overview
Tourism in Africa is a captivating journey that offers a blend of cultural diversity, breathtaking landscapes, and unparalleled wildlife encounters. With its rich heritage and abundant natural wonders, Africa has emerged as a prime destination for travelers seeking experiences and adventures. This overview explores the current state of tourism in Africa, shedding light on the number of annual visitors and the significant revenue generated by this sector. Additionally, we will delve into the factors that make Africa an attractive tourism hub, including its vibrant music, art, and culinary scene. We will also discuss the role of technology in shaping African tourism and examine the historical context and prospects of this thriving industry. Join us as we embark on an exploration of the wonders of tourism in Africa.
Key Takeaways
- Africa offers unique attractions and experiences for tourists, including natural beauty and cultural heritage.
- The tourism industry in Africa is rebounding from the impact of the pandemic, with international arrivals reaching 85% of pre-pandemic levels in the first quarter of 2023.
- Africa’s Travel and tourism sector has more than doubled in value in the past two decades, contributing 5.9% to Africa’s GDP and generating approximately 168 billion U.S. dollars in tourism receipts in 2022.
- Tourism in Africa has significant economic benefits, including revenue generation, job creation, infrastructure development, and poverty reduction.
What Is Tourism?
Tourism is a form of travel that involves visiting different places for leisure, pleasure, or business purposes, typically for a limited duration. In the context of Africa, tourism has become an increasingly important industry, with each country offering unique attractions and experiences.
From the iconic pyramids of Egypt to the vast savannahs of Kenya, Africa is a continent rich in natural beauty and cultural heritage. The diverse landscapes, wildlife, and historical sites make it a popular destination for tourists from around the world.
Countries such as South Africa, Kenya, Tanzania, and Morocco have emerged as top tourist destinations, attracting visitors with their stunning landscapes, wildlife safaris, and vibrant cultures. However, other countries in Africa also have their hidden gems waiting to be explored.
As we delve into the current state of tourism in Africa, it is important to understand the vast potential and challenges facing this industry.
What Is the Current State of Tourism in Africa?
The current state of tourism in Africa is rebounding from the pandemic, but it’s not quite back to pre-pandemic levels yet, with cautious optimism for 2024. Here’s a summary of the current state:
Recovery and Growth:
- International arrivals reached about 80% of pre-pandemic levels in the first quarter of 2023 according to UNWTO.
- According to the announcement of Forward Keys, the leading travel intelligence firm and Knowledge Partner of the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) at the Global Summit in Rwanda in the full 2023-year results showed by their latest air ticketing data, many African destinations entering a growth phase in the last quarter of 2023, with Cameroon (+27% international arrivals compared with 2019), Rwanda (+15%), Tanzania (+15%) and Namibia (+10%) leading the way and boasting double-digit growth.
- In July 2022, the number of tourists that arrived in Africa from overseas was around 5.1 million, which was significantly higher than the number in the same period in 2020 and 2021, due to the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the tourism industry according to Statista.
- By 2030, consumer spending on tourism, hospitality, and recreation in Africa is projected to reach about $261.77 billion, $137.87 billion more than in 2015. From 1998 to 2015, service exports, including “industries without smokestacks” such as tourism, have grown about six times faster than merchandise exports in Africa.
- According to the WTTC, Africa’s Travel and tourism sector has witnessed an extraordinary transformation, more than doubling in value in just two decades and contributing significantly to the continent’s economy.
- Africa recovered 92% of pre-crisis visitors in these nine months according to UNWTO.
- International tourism is expected to reach close to 90% of pre-pandemic levels by the end of 2023.
However, full recovery is still on the horizon, as the industry grapples with ongoing challenges like infrastructure limitations, geopolitical instability, and the lingering impact of the pandemic.
Challenges Remain:
- The industry is still facing challenges like infrastructure limitations and security concerns in some regions.
- The global economic slowdown could also impact tourism growth in Africa in the coming year.
There are still challenges to overcome, such as the ongoing effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, infrastructure development, and security concerns. To fully tap Africa’s tourism potential, both public and private sectors need to work together and implement effective policies and strategies. Overall, African tourism is on a positive trajectory. The industry is adapting to evolving preferences and capitalizing on its unique offerings to attract travelers. Continued focus on sustainability, responsible tourism practices, and diversified experiences will be key to sustaining this growth in the future.
How Many Visitors Does Africa Receive Annually?
Africa receives a significant number of visitors annually, both domestically and internationally. To understand the scale of tourism in Africa, it is important to consider the major tourists in terms of domestic and international arrivals. Here are some annual arrivals to the continent in different years:
According to the Africa Tourism Monitor, African international tourism arrivals increased slightly to 62.9 million in 2016 – a 0.64% increase.
Africa received 63.3 million international arrivals in 2017, marking a record high and representing an 8% growth compared to the previous year according to the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO).
According to the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), Africa received a total of 68.2 million international tourist arrivals in 2018.
In 2019, Africa received 69.9 million international tourist arrivals (excluding Egypt and Libya), representing a 2.4% increase from 2018 according to the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO).
According to the World Bank, Sub-Saharan Africa alone received 43 million international arrivals in 2021, still significantly lower than the 56 million in 2019.
Who Are the Major Tourists in Africa?
With an annual influx of visitors from both within and outside the continent, Africa attracts a diverse range of tourists. The continent’s rich cultural heritage, breathtaking landscapes, and unique wildlife make it a captivating destination for travelers.
In terms of domestic tourism, Africans themselves contribute significantly to the tourism industry. Many Africans travel within their continent to explore different countries, experience different cultures, and enjoy the beauty of their neighboring nations.
When it comes to international tourism, Africa welcomes visitors from all over the world. European countries such as France, Germany, and the United Kingdom are among the major sources of international tourists. Additionally, countries like China, the United States, and India also contribute to the growing number of visitors to Africa.
This intercontinental mix of tourists adds to the vibrant tapestry of Africa’s tourism industry.
How Much Revenue Does Tourism Generate for Africa?
Tourism in Africa is a significant contributor to the continent’s economy. According to Statista, travel and tourism contributed 5.9 percent to Africa’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP), with total tourism receipts amounting to approximately 168 billion U.S. dollars in 2022. This upward trend indicates the potential for further growth in the industry.
With consumer spending projected to reach $261.77 billion by 2030, tourism will continue to play a crucial role in Africa’s economic development.
What Makes Africa a Prime Tourism Destination?
Africa’s rich cultural heritage and diverse traditions make it an appealing destination for tourists. From ancient civilizations to vibrant festivals, visitors can immerse themselves in the unique customs and rituals of different African countries.
Additionally, Africa’s natural wonders, such as the majestic Victoria Falls and the vast Serengeti plains, offer breathtaking experiences that attract travelers from around the world.
How Does Africa’s Rich Cultural Heritage Contribute to Its Appeal as a Tourist Destination?
Africa’s rich cultural heritage is a major factor in its appeal as a prime tourism destination.
Tourists can encounter unique cultural experiences such as traditional music and dance, vibrant festivals, and authentic local cuisine.
These cultural encounters provide visitors with a deeper understanding and appreciation of Africa’s diverse traditions and customs, making their travel experiences richer and more memorable.
What Are Some Unique Cultural Experiences that Tourists Can Encounter in Africa?
Tourists visiting Africa can immerse themselves in a myriad of unique cultural experiences. Africa’s diverse and vibrant cultural heritage makes it a prime tourism destination.
From exploring the ancient ruins of Egypt to witnessing the traditional Maasai tribes in Kenya, there is something for everyone.
Tourists can also indulge in the rich music, dance, and art scenes across the continent. Whether it’s visiting the bustling markets of Marrakech or experiencing the vibrant festivals of Ghana, Africa offers an array of cultural experiences that are sure to leave a lasting impression.
What Are the Must-See Natural Wonders in Africa?
Africa’s remarkable natural wonders and diverse landscapes make it a prime tourism destination.
Africa is home to numerous natural wonders that showcase the continent’s diverse landscapes and ecosystems. Some of the must-see natural wonders in Africa include: Victoria Falls, Zambia/Zimbabwe: One of the most famous waterfalls in the world, Victoria Falls is located on the mighty Zambezi River between Zambia and Zimbabwe.
Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania: At 19,341 feet (5,895 meters) above sea level, Mount Kilimanjaro is Africa’s highest mountain and the highest free-standing mountain in the world.
Ngorongoro Crater, Tanzania: Known for its unique ecosystem and the world’s densest population of lions, Ngorongoro Crater is an impressive natural wonder.
Okavango Delta, Botswana: The Okavango Delta is a seasonally flooded marshland that acts like a massive oasis in the middle of the desert, offering a unique and serene experience.
Table Mountain, South Africa: Table Mountain is a prominent landmark in Cape Town, South Africa, offering stunning views and a popular hiking destination.
Serengeti Migration, Kenya/Tanzania: The Serengeti Migration is an incredible natural phenomenon where millions of animals, including wildebeest, zebra, and gazelle, move across the Serengeti Plains in search of water and food.
Fish River Canyon, Namibia: The Fish River Canyon is an enormous ravine and canyon stretching 100 miles (160 km) in length and reaching a width of 16.7 miles (27 km). These natural wonders offer visitors a glimpse into Africa’s diverse landscapes, from powerful waterfalls and towering mountains to unique ecosystems and breathtaking landscapes.
How Does Africa’s Diverse Landscapes and Natural Wonders Attract Tourists?
Africa’s diverse landscapes and natural wonders attract tourists for several reasons. Firstly, Africa is home to some of the world’s most iconic and breathtaking landscapes, such as the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania, the Sahara Desert, the Okavango Delta in Botswana, and the Victoria Falls in Zambia and Zimbabwe. These stunning natural wonders offer unique and unforgettable experiences for visitors.
Secondly, Africa’s diverse wildlife is a major draw for tourists. The continent is renowned for its incredible array of wildlife, including the “Big Five” game animals (elephant, lion, leopard, buffalo, and rhinoceros), as well as gorillas, chimpanzees, zebras, giraffes, and many more. Safari tours and wildlife viewing opportunities allow visitors to witness these majestic creatures in their natural habitats, making it a dream destination for nature enthusiasts and wildlife photographers.
Moreover, Africa’s natural wonders offer a range of activities for adventure seekers. From hiking Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania, the highest peak in Africa, to exploring the stunning underwater world of the Red Sea in Egypt or scuba diving with whale sharks in Mozambique, there are countless opportunities for thrilling adventures across the continent.
Additionally, Africa’s cultural heritage and historical sites attract tourists interested in learning about the rich history and diverse cultures of the continent. From the ancient pyramids of Egypt and the rock-hewn churches of Lalibela in Ethiopia to the vibrant markets of Marrakech in Morocco and the Swahili culture along the East African coast, Africa offers a wealth of cultural experiences.
Lastly, Africa’s conservation efforts and commitment to sustainable tourism have also contributed to its appeal. Many countries and organizations are working tirelessly to protect and preserve Africa’s natural wonders and wildlife, making it an attractive destination for conscious travelers who want to support responsible tourism.
What to Know Before Traveling to Africa?
As a traveler, there are things to know before traveling to Africa , it is important to research and understand the cultural norms and customs of the specific countries you plan to visit, as these can vary widely across the continent. It is also essential to check the visa requirements and ensure you have all necessary vaccinations before your trip. Additionally, it is advisable to pack appropriate clothing for the climate and to be prepared for potential language barriers by learning a few basic phrases in the local languages. Last but not least, obtain reliable travel insurance and carry fresh U.S. dollars, which are broadly accepted across many parts of the continent.
What Are the Key Trends Driving Tourism Growth in Africa?
There are several key trends driving tourism growth in Africa. Here are some of the most significant ones:
Economic growth: Africa has experienced significant economic growth in recent years, leading to an increase in disposable incomes and a growing middle class. This has resulted in more people having the financial means to travel and explore their continent.
Improved infrastructure: Many African countries have invested in improving their infrastructure, including airports, roads, and hotels. This has made it easier for tourists to access and explore different destinations within Africa, attracting more visitors to the continent.
Political stability: Several African countries have achieved political stability in recent years, which has enhanced their reputation as safe and attractive tourist destinations. This stability has also led to increased investment in the tourism sector, further driving growth.
Diversification of tourism offerings: African countries are increasingly diversifying their tourism offerings beyond traditional wildlife safaris. They are promoting cultural tourism, adventure tourism, eco-tourism, and beach tourism, among others. This allows them to attract a wider range of tourists with different interests and preferences.
Digital connectivity: The rapid expansion of mobile phone and internet penetration in Africa has opened up new opportunities for tourism growth. It has made it easier for tourists to research and book their trips, as well as share their experiences on social media, which in turn promotes the destination to a wider audience.
Sustainable tourism: There is a growing focus on sustainable tourism in Africa, with many countries and organizations implementing measures to protect the environment and support local communities. This not only appeals to environmentally conscious travelers but also helps preserve the natural and cultural heritage of the continent for future generations.
Collaborative efforts: African countries are increasingly working together to promote tourism in the region. This includes joint marketing campaigns, visa facilitation agreements, and the creation of regional tourism organizations. These collaborative efforts help showcase Africa as a diverse and accessible destination, attracting more tourists to the continent.
These key trends are contributing to the growth of tourism in Africa, making it an increasingly popular and sought-after destination for travelers from around the world.
What Is the Overall Importance of Tourism for Africa?
The importance of tourism in Africa cannot be overstated. Tourism in Africa plays a significant role in the continent’s economic and social development. It has the potential to drive economic growth, create employment opportunities, and promote cultural exchange.
Africa is known for its rich history, diverse wildlife, and breathtaking landscapes, making it a desirable destination for tourists from around the world. The revenue generated from tourism contributes to infrastructure development, conservation efforts, and poverty reduction.
Furthermore, tourism promotes cultural understanding and fosters a sense of belonging among communities, as it encourages interaction between locals and visitors. By showcasing Africa’s unique heritage and natural wonders, tourism helps to raise awareness and appreciation for the continent’s rich cultural and environmental assets.
With these benefits in mind, it is crucial to explore the key potential benefits of tourism for Africa.

What Are the Key Potential Benefits of Tourism for Africa?
Tourism in Africa brings forth numerous potential benefits, including economic growth, job creation, and cultural exchange. By harnessing its tourism potential, Africa can experience significant economic growth.
The tourism industry contributes to foreign exchange earnings, stimulates investment in infrastructure, and boosts income generation for local communities. Moreover, tourism creates a wide range of employment opportunities, from tour guides and hotel staff to artisans and entrepreneurs. This not only reduces unemployment rates but also empowers individuals and communities.
Additionally, tourism promotes cultural exchange, allowing visitors to immerse themselves in African traditions, customs, and cuisine, fostering understanding and appreciation.
What Are the Key Challenges Facing African Tourism?
One major obstacle facing African tourism is the lack of adequate infrastructure. This includes transportation networks, accommodation facilities, and communication systems. Without proper infrastructure, it becomes difficult for tourists to navigate and access various African tourism destinations.
The absence of reliable transportation links and quality accommodations hinders the growth of the tourism sector. Additionally, the lack of effective communication systems makes it challenging for tourists to obtain information about African travel destinations. This deficiency in infrastructure also affects the promotion of African tourism through brochures and other marketing materials.
However, despite these tourism challenges in Africa , the continent’s tourism sector has immense untapped potential. By addressing the infrastructure gaps and investing in modernization, Africa can attract more tourists and fully capitalize on its natural beauty, cultural heritage, and diverse attractions.
What Are the Untapped Potentials in Africa’s Tourism Sector?
Africa’s tourism sector holds tremendous untapped potential, waiting to be explored and harnessed for economic growth and development. Despite being blessed with diverse landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and abundant wildlife, Africa is still yet to fully capitalize on its tourism resources.
According to African tourism statistics, the continent receives only a fraction of the global tourist arrivals. This presents a significant opportunity for African countries to tap into the untapped potential in their tourism sector.
By investing in infrastructure development, promoting sustainable practices, and enhancing marketing strategies, African countries can attract more tourists and generate increased revenue. Moreover, the development of niche markets such as eco-tourism, adventure tourism, and cultural tourism can further unlock the untapped potential in Africa’s tourism sector.
Harnessing these potentials will not only contribute to the economic growth and development of African countries but also showcase Africa’s unique and diverse offerings to the world.
How Does Tourism Contribute to the Economic Growth and Development of African Countries?
The industry of Tourism in Africa generates revenue, creates job opportunities, and stimulates investment in infrastructure development.
With Africa’s diverse natural and cultural resources, the potential for tourism development is high, and it can catalyze sustainable economic growth and poverty reduction in the region.
How Is the Tourism Development Going in Africa?
The growth and development of tourism in Africa have significantly contributed to the economic progress of the continent. Africa is home to some of the best tourist places in the world, attracting millions of visitors each year.
The top tourist places in Africa, such as the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania, the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt, and the Victoria Falls in Zambia and Zimbabwe, have played a crucial role in driving economic growth and development in their respective countries. These popular destinations have not only created employment opportunities for local communities but also generated revenue through tourism-related activities, such as accommodation, transportation, and souvenir sales.
Additionally, tourism has stimulated investments in infrastructure development, such as airports, roads, and hotels, further boosting economic growth.
However, while tourism has brought significant economic benefits, it has also had cultural and environmental impacts, which will be discussed in the subsequent section.
What Are the Cultural and Environmental Impacts of Tourism in Africa?
The cultural and environmental impacts of tourism in Africa can be significant. As the continent experiences an increase in tourist activities, it is important to consider the effects on both the local communities and the environment.
One positive impact is the promotion and preservation of cultural heritage. Tourism provides opportunities for local communities to showcase their traditions, customs, and arts, fostering a sense of pride and belonging.
Additionally, ecotourism in Africa has gained popularity, leading to the conservation of natural resources and wildlife habitats.
However, there are also negative impacts to be aware of Over-tourism can lead to cultural commodification and loss of authenticity, while improper waste management and infrastructure development can harm fragile ecosystems.
Stakeholders must implement sustainable practices and regulations to mitigate these impacts and ensure a harmonious coexistence between tourism and culture, as well as the environment.
What Are Some of the Main Types of Tourism in Africa?
Some of the main types of tourism in Africa include: Ecotourism: Africa offers diverse and unique ecosystems, making it an ideal destination for ecotourism. Countries such as South Africa, Kenya, Namibia, Rwanda, and Zambia are known for their ecotourism initiatives.
Historical Sites and Monuments Tourism: Africa is rich in history and is home to numerous historical sites and monuments that attract tourists interested in cultural and historical experiences. Tea Tourism: Some African countries, such as Rwanda, are known for tea tourism, offering unique experiences related to the tea industry.
Safari Tourism: African safari tourism is a significant draw for visitors, generating over $29 billion annually. Countries such as Kenya, Tanzania, South Africa, Botswana, and Namibia are popular safari destinations. These types of tourism cater to a wide range of interests, including nature and wildlife, history and culture, and wellness and medical services, making Africa a diverse and appealing tourism destination.
How Popular Are Safari Tours in Africa?
Safari tours in Africa are incredibly popular, attracting millions of tourists each year. The continent’s diverse wildlife and stunning landscapes make it a top destination for wildlife enthusiasts and nature lovers.
From the vast savannahs of East Africa to the dense rainforests of Central Africa, safari tours offer a unique and unforgettable experience that is worth every penny.
Is African Wildlife Tourism Worth to Experience It?
Absolutely.
African wildlife tourism offers a unique and captivating experience that showcases the continent’s rich biodiversity and natural wonders.
Safari tours, in particular, are incredibly popular among tourists, providing an up-close encounter with majestic animals such as lions, elephants, and giraffes in their natural habitats.
The thrill of witnessing these magnificent creatures in the wild is unmatched, making African wildlife tourism a truly unforgettable adventure.
What Are Some of the Top Tourist Destinations in Africa?
Africa is a vast and diverse continent with numerous top tourist destinations. Here are some of the most popular top tourist destinations in Africa : Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania – Known as the highest peak in Africa, Kilimanjaro offers breathtaking views and attracts adventure enthusiasts from around the world for its challenging hiking routes.
Kruger National Park, South Africa – A world-renowned safari destination, Kruger National Park is home to an array of wildlife, including the Big Five (lion, leopard, elephant, rhino, and buffalo). Visitors can embark on thrilling game drives to witness these majestic creatures in their natural habitat.
Victoria Falls – Located on the border of Zambia and Zimbabwe, Victoria Falls is one of the world’s largest waterfalls. The sheer power and beauty of the falls make it a must-visit destination, offering activities like white-water rafting, bungee jumping, and scenic helicopter rides.
Abu Simbel Temples, Egypt – These ancient temples, carved into the mountainside, are a UNESCO World Heritage site. The colossal statues and intricate hieroglyphics make Abu Simbel a remarkable historical and cultural attraction.
Boulders Beach, South Africa – Situated near Cape Town, Boulders Beach is famous for its colony of African penguins. Visitors can get up close and personal with these adorable creatures while enjoying the picturesque surroundings of granite boulders and pristine beaches.
When planning a trip to Africa, it’s important to consider the best times to visit the top tourist destinations. The timing can greatly impact your experience and the activities available to you.
What Are the Best Times to Visit African Destinations?
To determine the ideal times to visit African destinations, it is important to consider the region’s climate and seasonal variations. Africa is a vast continent with diverse landscapes, offering a wide range of tourist spots throughout the year. Each destination has its unique charm and attractions, making it difficult to pinpoint the absolute best time to visit.
However, there are general guidelines that can help travelers plan their trips. For example, if you are interested in wildlife safaris, the dry season (from May to October) is usually recommended, as it offers better opportunities for spotting animals. On the other hand, coastal destinations like Cape Town in South Africa or Zanzibar in Tanzania are popular during their summer months (December to February).
Ultimately, the best time to visit African destinations depends on your preferences and the specific activities you wish to partake in.
Now, let’s explore which African countries are the top choices for tourism.
Which Are the Top African Countries for Tourism?
Below are some of the top African countries for tourism : South Africa: Known for its diverse landscapes, wildlife safaris, and vibrant cities like Cape Town and Johannesburg.
Morocco: Famous for its rich history, ancient cities like Marrakech and Fez, and beautiful landscapes including the Atlas Mountains and Sahara Desert.
Tanzania: Home to the iconic Serengeti National Park, Mount Kilimanjaro, and the stunning Zanzibar archipelago, offering a wide range of wildlife, nature, and beach experiences.
Kenya: Renowned for its world-class safari destinations such as Maasai Mara and Amboseli National Park, as well as its beautiful coastline and cultural experiences.
Egypt: Boasting ancient wonders like the Pyramids of Giza and the Nile River, as well as vibrant cities like Cairo and Luxor, offering a blend of history, culture, and adventure.
Ghana: Known for its rich cultural heritage, historic sites like Cape Coast Castle, and beautiful beaches along the Gulf of Guinea, making it a great destination for history and beach lovers. When considering the top African countries for tourism, one important aspect to discuss is the safety of traveling for tourists. Safety is a major concern for travelers, and it plays a significant role in their decision-making process.
Therefore, it is crucial to examine the safety measures and precautions taken by African countries to ensure a secure and enjoyable experience for tourists.
How Safe is Traveling for Tourists in African Countries?
Safety is a significant concern for travelers, and it is essential to understand the safety measures in place in various African countries. While some regions in Africa may have security challenges, many countries like Ghana, Rwanda, and Namibia among others have taken significant steps to ensure the safety of tourists. It is crucial for tourists to research and plan their trips, including choosing reliable tour operators and staying informed about any travel advisories.
Despite safety concerns, Africa offers a plethora of incredible tourist sites, making it a popular destination for travelers. From the iconic landscapes of South Africa to the wildlife-rich plains of Kenya and Tanzania, and the historical wonders of Egypt, Africa is home to numerous popular tourist destinations that offer unique experiences for visitors.
Are There Specialized Travel Agencies for African Tourism?
Yes, there are specialized travel agencies for African tourism. These agencies offer tailor-made tours and travel experiences throughout the continent, catering to a wide range of interests and budgets. Some of the specialized travel agencies for African tourism include: Africa Travel: Africa Travel is a specialist luxury tour operator that hand-crafts authentic African holiday itineraries and exclusive travel experiences throughout the entire continent.
The Africa Specialists: The Africa Specialists is a small, specialist tour operator that tailor-made luxury African safari itineraries to the countries of East and Southern Africa.
African Budget Safaris: African Budget Safaris offers affordable safari tours and travel experiences throughout Africa, catering to budget-conscious travelers.
Wild Frontiers: Wild Frontiers offers adventure travel experiences throughout Africa, including safaris, cultural tours, and trekking expeditions. These specialized travel agencies have extensive knowledge and experience in African tourism, offering personalized services and unique travel experiences to their clients. When planning a trip to Africa, many tourists may wonder if there are specialized travel agencies that cater specifically to African tourism.
Finding reputable travel agencies in Africa can be a crucial step in ensuring a smooth and enjoyable travel experience.
In this section, we will explore how tourists can locate and choose reliable travel agencies that specialize in African tourism.
How Can Tourists Find Reputable Travel Agencies in Africa?
Finding reputable travel agencies for African tourism can be achieved through various methods.
One way is to search online for African travel agencies or African tour operators. Many reputable agencies have websites that provide detailed information about their services, itineraries, and customer reviews.
Another method is to seek recommendations from friends, family, or colleagues who have traveled to Africa before. They can provide valuable insights and suggest reliable travel agencies they have personally used and had a positive experience with.
Additionally, travel forums and review websites can help identify reputable agencies, as they often feature discussions and ratings from fellow travelers.
By utilizing these methods, tourists can ensure they are choosing trustworthy and reliable travel agencies for their African adventures.
Now, let’s move on to the next section to explore the availability of travel insurance companies in Africa.
Are There any Travel Insurance Companies in Africa?
Yes, there are travel insurance companies in Africa , as well as companies that offer insurance coverage for travelers visiting the continent from other countries. These companies provide coverage for tourists visiting the continent, offering peace of mind and protection against potential risks and expenses. Some of these companies include: World Nomads: World Nomads is a popular travel insurance provider that offers coverage for travelers visiting Africa, including medical emergencies, trip cancellations, and more.
Insubuy: Insubuy is another platform that allows travelers to compare and purchase travel insurance or travel medical insurance for their trips to African countries.
First Allied: First Allied is a travel insurance company that covers dangerous countries in Africa, offering coverage for various risks such as health issues, infectious diseases, accidents, injuries, assaults, muggings, and trip delays and cancellations.
Just Travel Cover: Just Travel Cover offers travel insurance policies that include COVID-19 coverage for destinations such as Mauritius, Morocco, South Africa, and Seychelles. These travel insurance companies provide coverage for various risks and emergencies, ensuring that travelers have peace of mind and protection while visiting African countries.
For travelers seeking reputable travel agencies in Africa, it is essential to consider the availability of travel insurance as part of their planning process. By obtaining travel insurance, tourists can ensure that they are adequately covered in case of medical emergencies, trip cancellations, lost baggage, or any unforeseen circumstances that may disrupt their travel plans.
Africa tour operators and African travel resources often work closely with these insurance companies to provide comprehensive travel packages that include insurance coverage. It is advisable for tourists to research and compare different insurance options to find the most suitable coverage for their specific travel needs.
What Visa and Travel Requirements Should Tourists Know About When Visiting Africa?
When visiting Africa, tourists should be aware of the visa and travel requirements for their specific destination. Here are some key points to consider: Visa Procurement: Visa and entry requirements for African countries are subject to change. While the majority of visas in Africa can be obtained at the border, it is essential to check with the consulate or a reputable visa-handling company for the most up-to-date visa information before traveling.
Passport Validity: Tourists should ensure that their passport is valid for at least 6 months from their planned date of entry into the country.
Visa Exemptions: Some African countries offer visa exemptions for certain nationalities. For example, New Zealand and South African passport holders do not require a visa to visit Botswana for up to 90 days, and most nationalities, including UK, USA, Canadian, Australian, New Zealand, and South African passport holders, do not require a visa to visit Namibia and South Africa for up to 90 days.
Special Requirements: Some countries have special requirements, such as South Africa, which has specific requirements for traveling with children. It is important to obtain the correct documentation to avoid any entry issues.
Health and Safety: In addition to visa requirements, tourists should also be aware of health and safety protocols, especially in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Many African countries have implemented strict health and safety measures, including temperature checks, social distancing, and the wearing of masks. It is advisable for tourists to research and confirm the specific visa and travel requirements for their intended African destination well in advance of their trip to ensure a smooth and enjoyable travel experience.
Now, let’s move on to the next section on how to plan your trip to Africa.
How to Plan Your Trip to Africa?
When planning your trip to Africa , it is essential to consider various factors to ensure a smooth and enjoyable experience. With its diverse landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and abundant wildlife, Africa offers a wide range of tourist destinations for every kind of traveler. Planning a trip to Africa can be an exciting and rewarding experience. Here are some steps to help you plan your trip:
- Determine your interests
- Choose your destination
- Research visa and travel requirements
- Book your flight
- Arrange accommodations
- Plan your itinerary
- Consider using a tour operator
- Get travel insurance
- Pack appropriate clothing
- Research local customs and culture
By following these steps, you can plan a memorable and enjoyable trip to Africa. Now, let’s explore some interesting facts and statistics about tourism in Africa.
What Are Some Interesting Facts and Statistics About Tourism in Africa?
Africa’s tourism industry has experienced significant growth in recent years, attracting millions of visitors from around the world. Here are some interesting facts and statistics about tourism in Africa : Tourism Growth: The number of international tourist arrivals in Africa doubled from 24 million in 1995-1998 to 56 million in 2011-2014.
Tourism Revenue: By 2030, consumer spending on tourism, hospitality, and recreation in Africa is projected to reach about $261.77 billion, which is $137.87 billion more than in 2015.
Tourist Arrivals: In 2018, Africa saw an increase of 2.4% in international tourist arrivals, with 69.9 million visitors (excluding Egypt and Libya). This growth rate was slightly lower than the global average growth rate of 6%. In 2021, inbound visitor numbers to Africa increased by nearly 15% over the previous year.
Tourism Share: Africa held a 4.4 percent share in worldwide tourism arrivals and accounted for a 2.3 percent share of worldwide tourism receipts in 2015.
Popular Tourist Countries: In 2015, Morocco was the only African country to surpass 10 million international tourist arrivals. Other popular countries for international tourists in Africa include Egypt, South Africa, Tunisia, Zimbabwe, Kenya, Uganda, Namibia, and Senegal.
Tourist Origins: Tourists in Africa mostly come from Europe and the US, with France being the number one source, followed by the UK and the US. These facts and statistics highlight the significant growth and potential of the tourism industry in Africa, as well as the diverse range of countries and attractions that the continent has to offer to international visitors.
How Does Africa’s Tourism Industry Compare to Other Continents?
The comparative strength of Africa’s tourism industry can be seen through its remarkable growth, diverse offerings, and significant economic impact.
While Africa may not rank as high as other continents in terms of tourist arrivals, it has been steadily climbing the ranks in recent years. While Africa’s tourism industry is still developing, it holds significant potential and demonstrates promising growth trends:
Growth Rate: Africa boasts the second-fastest growing tourism industry globally, trailing only Asia-Pacific.
Economic Impact: Tourism contributes a substantial 5.9% to Africa’s GDP in 2022 and employs around 13.1 million people in 2012 according to the World Bank.
Global Share: Although Africa held a 4.4 percent share in worldwide tourism arrivals and accounted for a 2.3 percent share of worldwide tourism receipts in 2015 according to UNCTAD, this number is steadily increasing.
Emerging Markets: Within Africa, domestic tourism is flourishing, with African tourists themselves becoming a driving force in the industry.
What’s the Role of Technology in Shaping African Tourism?
Technology plays a significant role in shaping the tourism industry in Africa. With the advent of the digital age, African countries have embraced technology to showcase their unique attractions and experiences to a global audience.
One of the key ways technology has facilitated this is through the rise of African travel bloggers and travel blogs. These platforms have become a powerful tool for promoting African destinations, as they offer firsthand insights, recommendations, and personal experiences that resonate with travelers seeking authentic and immersive experiences.
African travel bloggers have harnessed the power of social media and online platforms to reach a wider audience, showcasing the diverse landscapes, rich cultures, and vibrant communities that make Africa a must-visit destination.
Through technology, African tourism is being shaped by these influential voices, creating a sense of belonging for travelers seeking to explore the continent.
How Does the Vibrant Africa’s Music, Art, and Culinary Scene Enhance the Overall Tourism Experience?
The vibrant music, art, and culinary scene in Africa enriches the overall tourism experience, offering visitors an authentic immersion into the continent’s cultural heritage.
Africa’s diverse and vibrant music traditions, ranging from traditional drumming and dance rituals to modern genres like Afrobeats, captivate tourists with their infectious rhythms and soulful melodies.
Art enthusiasts are drawn to Africa’s thriving art scene, which showcases a rich tapestry of styles and techniques, reflecting the continent’s history, traditions, and contemporary issues.
The culinary scene in Africa is equally enticing, with a wide array of flavors, spices, and techniques that vary from region to region. From the aromatic spices of North African cuisine to the fiery flavors of West African dishes, visitors can embark on a gastronomic journey that tantalizes their taste buds.
The African Tourism Association and Travel Africa Magazine are valuable resources for travelers seeking information and recommendations on the best music, art, and culinary experiences across the continent.
What Is the History of Tourism in Africa?
Tourism in Africa has witnessed steady growth, driven by increasing global interest in exploring the continent’s diverse landscapes and rich cultural heritage.
The history of tourism in Africa can be traced back to the colonial era when Europeans began to explore the continent for its vast resources and exotic wildlife. However, it was not until the mid-20th century that tourism started to gain momentum in Africa.
The establishment of national parks and protected areas, such as the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania and Kruger National Park in South Africa, played a significant role in attracting tourists.
In 1975, the African Travel Association was formed to promote tourism in the region and showcase the unique African tourist spots.
Today, Africa is known for its iconic landmarks like the Pyramids of Egypt and Victoria Falls, drawing visitors from all over the world.
As we delve into the prospects and trends for tourism in Africa, it is evident that the continent’s abundant natural beauty and cultural heritage will continue to attract travelers seeking authentic experiences and a sense of belonging.
What Are the Future Prospects and Trends for Tourism in Africa?
Moving forward from the history of tourism in Africa, we now turn our attention to the prospects and emerging trends in the industry on the continent.
Africa has immense potential to become one of the most sought-after tour destinations in the world. With its rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and unique wildlife, Africa offers a captivating experience for travelers.
The African Travel and Tourism Association (ATTA) plays a crucial role in promoting and developing tourism in the region. It works closely with governments, tour operators, and local communities to ensure sustainable and responsible tourism practices.
The future of tourism in Africa looks promising, with an increasing number of international tourists showing interest in exploring the continent. As infrastructure and connectivity improve, Africa is poised to attract more visitors, generating economic growth and creating opportunities for local communities.
In conclusion, tourism in Africa has experienced significant growth and has become a prime destination for travelers worldwide. The continent attracts a large number of visitors annually, generating substantial revenue.
The vibrant music, art, and culinary scene in Africa further enhance the tourism experience. These cultural expressions provide unique and immersive opportunities for tourists to engage with the local communities and experience the rich diversity of African cultures.
With the role of technology shaping the industry, tourism in Africa is set to benefit from advancements in digital platforms and online booking systems. This will make it easier for travelers to access information, plan their trips, and connect with local tour operators.
Furthermore, the rich history of tourism in Africa adds to its appeal. From the ancient pyramids of Egypt to the historic sites of South Africa, the continent offers a wealth of archaeological and cultural landmarks that attract history enthusiasts from around the world.
Considering these factors, the prospects and trends for tourism in Africa are promising. As infrastructure continues to improve, accessibility increases and sustainability practices are prioritized, the continent has the potential to become an even more popular and sought-after travel destination.
Like a blooming flower in a vast garden, Africa’s tourism industry is poised to flourish and continue captivating travelers with its natural beauty, cultural richness, and warm hospitality.
Biodiversity Conservation and Tourism Sustainability in Africa
- First Online: 18 April 2023
Cite this chapter

- Bukola Omotomilola Adetola 4
Part of the book series: Sustainable Development and Biodiversity ((SDEB,volume 32))
278 Accesses
1 Citations
3 Altmetric
The long-term viability of the tourism industry and the preservation of its principal attraction (nature) are inextricably linked. Biodiversity conservation is a fundamental obligation of all economic sectors and a unique paradigm in the tourist sector that makes tourism more biodiversity-friendly. Assets of biodiversity are powerful forces shaping tourism’s essence, including the human drive to see and experience the pristine ecological settings. Moreover, Africa boasts of rich diversity, and in this continent, biodiversity endowment offers opportunities for economic, social, and ecological development. Whether scuba diving on coral reefs or watching wildlife, most tourists enjoy the natural beauty (animals and vegetation) that surrounds them. However, the high rates of tourist expansion must be balanced against the problems that come with it, such as massive volumes of traffic, trash, a huge area of land and resource consumption associated with travel, and impacts on fragile ecosystems among others. The tourism sector appears to place a long-term emphasis on environmental conservation and protection because of the importance and uniqueness of the environmental quality and biodiversity for tourism, and they encourage and support sustainable tourism operations. Responsible tourism benefits indigenous communities and residents by improving their standard of living while also preserving culture and biodiversity.
Ecotourism, a sustainable tourism strategy, is an interface of conservation concerns and tourism interest, a synergy that jointly preserves the environment’s quality while protecting nature and promoting tourism. Consequently, Africa’s response to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) will be ineffective unless its biodiversity is conserved and used sustainably.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Adetola BO, Adetoro OA (2014) Threats to biodiversity conservation in Cross River National Park. Nigeria Int J Conserv Sci 5(4):547–552
Google Scholar
Adetola BO, Akinboboye TS (2020) Visitors’ connection with ex-situ conservation in zoos: catalyst for visitation intention to in-situ ecotourism destinations. Journal of Tourism Res 25:5–29
Adetola BO, Alarape AA, Ayodele IA (2021) Forest resources as ecotourism attraction: Cross River National Park, Nigeria. Ruhuna J Sci 12(1):26–39
Article Google Scholar
AfDB-African Development Bank (2015) African natural resources Center (ANRC) strategy (2015–2020). Revised Version. ANRC Department
Airey D, Chong K (2011) Tourism in China: policy and development since 1949. Routledge, Oxford
Book Google Scholar
Association of Bhutanese Tour Operators (2010) UNWTO Tourism Vision 2020 Forecast Released. http://www.abto.org.bt/2010/06/unwto-tourism-2020-vision-forecast-released/
Aswani S, Albert S, Love M (2017) One size does not fit all: critical insights for effective community based resource management in Melanesia. Mar Policy 81:381–391
Atanga RA (2019) Stakeholder views on sustainable community-based ecotourism: a case of the Paga crocodile ponds in Ghana. GeoJ Tourism Geosites 25(2):321–333
Basupi B, Pansiri J, Lenao M (2017) Botswana tourism policy landscape–successes and challenges. Botswana J Business 10(1):83–96
BirdLife International Press Release (2008) Avitourism ‘Takes off’ in South Africa (Online). http://www.birdlife.org/news/news/2008/04/SA_Birding_Routes.html . Accessed 09 April 2008
Blanc JJ, Barnes FW, Craig GC, Dublin HT, Thouless CR, Douglas-Hamilton I, Hart JA (2007) African elephant status report 2007: an update from the African elephant database. IUCN, gland, Switzerland: occasional paper series of the IUCN species survival commission, no. 33. IUCN/SSC African Elephant Specialist Group. http://www.africanelephant.org/aed/aesr2007.html
Borokini TI (2014) A systematic compilation of endemic flora in Nigeria for conservation management. J Threatened Taxa 6(11):6406–6426
Bramwell B (2010) Participative planning and governance for sustainable tourism. Tour Recreat Res 35(3):239–249. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508281.2010.11081640
Buckley R (2004) Environmental impacts of ecotourism: impacts of ecotourism on bird. Ecotourism series no 2. CAB international. 416 pp
Ceballos-Lascurain H (1990) Tourism, ecotourism, and protected areas. Paper presented at the 34th working session of the Commission of National Parks and Protected Areas, Perth, Australia
Chen LL, Devereux J (1999) Tourism welfare in sub-Saharan Africa: a theoretical analysis. J Afr Econ 8(2):209–227
Christie IT, Crompton DE (2001) “Tourism in Africa”, Africa region working paper series no. 12. The World Bank, Washington DC
Drumm A, Moore A (2002) Ecotourism development: an introduction to ecotourism planning Vol.1. The Nature Conservancy, USA. 85 pp
Dye TR (2008) Understanding public policy, 12th edn. Pearson/Prentice Hall. 354pp
Eilat AT, Einav L (2003) The determinants of international tourism: a three-dimensional panel data analysis. Unpublished Working Paper
Fennel D (2008) Ecotourism. TJ International Ltd, Cornwall
First National Biodiversity Report (2001) Ministry of Home Affairs Housing and Environment, First National Report to the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity. Retrieved from https://www.cbd.int/doc/world/mv/mv-nr-01-en.pdf
Forestry Management Evaluation and Coordinating Unit (FORMECU), (1996) Nigerian forestry action programme volume II: Main report Federal Ministry of agriculture and natural resources. Abuja
GHK Consulting Ltd., GFA-Race Partners Ltd. (2004) Revealing the value of the natural environment in England, a report to the Department for Environment. Food and Rural Affairs, London
Gössling S, Hall C, Weaver D (2009) Sustainable tourism futures; perspectives on systems, restructuring, and innovations. Routledge, New York; Oxon
Hall CM (2008) Tourism planning: policies, processes, and relationships. Pearson Education, London
Hottola P (2009) Tourism strategies and local responses in southern Africa. CABI, Wallingford
Houston, JR (1996). ‘International Tourism and US Beaches’, Shore and Beach (1996), quoted in 1998 Year of the Ocean-Coastal Tourism and Recreation (Online). http://www.yoto98.noaa.gov/yoto/meeting/tour_rec_316.html
Huybers T, Bennett J (2002) Environmental management and the competitiveness of nature-based tourism destinations. Edward Edgar Publishing. 192 pp
IUCN (1997) Ecotourism. In: Beyond fences: seeking social sustainability in conservation. IUCN, Gland. Pp 22
Kameri-Mbote P, Cullet P (2002) Biological diversity management in Africa: policy perspectives. Rev Eur Community Int Environ Law 11(1):38–52
Kato K (2018) Debating sustainability in tourism development: resilience, traditional knowledge, and community: a post-disaster perspective. Tourism Planning Dev 15(1):55–67. https://doi.org/10.1080/21568316.2017.1312508
Kenya National Bureau of Statistics (2017) Statistical abstract 2017. Accessed 27 January 2018
Kenya Tourism Board (2016) Sustainable tourism report. Available at https://magicalkenya.com/wpcontent/uploads/2020/05/Final-KTB-Sustainable-Tourism-Brochure-2016-1.pdf
Kenya Travel Tips (2018) Tourism in Kenya. Available at https://www.kenyatraveltips.com/tourism-in-kenya/
Kester IGC (2003) International tourism in Africa. Tour Econ 9(2):203–221
Kossomann CM, Behgel J, Bailey M (2016) Action and inertia in collaborative governance. Mar Policy 72:21–30
Kraft ME, Furlong SR (2015) Public policy: politics, analysis, and alternatives, 2nd edn. CQ Press, Sage. 459 pp
Kutay, K (1989) Ecotourism: travel’s new wave. Vis a Vis, July, 4–80
Manwa H, Modirapula T (2019) The role of Botsalano game reserve in sustainable livelihoods and poverty alleviation through community-based tourism development in South Africa. African Renaissance 16(1):315–333
Melita AW, Mendlinger S (2013) The impact of tourism revenue on the local communities’ livelihood: a case study of Ngorongoro conservation area, Tanzania. J Serv Sci Manag 6:117–126
Miller GA, Twining-Ward L (2005) Monitoring for a sustainable tourism transition. The challenge of developing and using indicators. CABI Publishing. 59 p. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851990514.0000
Moswete N, Thapa B, Child B (2012) Attitudes and opinions of locals and national public sector stakeholders towards Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park, Botswana. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 19(1):67–80
Paterson AR (2009) Legal framework for protected areas: South Africa. IUCN SANParks, Gland, p 2016
Qian C, Sasaki N, Shivakoti G, Zhang Y (2016) Effective governance in tourism development – an analysis of local perception in the Huangshan mountain area. Tour Manag Perspect 20:112–123
Rinfret S, Scheberie D, Pautz M (2018) Chapter 2: the policy process and policy theories. In Public policy: a concise introduction. SAGE Publications, pp 19–44
Roy AKD (2016) Local community attitudes towards mangrove forest conservation: lessons from Bangladesh. Mar Policy 74:186–194
Sabuhoro E, Wright BA, Munanura I, Nyakabwa IN (2017) The potential of ecotourism opportunities to generate support for gorilla conservation amongst local communities Neighboring volcanoes National Park in Rwanda. J Ecotour:1–17
Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (2007) Managing tourism and biodiversity , User’s manual on the CBD guidelines on biodiversity and tourism development , Secretariat of the CBD, Montreal, 12 pp
Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (2008) The value of nature: ecological, economic, cultural and social benefits of protected areas, secretariat of the CBD, Montreal
Shibru T, Martha G (1998) Biodiversity management in Ethiopia. In: Mugabe J, Clark N (eds) Managing biodiversity—National Systems of conservation and innovation in Africa. ACTS Press, Nairobi
South African National Parks Annual Report (2015). http://www.sanparks.org/assets/docs/general/annual-report-2015.pdf . Accessed 30 Jan 2022
Steck B (2004) Sustainable tourism as a development option practical guide for developers and decision makers, Eschborn. 63 pp
Stéphane DB (1995). ‘La convention de Paris de 1994 sur la désertification’, in Stratégies énergétiques Biosphère & Société - Le droit international face à l’éthique et à la politique de l’environnement 143-150
Steyn JN, Spencer JP (2011) South African tourism: an historic Evaluation of macro tourism policies. Afr J Phys Health Educ Recreation Dance 17(2):178–200
Tapper R, Cochrane J (2005) Forging links between protected areas and the tourism sector: how tourism can benefit conservation. UNEP report. https://wedocs.unep.org/handle/20.500.11822/8765
The International Ecotourism Society (TIES) (1990) What is ecotourism. https://www.ecotourism.org/what-is-ecotourism . Accessed Aug 2014
TIES (2008) The components of successful ecotourism. The International Ecotourism Society (TIES). Retrieved from https://www.scirp.org/(S(czeh2tfqyw2orz553k1w0r45))/reference/referencespapers.aspx?referenceid=2533924
Tinker C (1995) A “new breed” of treaty: the United Nations convention on biological diversity. Pace Environ Law Rev 13(1):191–218. https://digitalcommons.pace.edu/pelr/vol13/iss1/8
Tourism Australia (2009) Activities factsheet—year ending June 2009 (Online). http://www.ret.gov.au/tourism/tra/snapshots/sheets/Pages/default.aspx . Accessed 7 Sep 2010
UNEP (2010) State of biodiversity in Africa. http://www.unep.org/delc/Portals/119/State%20of%20biodiversity%20in%20Africa.pdf . Accessed 16 Dec 2015
UNESCO. (2004) Cape floral region protected areas. https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1007/ . Accessed 25 Oct 2019
United Nations Statistics Division (2010) Tourism as an internationally traded service and beyond. Newsletter of the Interagency Task Force on Statistics of International Trade in Services. No. 6, December 2010, p. 1. Retrieved from http://unstats.un.org/unsd/tradeserv/tfsits/newsletter/TFSITS_newsletter_6.pdf
US Agency for International Development (USAID) Centre for Applied Research (2016). Review of community-based natural resource management in Botswana. Report prepared for Southern African Environmental Programme (SAREP)
US Fish and Wildlife Service (2007) National Survey of fishing, hunting and wildlife-associated recreation 2006 , Washington
Van der Merwe P, Saayman M (2003) Determining the economic value of game farm tourism. Koedoe 46(2):103–112
World Resources Institute (2004) Reefs at risk in the Caribbean. WRI, Washington. https://www.wri.org/research/reefs-risk-caribbean
World Tourism Organization Barometer (2015). https://tourlib.net/wto/UNWTO_Barometer_2015_01.pdf
World Tourism Organization UNWTO (2015a) Exports from International Tourism Rise 4% in 2015. http://media.unwto.org/press-release/2016-05-03/exports-international-tourism-rise-4-2015
World Tourism Organization UNWTO (2015b) Why tourism? http://www2.unwto.org/content/why-tourism
WTTC (2013) Travel and tourism. Economic impact 2013. World Travel and Tourism Council, London
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Ecotourism and Wildlife Management, School of Agriculture and Agricultural Technology, Federal University of Technology, Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria
Bukola Omotomilola Adetola
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bukola Omotomilola Adetola .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Microbiology, Bayelsa Medical University, Yenagoa, Bayelsa State, Nigeria
Sylvester Chibueze Izah
Goodnight Family Department of Sustainable Development, Living Learning Center, Appalachian State University, Boone, NC, USA
Matthew Chidozie Ogwu
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Adetola, B.O. (2023). Biodiversity Conservation and Tourism Sustainability in Africa. In: Izah, S.C., Ogwu, M.C. (eds) Sustainable Utilization and Conservation of Africa’s Biological Resources and Environment. Sustainable Development and Biodiversity, vol 32. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6974-4_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6974-4_2
Published : 18 April 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-6973-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-6974-4
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
World Bank Approves $68 Million to Support Diversification of Tourism in The Gambia
WASHINGTON, June 13 , 2022 – The World Bank’s Board of Executive Directors approved on June 9, a $68 million grant from the International Development Association (IDA)* to support the diversification and climate resilience of the tourism sector in The Gambia.
The Tourism Diversification and Resilience in The Gambia project aims to assist the country by strengthening the institutional and policy framework, improve capabilities and access to funds for tourism related Micro Small Medium Enterprises (MSME) suppliers, and enhance the attractiveness of selected existing but underdeveloped destinations. The project will also strengthen the sustainability of the coastal areas.
“The Gambia’s tourism sector is a key contributor to GDP and employment generation, but it is prone to both, endogenous and exogenous risks that limit the sector’s potential for inclusive and resilient growth ,” said Feyi Boroffice, World Bank Resident Representative for The Gambia.
The five-year project will take a targeted approach to integrate gender and climate actions across components and leverage significant global knowledge and experience in tourism recovery, particularly related to building back better in post COVID-19 situations.
The project goal would be achieved through the following main interventions:
1. Policy framework and MSME participation which aims to address selected/identified key bottlenecks in the tourism ecosystem in The Gambia, to ensure the sector realizes its potential as a source of sustainable and inclusive growth. The activities under this will focus on: (a) strengthening capacity for collecting relevant tourism data to inform policy decision-making; (b) enhancing marketing to promote recovery and diversification beyond traditional source markets and segments; and (c) promoting the diversification of the destination and products beyond ‘sun and sea’. (d) promoting tourism MSMEs’ sustainable integration into value chains with established end markets
2. Infrastructure support for the diversification and resilience of the tourism sector. This component will focus on strengthening and upgrading infrastructure to better preserve existing assets by being more resilient to the impacts of hazards and climate change as well as enhance the attractiveness of tourism sites and promote economic development.
“ The project takes a holistic approach to tourism development by focusing on tourism infrastructure, enablers, attractors and promoters to support the tourism ecosystem, provide opportunities for women and build climate resilience,” said Rafael Pardo, Financial Sector Specialist and Project Task Team Leader
* The World Bank’s International Development Association (IDA), established in 1960, helps the world’s poorest countries by providing grants and low to zero-interest loans for projects and programs that boost economic growth, reduce poverty, and improve poor people’s lives. IDA is one of the largest sources of assistance for the world’s 74 poorest countries, 39 of which are in Africa. Resources from IDA bring positive change to the 1.3 billion people who live in IDA countries. Since 1960, IDA has provided $458 billion to 114 countries. Annual commitments have averaged about $29 billion over the last three years (FY19-FY21), with about 70 percent going to Africa.
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here .

COMMENTS
The Regional Commission of Africa meeting was held as tourism's recovery gets underway across the continent. According to the latest UNWTO data, for the first seven months of the year, international arrivals across Africa were 171% up on 2021 levels, driven largely by regional demand. To help Members capitalize on the sector's return, and ...
Africa's travel and tourism sector employed more than 24 million people in 2019, according to the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC). But COVID-19 has created an unprecedented crisis for the tourism industry in Africa and around the world, crushing the supporting food, service, and manufacturing sectors that depend on tourism for ...
5.8 Opportunity: Diversification and collaboration 25 6. UNLOCKING THE OPPORTUNITY 27 CONCLUSION 29. ... Despite this bounce back in 2012, Travel & Tourism in Africa failed to maintain any sustained period of growth in the 2010s. Slow economic growth, disease outbreaks, political instability, and a lack of government support for ...
Travel & Tourism in Africa has expanded significantly since the new millennium. In 2022, it accounted for nearly 6% of the region's economy and supported 22 million jobs. This report brings a much-needed focus on Africa's Travel & Tourism and underscores its role in promoting economic, environmental, and social progress across the continent.
Through the African Union's Agenda 2063, the continent is building its productive capacities, strengthening regional integration, and embracing economic diversification. On this note, tourism in Africa continues to develop and strongly contribute to the continent's gross domestic product (GDP). At the global level, the United Nations ...
Tourism in Africa has experienced not only strong growth in terms of arrivals, but also in terms of expenditures and revenues and this has been driven primarily by a high number of international arrivals. ... Over the past six decades, tourism has experienced continued expansion and diversification, becoming one of the largest and fastest ...
African Destinations Meet to Plan Growth and Sustainable Future for Tourism. Africa; 9 Jun 2020 Recovery and resilience were the central themes as the members of the World Tourism Organization's Regional Commission for Africa (CAF) met for the 63rd time today.Reflecting the extraordinary circumstances, the meeting was held virtually, bringing together Ministers of Tourism from across the ...
Governments in Africa are showing increasing interest in tourism as a source of growth and diversification. Recent work indicates that tourism in Africa can contribute effectively to economic development. The tourism industry throughout Africa often operates below international competitive standards, but several products already meet international standards of excellence.
Governments in Africa are showing increasing interest in tourism as a source of growth and diversification. Recent work indicates that tourism in Africa can contribute effectively to economic development. The tourism industry throughout Africa often operates below international competitive standards, but several products already meet international standards of excellence.
Tourism in Africa : harnessing tourism for growth and improved livelihoods / Iain Christie, Eneida Fernandes, Hannah Messerli, and Louise Twining-Ward. pages cm. — (Africa development forum series) Includes bibliographical references and index. ISBN 978-1-4648-0190-7 — ISBN 978-1-4648-0197-6 (electronic) 1. Tourism—Africa, Sub-Saharan. 2.
By 2030, consumer spending on tourism, hospitality, and recreation in Africa is projected to reach about $261.77 billion, $137.87 billion more than in 2015. From 1998 to 2015, service exports ...
The importance of tourism toward the realization of economic diversification and structural transformation in Africa was conceptualized in the report by highlighting the sector's contribution to foreign exchange constraint easing, job creation, and its linkage with other sectors of the economy (p. 3).
Tanzania is a globally recognized destination for nature-based tourism, a competitive market segment in eastern and southern Africa. Beyond attracting tourists, the country's landscapes and seascapes produce a wide range of ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration and biodiversity co-benefits that are not efficiently priced and often generate little or no financial return.
sub-Saharan African region to put in place strategic plans to develop the tourism sector as an. economic gro wth engine and a catalyst for development in the region at l arge and at c ountry ...
Tourism in Africa is a captivating journey that offers a blend of cultural diversity, breathtaking landscapes, and unparalleled wildlife encounters. With its rich heritage and abundant natural wonders, Africa has emerged as a prime destination for travelers seeking experiences and adventures. This overview explores the current state of tourism ...
Abstract. The long-term viability of the tourism industry and the preservation of its principal attraction (nature) are inextricably linked. Biodiversity conservation is a fundamental obligation of all economic sectors and a unique paradigm in the tourist sector that makes tourism more biodiversity-friendly.
The following are key underpinnings of the continent's emergence in the global tourism economy. Africa offers abundant diversity; access from growing source markets (Europe, USA and Asia) to African destinations is improving through hubs such as Johannesburg, Nairobi, Addis Ababa and Lagos; there is a major consumer shift from pre-paid packages ...
This paper aims to use an augmented tourism demand model to examine the determinants of tourism diversification by using the data from 46 tourism markets and seven tourism activities in ... (2010) Using the panel cointegration approach to analyse the determinants of tourism demand in South Africa. Tourism Economics 16(3): 715-729. Crossref. ISI.
The meeting was organized by the Division for Africa, Least Developed Countries and Special Programmes, and brought together senior experts, policy makers and private sector representatives to discuss the role of tourism in economic diversification and poverty reduction in poor and vulnerable developing countries. Participants identified economic channels through which tourism could drive ...
WASHINGTON, June 13, 2022 - The World Bank's Board of Executive Directors approved on June 9, a $68 million grant from the International Development Association (IDA)* to support the diversification and climate resilience of the tourism sector in The Gambia.. The Tourism Diversification and Resilience in The Gambia project aims to assist the country by strengthening the institutional and ...
The complex nature of tourism, its strong inter-sectoral relationships and regional dimension challenge innovation. The advent of smart specialisation, which focuses on regional diversification across sectors, offers considerable and hitherto largely unrealized potential for developing innovative tourism policies within this new agenda. This paper addresses the understudied concept of tourism ...