- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Center for Arms Control and Non-Proliferation
April 27, 2017

Fact Sheet: Ballistic vs. Cruise Missiles

Ballistic missiles are powered initially by a rocket or series of rockets in stages, but then follow an unpowered trajectory that arches upwards before descending to reach its intended target. Ballistic missiles can carry either nuclear or conventional warheads.
There are four general classifications of ballistic missiles based on their range, or the maximum distance the missile can travel:
- Short-range: less than 1,000 kilometers (approximately 620 miles), also known as “tactical” ballistic missiles.
- Medium-range: between 1,000 and 3,000 kilometers (approximately 620-1,860 miles), also known as “theater” ballistic missiles.
- Intermediate-range: between 3,000 and 5,500 kilometers (approximately 1,860-3,410 miles)
- Long-range: more than 5,500 kilometers (approximately 3,410 miles), also known as intercontinental or strategic ballistic missiles. Intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) can fly much further than the minimum range; for example, Russia could hit Chicago with an ICBM launched from the Krasnoyarsk ICBM base, which is located 9,156 kilometers (5,689 miles) away.

Ballistic missiles have three stages of flight:
Boost Phase begins at launch and lasts until the rocket engine(s) stops firing and the missile begins unpowered flight. Depending on the missile, boost phase can last three to five minutes. Most of this phase takes place in the atmosphere.
Midcourse Phase begins after the rocket(s) stops firing. The missile continues to ascend toward the highest point in its trajectory, and then begins to descend toward Earth. This is the longest phase of a missile’s flight; for ICBMs, it can last around 20 minutes. During midcourse phase, ICBMs can travel around 24,000 kilometers per hour (15,000 miles per hour).
Terminal Phase begins when the detached warhead(s) reenter the Earth’s atmosphere and ends upon impact or detonation. During this phase, which can last for less than a minute, strategic warheads can be traveling at speeds greater than 3,200 kilometers per hour (1,988 miles per hour).

Cruise missiles remain within the atmosphere for the duration of their flight and can fly as low as a few meters off the ground. Flying low to the surface of the earth expends more fuel but makes a cruise missile very difficult to detect.
Cruise missiles are self-guided and use multiple methods to accurately deliver their payload, including terrain mapping, global positioning systems (GPS) and inertial guidance, which uses motion sensors and gyroscopes to keep the missile on a pre-programmed flight path. As advanced cruise missiles approach their target, remote operators can use a camera in the nose of the missile to see what the missile sees. This gives them the option to manually guide the missile to its target or to abort the strike.
To learn about missile defense, check out our fact sheet .
Sources: Department of Defense, Missile Defense Agency, Federation of American Scientists .

820 1st Street NE, Suite LL-180 Washington, D.C. 20002 Phone: 202.546.0795
Switch language:

Tomahawk Long-Range Cruise Missile
Tomahawk is a long-range, all-weather, subsonic cruise missile in service with the surface ships and submarines of the US and the UK’s Royal Navy.
Long-range subsonic cruise missile
Manufacturer
US Navy and Royal Navy
Williams International F415 cruise turbo-fan
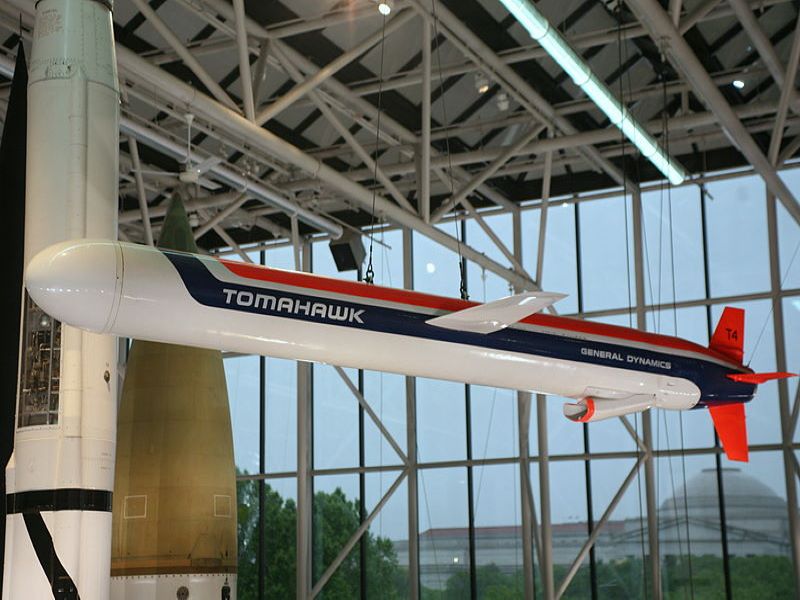

Tomahawk is a long-range, all-weather, subsonic cruise missile in service with the surface ships and submarines of the US and the UK’s Royal Navy. Originally produced by General Dynamics, Tomahawk is currently manufactured by Raytheon.
The Tomahawk Land Attack Missile (TLAM) can strike high-value or heavily defended land targets. The Block II TLAM-A missile achieved initial operating capability in 1984. The missile was first deployed in combat during Operation Desert Storm in 1991.
Recommended White Papers
Angle of Arrival/Direction-Finding Techniques
Advanced geolocation capabilities, recommended buyers guides.
Military messaging and naval communications software providers for the naval defence industry
Maritime solutions: subsystems for the naval industry, tomahawk missile variants.
The Tomahawk family of missiles includes a number of variants, carrying different warheads. The UGM-109A Tomahawk (Block II TLAM-A) carries a W80 nuclear warhead.
RGM / UGM-109C (Block III TLAM-C) is a conventional unitary variant, carrying a 1,000lb-class warhead. RGM / UGM-109D (Block III TLAM-D) is a submunitions dispenser variant armed with 166 combined-effects bomblets.
RGM / UGM-109E Tomahawk (Block IV TLAM-E) is the latest member in the Tomahawk missile family. It carries a 1,000lb-class unitary warhead for a maximum range of 900nmi.
The Tomahawk Block IV missiles were converted and upgraded to Block V in 2017. The upgraded Tomahawk includes extended range, enhanced navigation and communication systems and modernised data-link radio.
The upgrades were performed at Raytheon’s Tucson, Arizona facility. The US Navy will use the upgraded Tomahawk cruise missiles beyond 2040. Raytheon was contracted to integrate the upgraded navigation and communication systems into the Block IV Tactical Tomahawk (TACTOM) missile in March 2020. The upgraded version is known as the Block V TACTOM.
The Block Va variants will be named Maritime Strike and have the capability of hitting a moving target. The Block Vb will feature the Joint Multi-Effects Warhead System.
Tomahawk design features
The Tomahawk is designed to operate at very low altitudes while maintaining high-subsonic speeds. Its modular design enables the integration of numerous types of warheads, guidance and control systems.
The missile carries a nuclear or conventional payload. It can be armed with a nuclear or unitary warhead or a conventional submunitions dispenser with combined-effect bomblets. The missile has a 5.56m length, 51.8cm diameter and a 2.67m wingspan. The weight of the missile is 1,315kg. It has a life span of 30 years.
The Tomahawk weapon system includes the Tomahawk missile, Theatre Mission Planning Centre (TMPC) / Afloat Planning System and the Tomahawk weapon control system (TWCS) for surface vessels or combat control system (CCS) for submarines.
Guidance and control
The Tomahawk Block IV uses GPS navigation and a satellite data-link to continue through a pre-set course. The missile can be reprogrammed in-flight to a new target.
The two-way satellite communications are used to perform post-launch mission changes throughout the flight. The on-board camera provides imagery of the target to the commanders before the strike.
The guidance system is assisted by Terrain Contour Matching (TERCOM). The Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation (DSMAC) system or GPS provide terminal guidance.
The Tactical Tomahawk Weapons Control System (TTWCS) integrated within the ship’s systems computes the path to engage targets. The system enables the planning of new missions on board the launch vessel. TTWCS is also used to communicate with multiple missiles for reassigning the targets and redirecting the missiles in flight.
The Block IV Tomahawk missile is outfitted with advanced electronic support measure (ESM) seeker in Block IV Tomahawk missile. Its joint multi-effects warhead enables the commander to control the blast.
The Tomahawk Block IV missile is powered by a Williams International F415 cruise turbo-fan engine and ARC MK 135 rocket motor. The propulsion provides a subsonic speed of 880km/h.
Tomahawk launch platforms
The missile can be launched from over 140 US Navy ships and submarines and Astute and Trafalgar class submarines of the Royal Navy. All cruisers, destroyers, guided missile and attack submarines in the US Navy are equipped with a Tomahawk weapons system.
US Navy launch platforms were modified to accommodate upgraded Tomahawk missile variants. Four Ohio class nuclear ballistic missile submarines were converted into cruise missile submarines for firing Tomahawk missiles. The Virginia class submarines and the Royal Navy Astute class submarines were also fitted with new vertical launch modules for Tomahawk missile.
Tomahawk orders and deliveries
The US signed a foreign military sales (FMS) agreement with the UK in 1995 to supply 65 Tomahawks for use with the Royal Navy nuclear submarines. The first batch of missiles was delivered in 1998.
The US Government approved an agreement in 2003 to deliver 65 Tomahawk Block IV missiles for the UK. In August 2004, the US Navy placed a $1.6bn multi-year procurement contract with Raytheon for 2,200 Tomahawk Block IV missiles.
Raytheon was awarded a $346m production contract for 473 Tomahawk Block IV cruise missiles in March 2006. The contract includes 65 submarine torpedo tube-launched missiles for the Royal Navy. The Block IV entered service with the Royal Navy in March 2008.
Raytheon was awarded a $207m-worth firm-fixed-price contract in March 2009 for 207 Tomahawk Block IV All-Up-Round (AUR) missiles.
The 2,000th Tomahawk Block IV missile was delivered to the US Navy in February 2010.
The US Navy placed a $338m contract with Raytheon in June 2012 for the delivery of 361 Tomahawk Block IV tactical cruise missiles. Another contract worth $254.6m was awarded for Tomahawk Block IV in the same year.
Raytheon delivered the 3,000th Tomahawk Block IV to the US Navy in January 2014 as part of the ninth Block IV production contract.
The US Navy awarded a $251m contract to Raytheon for the production and delivery of Tomahawk Block IV missiles for both the US Navy and Royal Navy in September 2014.
A $25.9m contract for Tomahawk missile composite capsule launching systems (C/CLS) was awarded in December 2014. The C/CLS is integrated with the nuclear-powered fast-attack submarines and nuclear-powered guided-missile submarines, allowing the missile to be launched from submarines.
Tomahawk Block IV missile demonstrated its moving target capability in tests conducted in February 2015.
Raytheon received a $122m contract from the US Navy in March 2015 for the production of 114 Tomahawk Block IV all-up round missiles. Raytheon conducted an active seeker test flight for the Tomahawk Block IV cruise missile in January 2016.
The 4,000th Tomahawk Block IV missile was delivered to the US Navy in August 2017. The US Navy warships and submarines launched 66 GPS-enabled Tomahawk missiles at Syrian chemical weapon facilities in 2018.
Raytheon planned to undertake recertification and modernisation programmes for Tomahawk Block IV missile in 2019 to add maritime strike capability and multiple-effects warhead upgrades to the missiles.
Raytheon received a $349m contract for phase two of the Maritime Strike Tomahawk Rapid Deployment Capability to improve the Tomahawk cruise missile system in August 2019. Work will be executed in various locations across the US until February 2023.
Related Projects
More Projects
Transwing Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL) UAS, US
Combat boat 90 (cb90), sweden, naval station mayport, jacksonville, florida, kings bay naval submarine base, sign up for our daily news round-up.
Give your business an edge with our leading industry insights.
Sign up to the newsletter
Your corporate email address.
Naval Technology In Brief
Global Defence Technology
Thematic Take
I consent to Verdict Media Limited collecting my details provided via this form in accordance with Privacy Policy
Thank you for subscribing
View all newsletters from across the GlobalData Media network.
Advertisement
How Cruise Missiles Work
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email

Tomahawk cruise missiles frequently appear in the news because they are the U.S. weapon of choice for a variety of quick-strike operations. With all of the missiles in the U.S. arsenal, have you ever wondered why cruise missiles seem to come up so often?
In this edition of HowStuffWorks , we will look at cruise missiles so that you can understand what they are, how they operate and why they are ideal for certain scenarios.

A cruise missile is basically a small, pilotless airplane . Cruise missiles have an 8.5-foot (2.61-meter) wingspan, are powered by turbofan engines and can fly 500 to 1,000 miles (805 to 1,610 km) depending on the configuration.
A cruise missile's job in life is to deliver a 1,000-pound (450-kg) high-explosive bomb to a precise location -- the target. The missile is destroyed when the bomb explodes. Since cruise missiles cost between $500,000 and $1,000,000 each, it's a fairly expensive way to deliver a 1,000-pound package.

Cruise missiles come in a number of variations (see the links at the end of the article for more information) and can be launched from submarines , destroyers or aircraft.

When you hear about hundreds of cruise missiles being fired at targets, they are almost always Tomahawk cruise missiles launched from destroyers.

Cruise missiles are 20 feet (6.25 meters) long and 21 inches (0.52 meters) in diameter. At launch, they include a 550-pound (250-kg) solid rocket booster and weigh 3,200 pounds (1450 kg).
The booster falls away once it has burned its fuel. The wings, tail fins and air inlet unfold, and the turbofan engine takes over.
This engine weighs just 145 pounds (65 kg) and produces 600 pounds of thrust burning RJ4 fuel. The fuel load is 800 to 1,000 pounds (about 450 kg) of fuel at launch, or approximately 150 gallons (600 liters). The missile has a cruising speed of 550 mph (880 kph).

The hallmark of a cruise missile is its incredible accuracy. A common statement made about the cruise missile is, "It can fly 1,000 miles and hit a target the size of a single-car garage." Cruise missiles are also very effective at evading detection by the enemy because they fly very low to the ground (out of the view of most radar systems ).
Four different systems help guide a cruise missile to its target:
- IGS - Inertial Guidance System
- Tercom - Terrain Contour Matching
- GPS - Global Positioning System
- DSMAC - Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation
The IGS is a standard acceleration-based system that can roughly keep track of where the missile is located based on the accelerations it detects in the missile's motion ( click here for a good introduction). Tercom uses an on-board 3-D database of the terrain the missile will be flying over. The Tercom system "sees" the terrain it is flying over using its radar system and matches this to the 3-D map stored in memory. The Tercom system is responsible for a cruise missile's ability to "hug the ground" during flight. The GPS system uses the military's network of GPS satellites and an onboard GPS receiver to detect its position with very high accuracy.
Once it is close to the target, the missile switches to a "terminal guidance system" to choose the point of impact. The point of impact could be pre-programmed by the GPS or Tercom system. The DSMAC system uses a camera and an image correlator to find the target, and is especially useful if the target is moving. A cruise missile can also be equipped with thermal imaging or illumination sensors (as used in smart bombs ).
Frequently Asked Questions
How do cruise missiles navigate to their target, what advancements have been made in cruise missile technology, lots more information, related articles.
- How Stinger Missiles Work
- How Sidewinder Missiles Work
- How Smart Bombs Work
- How MOAB Works
- How Patriot Missiles Work
- How Stealth Bombers Work
- How Apache Helicopters Work
- How F-15s Work
- How Airplanes Work
- How Gas Turbine Engines Work
- How Radar Works
- How GPS Receivers Work
- How Rocket Engines Work
More Great Links
- USAF Fact Sheet: AGM-86B/C Missiles
- U.S. navy Fact File: Tomahawk Cruise Missile
- BBC News: NATO's firepower: The cruise missile
- Time.com: Tomahawk Cruise Missile
- Analysis: Tomahawks, Submarines and the F-111
Launch systems
- Arleigh Burke Class (AEGIS) Guided Missile Destroyers, USA
- SSN Los Angles Class Attack Submarine, USA - U.S. subs that launch cruise missiles
- SSN Astute Class Attack Submarine, UK - Royal Navy subs that launch cruise missiles
- B-52H Stratofortress Long-Range Multi-Role Bomber, USA
- B-2 Spirit Stealth Bomber, USA
Miscellaneous
- Williams F107-WR-101 Turbofan Engine
- Digital Imagery Workstation Suite (DIWS) - generates the Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation (DSMAC) reference scenes
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:

- Missiles of the World
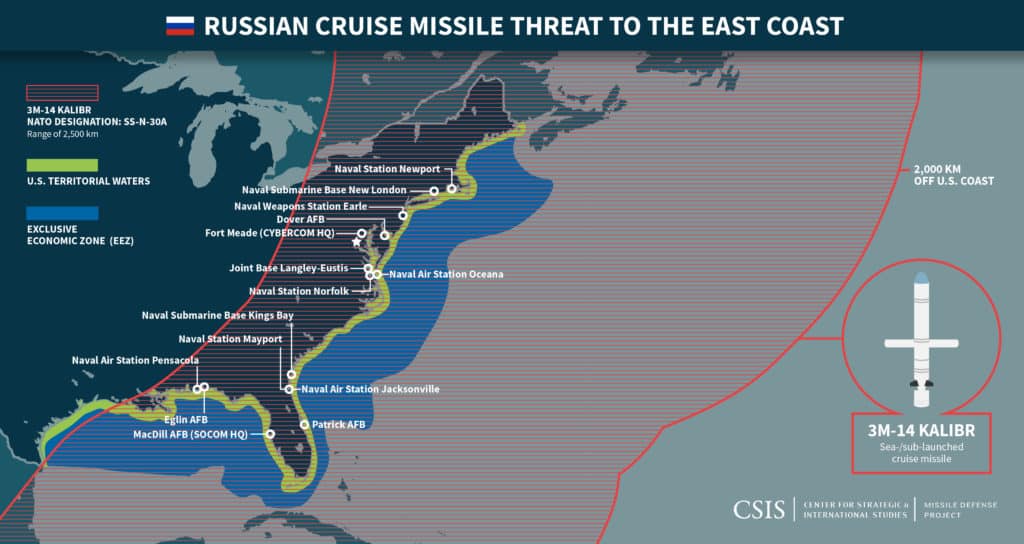
3M-14 Kalibr (SS-N-30A)
The 3M14 Kalibr (NATO: SS-N-30A) is a Russian land attack cruise missile (LACM) and improved version of the 3M-14E “Club” LACM. The SS-N-30A has an estimated range of around 1,500 to 2,500 km and has become a mainstay in the Russian Navy’s ground-strike capabilities.
Kalibr (SS-N-30A) at a Glance

Kalibr Development
Although commonly referred to as the Kalibr cruise missile in media reports, the SS-N-30A is in fact just one part of the larger Kalibr family of Russian sea-launched missiles, which includes the SS-N-27 (Sizzler) anti-ship cruise missile and the 91R anti-submarine missile. All three Kalibr missiles share common Kalibr vertical launch system (VLS) tubes, which are quickly becoming a mainstay of the Russian Navy’s cruise missile launch capabilities. According the U.S. Office of Naval Intelligence, a “high ranking Russia defense industry official” said of Kalibr system in 2011:
“Russia plans to deploy KALIBR capability on all new design construction nuclear and non-nuclear submarines, corvettes, frigates, and larger surface ships. KALIBR provides even modest platforms, such as corvettes, with significant offensive capability and, with the use of the land attack missile, all platforms have a significant ability to hold distant fixed ground targets at risk using conventional warheads. The proliferation of this capability within the new Russian Navy is profoundly changing its ability to deter, threaten or destroy adversary targets. It can be logically assumed that KALIBR capability will be retrofitted on those larger Soviet legacy ships and submarines that undergo major overhauls and/or modernization.” 1

Service History
Export variants.
- Office of Naval Intelligence, The Russian Navy: A Historic Transition (Office of Naval Intelligence, December 2015): 33, http://www.oni.navy.mil/Portals/12/Intel%20agencies/russia/Russia%202015print.pdf?ver=2015-12-14-082038-923.
- Christopher P. Cavas, “Is Caspian Sea Fleet a Game-Changer?” Defense News , October 11, 2015, http://www.defensenews.com/story/defense/naval/ships/2015/10/11/caspian-sea-russia-navy-missiles-attack-strike-military-naval-syria-frigate-corvette-lcs-littoral-combat-ship/73671188/
- USNORTHCOM and NORAD Posture Statement: Hearing before the Committee on Armed Services, Subcommittee on Strategic Forces House of Representatives, 114th Cong, 2 (April 14, 2016) (statement by Admiral William E. Gortney, Commander, U.S. Northern Command and North American Aerospace Defense Command), http://docs.house.gov/meetings/AS/AS29/20160414/104621/HHRG-114-AS29-Wstate-GortneyB-20160414.pdf
- Vladimir Isachenkov, “Russia conducts war games involving numerous missile launches,” Associated Press, October 30, 2015, http://www.usnews.com/news/world/articles/2015/10/30/russia-holds-war-games-involving-numerous-missile-launches
- Janes’s Weapons, Naval 2012-2013 (Janes Information Group, 2012), 15.
- “Russia Beefs Up Baltic Fleet Amid NATO Tensions: Reports”, Reuters, October 26, 2016, http://www.reuters.com/article/us-russia-defence-baltic-sweden-idUSKCN12Q1HB.
- Mission Statement
- Advisors to the Board
- Military Fellows
- Jobs at MDAA
- Arizona AETOS ’25
- University of Hawaii Space Science Initiative
- USC SHIELD ’24
- USC SHIELD ’23
- USC SHIELD ’22
- USC SHIELD Alerts
- USC SHIELD in the News
- 2024 European Missile Defender of the Year and Regional IAMD Coalitions Conference
- Ronald Reagan Missile Defense Site, Vandenberg SFB
- Kauai Veteran’s Eternal Memorial and Missile Defense Viewing Site
- Lessons Learned Series
- Write Your Representative
- April 12th, 2022 U.S. Missile Defense – An Overview of Past, Current, and Future Roles and Responsibilities
- Virtual CRT: U.S. Missile Defense – An Overview of Past, Current, and Future Roles and Responsibilities
- MDAA Alert: The Roles and Responsibilities of Missile Defense
- Threat News
- Missile Defense News
- Air Defense News
- MDAA in the News
- Threat Basics
- Ukrainian War Updates
- Taiwan Incursion Updates
- Global Missile Tracker
- Space Threats Updates
- Notable Missile Tests
- Combat Launches
- Future Missile Threats
- U.S. Missile Defense
- Missile Defense of U.S. Partners
- Missile Defense Intercept Test Record
- Operational Intercepts by System
- Future BMD Systems
- Discontinued Programs
- U.S. Air Defense
- Air Defense of U.S. Partners
- Future Air Defense Systems
- Alerts Archive
- MDAA U.S. Ballistic Missile Defense Overview
- MDAA System/Issue Briefs
- MDAA Country Briefs
- Foreign Military Sales by Country
- 3D Panoramas
- Additional Resources

- Cruise Missile Basics
What is a cruise missile?
Cruise missiles, although similar to ballistic missiles in some regards, provide an alternate means to deliver a lethal payload rapidly and accurately to a target. Cruise missiles differ from ballistic missiles in that they fly towards their target at lower altitudes, remaining within the Earth’s atmosphere throughout their trajectory. Cruise missiles are defined as “an unmanned self-propelled guided vehicle that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path and whose primary mission is to place an ordnance or special payload on a target.” [1] Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned control-guided helicopters or aircraft can be included in this definition [2] , but will not be discussed on this page.
The cruise missile has its beginnings in World War I, when the U.S. Army developed the Kettering Bug, an unmanned aerial bomb designed to strike targets beyond the range of artillery and too dangerous for piloted aircraft. However, the Kettering Bug was never used in combat. [3] Instead, the modern cruise missile originates more from the V-1 Flying Bomb used by the Germany in the last months of World War II. [4]
Launch Platforms
Cruise missiles are capable of being launched from multiple ground, air, sea and submarine platforms. Both fighter and long-range bomber aircraft are capable of carrying and launching cruise missiles. [5] On the ground, cruise missiles are most commonly launched by road-mobile systems due to the inherent advantages of mobility, but they can also be launched from fixed platforms. [6]

Russian warships in the Caspian Sea launch Kalibr cruise missiles towards targets inside Syria.
At sea, various surface ships and submarines can launch cruise missiles. Submarines are capable of launching while surfaced or submerged using torpedo fixtures or vertical launch tubes. [7] In April 2010 Kontsern-Morinformsistema-Agat, a Russian company, began marketing a version of the Russian Kalibr cruise missile housed in and capable of being launched from a standard shipping container. [8] This would allow any vehicle capable of carrying a standard shipping container to become a discreet platform from which to launch cruise missiles. [9]
Propulsion and Flight
Cruise missiles utilize jet engines as their primary method of propulsion. Most cruise missiles are subsonic and use Turbofan and Turbojet engines. While less common, supersonic and hypersonic cruise missiles utilize Ramjet and Scramjet engines. [10] Some also use rocket motor propulsion as a booster in the first phase of flight [11] or to accelerate to supersonic speeds in the terminal phase. [12]
Cruise missiles can fly to their targets at varying altitudes as long as they remain within the atmosphere. The trajectory of most remains close to the Earth’s surface, sometimes skimming just meters above the ground. Their low flight path makes it much harder for most radar and sensor systems to detect the missile, unless the radar or sensor system is airborne and directed towards the ground. [13] Some cruise missiles will fly only at high altitudes and dive sharply down once they reach their target. Flying at high altitude can extend the range of the missile because it’s more fuel-efficient than flying at lower altitudes. However, this also makes the missile more susceptible to missile defense systems since today’s radars and sensors are typically positioned to detect and track high altitude threats. [14] Cruise missiles can also mix their flight trajectory between high and low altitude in order to get the benefits of both. In this instance, cruise missiles will typically fly at a high altitude early in their flight to help extend their range, but as they approach their target, or missile defenses, they will fly down to a lower sea skimming/terrain hugging altitude to help it evade detection and defenses. [15]
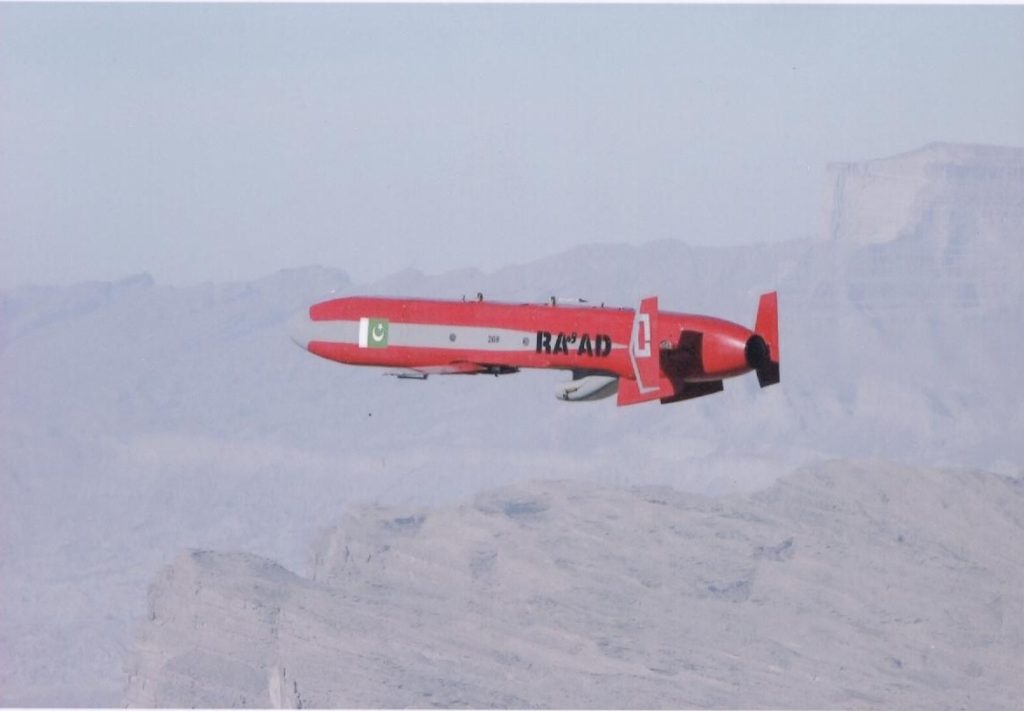

Flight test of Pakistan’s Ra’ad cruise missile.
Cruise missiles can use multiple guidance methods in order to accurately place their ordinance on the desired target and avoid missile defense systems. One of the first methods used by cruise missiles was inertial guidance, which is still used today and allows the missile to fly along a flight path programmed prior to launch. [16] Another guidance method is terrain contour matching (TERCOM), which compares a terrain map to the current terrain the missile is flying over to ensure the missile is flying on the correct path. [17] Some use GPS systems, which require connection to either GPS or GLONASS satellite system, but can help ensure the missile follows the correct flight path and strikes the final target using specific coordinates with a high degree of accuracy. [18]
Other guidance methods are primarily used in the terminal phase of flight to increase accuracy. One is a laser guided system which uses a sensor to detect its target painted by a laser, however this can be unreliable because dust and smoke can interfere with the laser or the missile may not always be able to see the laser or painted target. [19] Another terminal guidance method is TV guidance, in which an operator uses a camera in the nose of the missile to visually identify and manually guide the missile to the target in its final phase. This method also gives the operator the option to abort the strike in the final phase if an anomaly is detected. [20] A radar seeker is also used in the nose of some missiles to identify and/or keep the missile on target in the terminal phase. These radar seekers use either passive radar, which detect radar emissions of their target, or active radar, which emit their own radar to detect their target. [21] Infrared (IR) guidance – directing the missile towards heat emitting objects, such as engines [22] – may also be used by cruise missiles in the terminal phase. [23] However, because of its simplicity, IR guidance cannot differentiate between friendly, adversarial, or extraneous IR signals in a crowded battlefield, and is usually used in conjunction with other guidance systems. [24] The last guidance system used by cruise missiles is Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation (DSMAC), which uses a camera in the missile to find the desired target and match it to a stored image using an image correlator. [25]
Cruise missiles are typically armed with conventional or nuclear warheads, but can also be equipped with chemical or biological warheads. [26] The warhead weight and yield can vary widely, depending on the specific cruise missile and its mission.
[1] “Cruise Missiles.” Federation of American Scientists. http://fas.org/nuke/intro/cm/
[3] “Kettering Bug.” UAVGLOBAL. http://www.uavglobal.com/kettering-bug/ ; “War Machines: Cruise Missile.” National Geographic. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AD8Kr0f1tEY
[4] Hickman, Kennedy. “World War II: V-1 Flying Bomb.” About Education. http://militaryhistory.about.com/od/artillerysiegeweapons/p/v1.htm
[5] N.R.P. “Explained: How Cruise Missiles Work!” Defencyclopedia. https://defencyclopedia.com/2014/08/01/explained-how-cruise-missiles-work/
[8] Stott, Michael. “Deadly New Russian Weapon Hides in Shipping Container.” Reuters. http://www.reuters.com/article/us-russia-weapon-idUSTRE63P2XB20100426
[9] Lewis, Jeffrey, Nikolai Sokov. “Sokov on Russian Cruise Missiles.” Arms Control Wonk. http://www.armscontrolwonk.com/archive/207801/sokov-on-russian-cruise-missiles/
[11] Brain, Marshall. “How Cruise Missiles Work.” How Stuff Works. http://science.howstuffworks.com/cruise-missile.htm
[12] N.R.P. “Explained: How Cruise Missiles Work!” Defencyclopedia. https://defencyclopedia.com/2014/08/01/explained-how-cruise-missiles-work/
[22] Kopp, Carlo. “Heat-Seeking Missile Guidance.” Air Power Australia. http://ausairpower.net/TE-IR-Guidance.html
[23] N.R.P. “Explained: How Cruise Missiles Work!” Defencyclopedia. https://defencyclopedia.com/2014/08/01/explained-how-cruise-missiles-work/
[25] Brain, Marshall. “How Cruise Missiles Work.” How Stuff Works. http://science.howstuffworks.com/cruise-missile.htm
[26] “Ballistic and Cruise Missile Threat.” Federation of American Scientists. http://fas.org/irp/threat/missile/naic/part02.htm ; Norris, Robert S., Hans M. Kristensen. “Nuclear Cruise Missiles.” Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. http://bos.sagepub.com/content/63/6/60.full
Missile Threat and Proliferation
- Missile Payload Destruction Cost Comparisons
- Technological Threat Assessment
- War By 2025 Threat Analysis
- Ballistic Missile Basics
- Hypersonic Weapon Basics
- Rocket and Mortar Basics
- Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) Basics
- Non-State Actors
- Israel-Hamas War Updates
- United States Incursion Tracker
- World Drone Comparison
- Dong Feng-16 (CSS-11)
- Dong Feng-15 (CSS-6)
- Dong Feng-11 (CSS-7)
- M-7 (8610)/CSS-8
- Dong Feng-12 (CSS-X-15)
- Dong Feng-3 (CSS-2)
- Dong Feng-21 (CSS-5)
- Dong Feng-21D (CSS-5)
- Dong Feng-26
- Dong Feng-4 (CSS-3)
- Dong Feng-5 (DF-5)
- Dong Feng-31 (CSS-10)
- Dong Feng-41(CSS-X-20)
- DH-10 / CJ-10
- Changjian-20 (CJ-20)
- DF-ZF Hypersonic Glide Vehicle
- Dong Feng-17
- Chinese Spy Balloons
- Hwasong-17/KN-27
- Pukguksong-3 (KN-26)
- KN-02 (Toksa)
- Hwasong-5 (Scud-B Variant)
- Hwasong-6 (Scud-C Variant)
- Hwasong-9 (Scud-ER/Scud-D Variant)
- Polaris-2 (Pukguksong-2/KN-15)
- Taepodong-1
- Hwasong-12/KN-17
- Taepodong-2
- KN-08 / Hwasong-13
- Hwasong-14/KN-20
- Hwasong-15/KN-22
- 3M22 Zircon
- Avangard (Hypersonic Glide Vehicle)
- RS-26 Rubezh
- OTR-21 Tochka (SS-21 Scarab)
- SS-1 Scud-A
- R-17 Elbrus (SS-1 Scud-B)
- S-300P Air and Missile Defense System
- S-300V Air and Missile Defense System
- S-400 Triumf Air Defense System
- SS-1d Scud-C
- R-17 VTO/SS-1e (Scud-D)
- Iskander-M (SS-26)
- Kh-47M2 Kinzhal (“Dagger”)
- SS-18 Satan/R-36M2 Voyevoda
- SS-19 Stiletto
- RS-12M Topol (SS-25 Sickle)
- SS-27 / Topol-M
- SS-27 Mod 2 / RS-24 Yars
- RS-28 Sarmat (Satan 2)
- AS-15 Kent (Kh-55 Granat)
- RK-55 Relief (SS-N-21 Sampson)
- 3M-54 Klub (SS-N-27 Sizzler)
- 3M-14 Kalibr (SS-N-30A)
- P-15 Termit (SS-N-2 Styx)
- P-6 Progress/SS-N-3C Shaddock
- P-120 Malakhit (SS-N-9 Siren)
- P-270 Moskit/SS-N-22 Sunburn
- P-500 Bazalt (SS-N-12 Sandbox)
- P-700 Granit/SS-N-19 “Shipwreck”
- KH-35 (SS-N-25 Switchblade)
- P-800 Oniks (SS-N-26 Strobile)
- P-1000 Vulkan
- R-29R / SS-N-18 Stingray
- R-29RM / SS-N-23 Skiff
- SS-N-30 Bulava
- Tondar-69 (M7, CSS-8)
- Natanz Enrichment Facility
- Fordow Uranium Enrichment Plant
- Arak Heavy Water Nuclear Reactor
International Cooperation
Missile Defense Advocacy Alliance
515 King Street Suite 330 Alexandria VA, 22314 Phone: 703.299.0060 [email protected]
Quick Links
- Privacy Policy
© Missile Defense Advocacy Alliance 2024
The Air Force’s New Stealth Cruise Missile Is a Go. But Do We Need It?
Let's make sense of the controversial Long Range Stand Off.
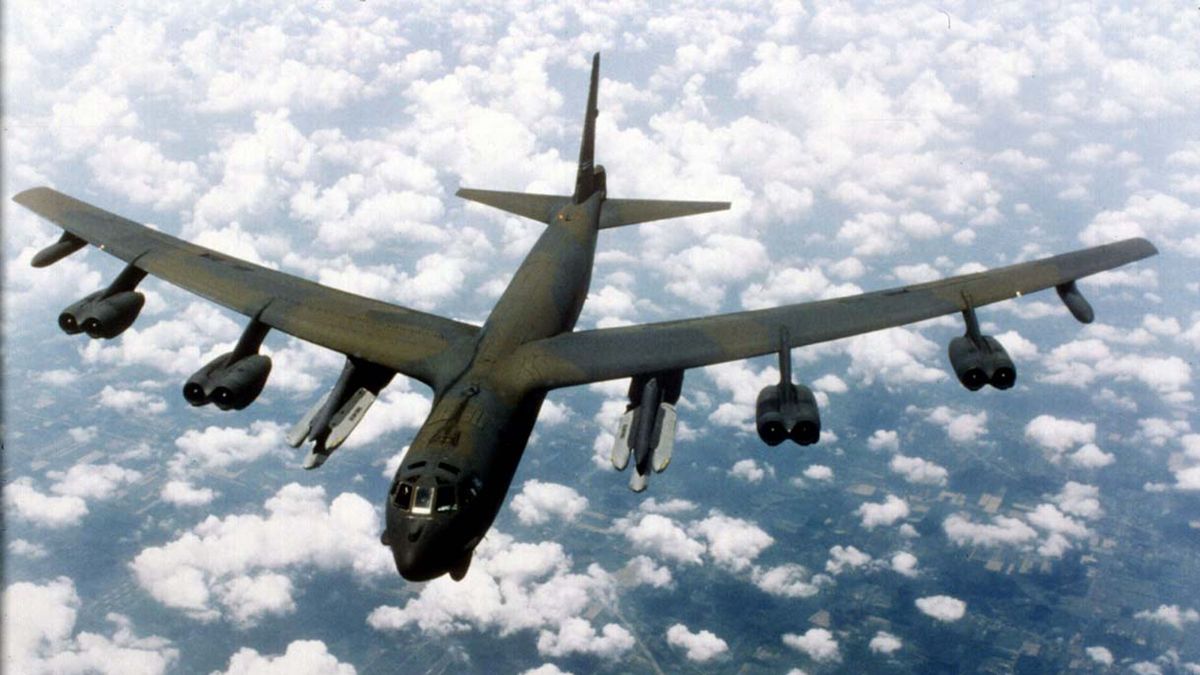

- The Long Range Stand Off (LRSO) missile will arm Air Force strategic bombers.
- LRSO will have the range to make even B-52s effective nuclear platforms.
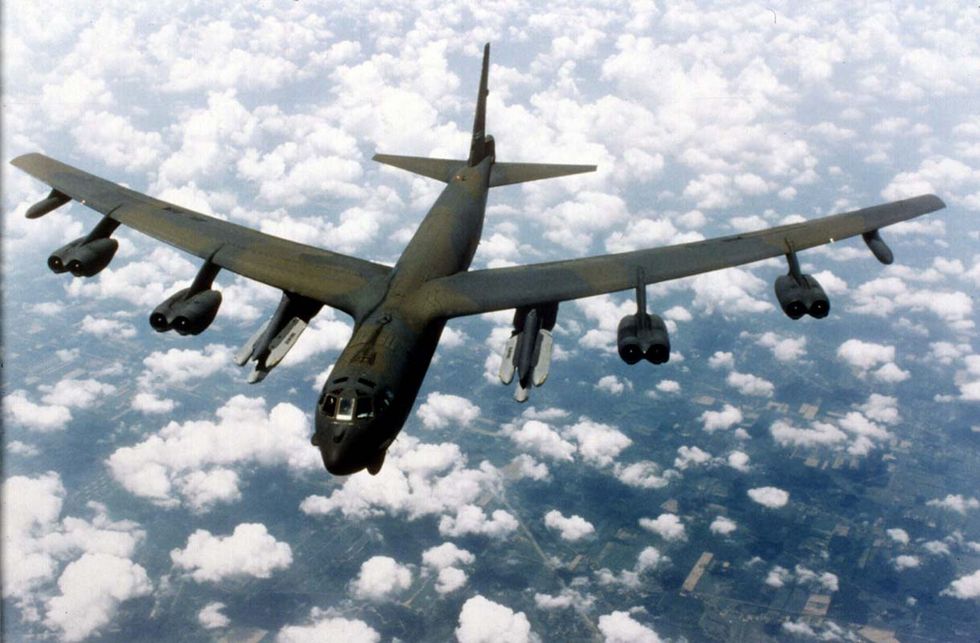

The U.S. Air Force has awarded Raytheon a contract to develop the service’s next-generation stealth cruise missile. The Long Range Stand Off (LRSO) missile will arm B-21 Raider and B-52 Stratofortress bombers, allowing them to launch missiles against targets without penetrating enemy airspace.
The Air Force flies two types of nuclear-capable bombers: the B-2 Spirit and B-52H Stratofortress. (The B-1 Lancer is no longer capable of carrying nukes and is now a conventional munitions-only bomber.) The bombers are armed with two kinds of nuclear weapons: the B61 and B83 free-fall gravity bombs, as well as the AGM-86B Air Launched Cruise Missile (ALCM).
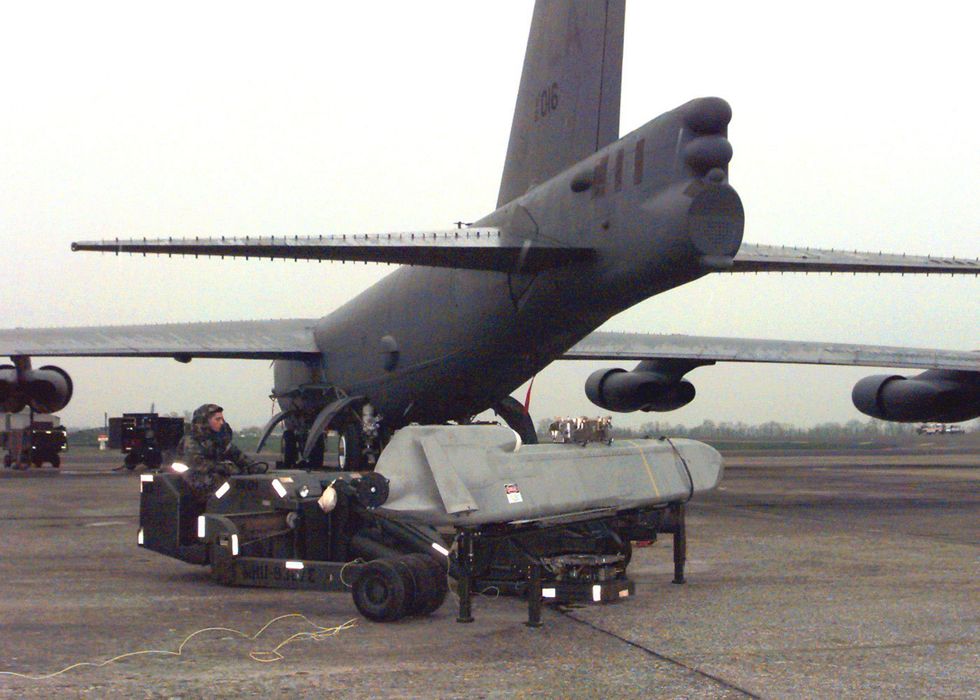

While free-fall bombs typically have large explosive yields (the B83 has a yield of 1,300 kilotons, for example), the bomber must overfly the target. On the plus side, bomber crews can cancel the drop at the last minute. Bombers can launch the ALCM at targets up to 1,500 miles away, but enemies can shoot the cruise missile down. A cruise missile also takes up to 2 hours to reach its target, and it can’t be recalled during that time.
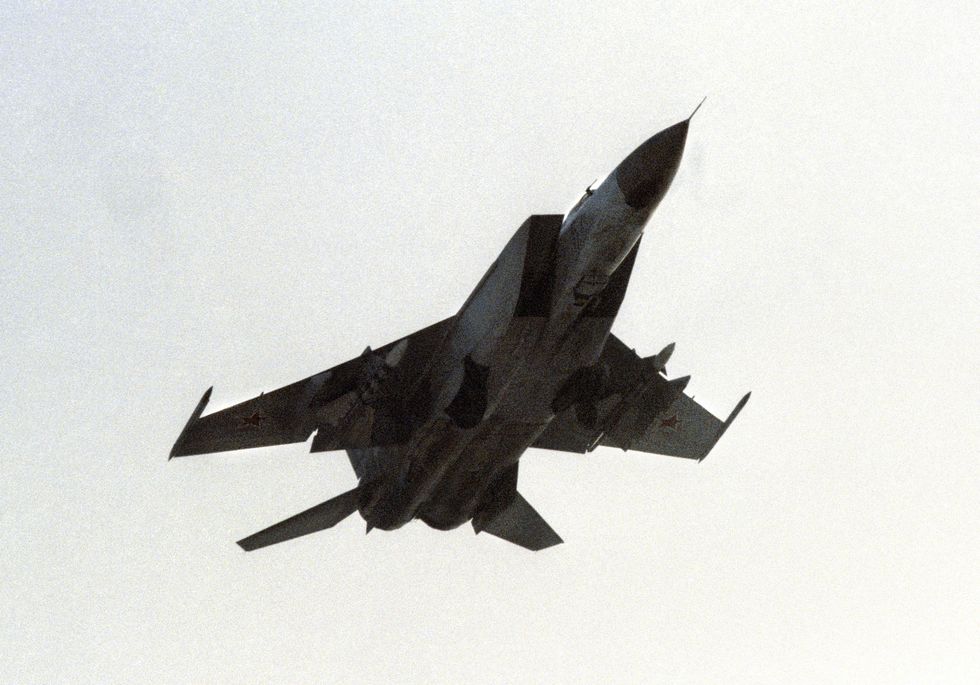

In the 1970s, nuclear bombers were on the verge of extinction. Advances in long-range air defense missiles and high-speed interceptors such as the Soviet MiG-25 made big, lumbering bombers like the B-52 sitting ducks in enemy airspace. But cruise missiles— effectively small, unmanned airplanes powered by turbofan engines, and low-flying to evade radar—allow bombers to launch against enemy targets long before they’re under threat.
A B-52, for example, could fire a salvo of ALCMs far from Soviet airspace, targeting enemy air defense installations. The B-52 could use ALCMs to blast a path to its main target, nuking MiGs on runways, radar sites, and enemy headquarters while remaining safely out of reach. Once the path is clear, the B-52 can then infiltrate enemy airspace and finally drop a high-yield gravity bomb on the target.
Cruise missiles are critical to the usefulness of bombers in a nuclear war. Without them, bombers would probably have to withdraw from the nuclear triad , removing a key capability—the ability to recall or cancel a nuclear strike—from America’s nuclear toolbox.
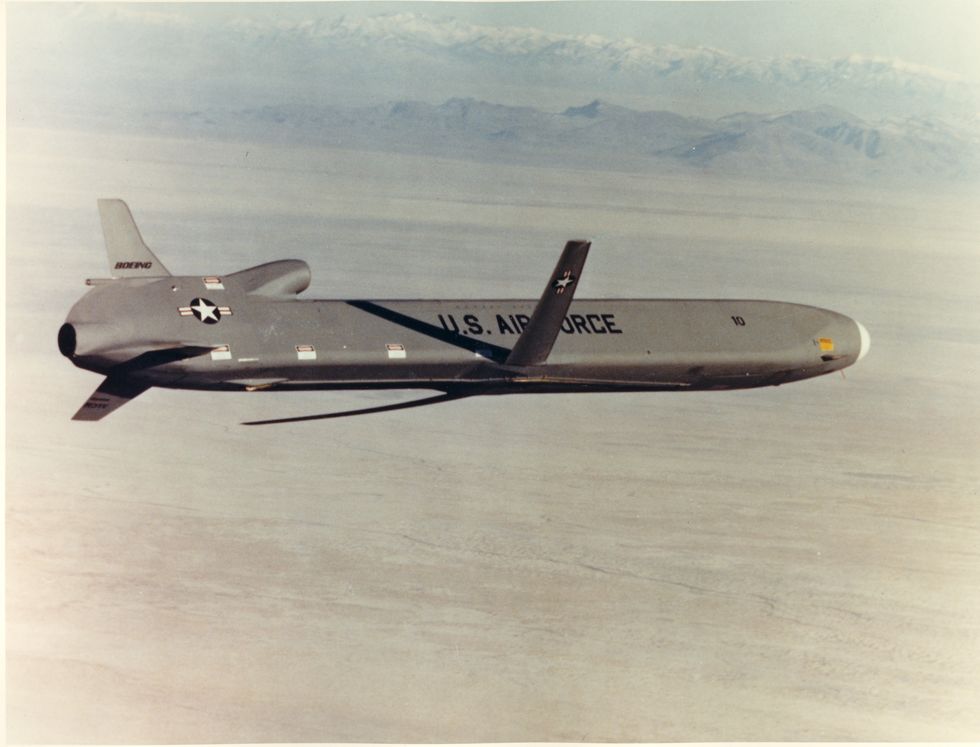

The Air Force has relied on the AGM-86B Air Launched Cruise Missile since the 1970s. Like any aging technology, the missile is increasingly difficult to maintain. The ALCM also lacks radar-evading stealth technology that would make it more difficult to detect by enemy defenses, increasing its likelihood of reaching its target.
LRSO, then, will be a stealthy missile with about the same range of 1,500 miles. The missile will also use the W80-4 thermonuclear warhead, a refurbished version of the older W80-1 thermonuclear warhead, with a customizable yield of 5 to 150 kilotons .
The new cruise missile is controversial. In 2015, a number of key U.S. Senators asked then-U.S. President Barack Obama to cancel the LRSO , saying the new missile was unnecessary given the development of the B61-12 nuclear gravity bomb and the forthcoming B-21 Raider bomber. Others warn that LRSO is “unnecessary” and “destabilizing.”
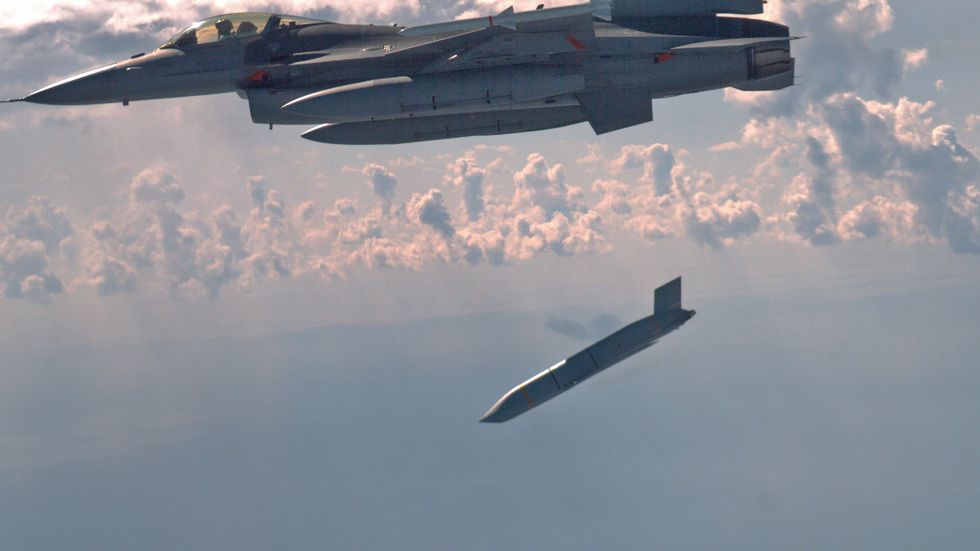

So, does the Air Force need its new stealth cruise missile? If it wants to keep the bomber leg of the nuclear triad , then the answer is yes. A B-21 Raider without cruise missiles would have to overfly every target to destroy it, a requirement that would dangerously expose the bomber and potentially add hours to a combat mission.
If such a bomber is tasked with destroying an enemy communications or headquarters site that transmits orders to launch more missiles, it could arrive at the target too late to interrupt the enemy’s plans— if it arrives at all.
In an ideal world, the U.S. could bargain with the other nuclear powers to gradually reduce—and even eliminate—nuclear weapons worldwide. An adversary must, however, recognize that America’s nukes are a threat in order to want to bargain to get rid of them.
Building LRSO isn’t the end of the world ... but using them is. Between those two points, the U.S. can trade nuclear missiles away in exchange for missiles in Russia or China targeting this country.
🎥 Now Watch This:

Kyle Mizokami is a writer on defense and security issues and has been at Popular Mechanics since 2015. If it involves explosions or projectiles, he's generally in favor of it. Kyle’s articles have appeared at The Daily Beast, U.S. Naval Institute News, The Diplomat, Foreign Policy, Combat Aircraft Monthly, VICE News , and others. He lives in San Francisco.
.css-cuqpxl:before{padding-right:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;} Pop Mech Pro .css-xtujxj:before{padding-left:0.3125rem;content:'//';display:inline;}

Could Freezing Your Brain Help You Live Forever?

Air Force’s Combat Drone Saga Has Taken a Turn

China’s Building a Stealth Bomber. U.S. Says ‘Meh’

A Supersonic Bomber's Mission Ended in Flames

Who Wants to Buy the A-10 Warthog?

US Army Accepts Delivery of First M10 Assault Gun

Underwater UFO is a Threat, Says Ex-Navy Officer

DIY Car Key Programming: Why Pay the Dealer?
Use Induction Heat to Break Free Rusted Bolts

How to Replace Your Car’s Brakes

The Air Force is Resurrecting a B-1 Bomber
Iran says it has developed long-range cruise missile
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Dubai newsroom Editing by Alistair Bell and Grant McCool
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron

Ethiopia's Amhara militia says resettlement plan 'beats war drum'
Leaders of a militia in Ethiopia's Amhara region accused the administration in neighbouring Tigray of "beating a war drum" over plans to return hundreds of thousands of Tigrayans to territories Amhara fighters captured during a civil war.

A New Pacific Arsenal to Counter China
With missiles, submarines and alliances, the Biden administration has built a presence in the region to rein in Beijing’s expansionist goals.
By John Ismay , Edward Wong and Pablo Robles April 26, 2024
U.S. officials have long seen their country as a Pacific power, with troops and arsenals at a handful of bases in the region since just after World War II.
U.S. military or partner bases
But the Biden administration says that is no longer good enough to foil what it sees as the greatest threat to the democratic island of Taiwan — a Chinese invasion that could succeed within days.
The United States is sending the most advanced Tomahawk cruise missiles to Japan and has established a new kind of Marine Corps regiment on Okinawa that is designed to fight from small islands and destroy ships at sea.
The Pentagon has gained access to multiple airfields and naval bases in the Philippines , lessening the need for aircraft carriers that could be targeted by China’s long-range missiles and submarines in a time of war.
The Australian government hosts U.S. Marines in the north of the country, and one of three sites in the east will soon be the new home for advanced American-made attack submarines. The United States also has a new security agreement with Papua New Guinea.
Potential submarine bases
Xi Jinping, China’s leader, and other officials in Beijing have watched the U.S. moves with alarm. They call it an encirclement of their nation and say the United States is trying to constrain its main economic and military rival.
Since the start of his administration, President Biden has undertaken a strategy to expand American military access to bases in allied nations across the Asia-Pacific region and to deploy a range of new weapons systems there. He has also said the U.S. military would defend Taiwan against a Chinese invasion.
On Wednesday, Mr. Biden signed a $95 billion supplemental military aid and spending bill that Congress had just passed and that includes $8.1 billion to counter China in the region. And Secretary of State Antony J. Blinken traveled to Shanghai and Beijing this week for meetings with Mr. Xi and other officials in which he raised China’s military activity in the Taiwan Strait and the South China Sea, calling it “destabilizing.”
Mr. Xi told Mr. Blinken on Friday that the United States should not play a “zero-sum game” or “create small blocs.” He said that “while each side can have its friends and partners, it should not target, oppose or harm the other,” according to an official Chinese summary of the meeting.
Earlier in April, the leaders of the Philippines and Japan met with Mr. Biden at the White House for the first such summit among the three countries. They announced enhanced defense cooperation, including naval training and exercises, planned jointly and with other partners. Last year, the Biden administration forged a new three-way defense pact with Japan and South Korea.

President Biden held a trilateral meeting earlier this month with the leaders of Japan and the Philippines at the White House.
Yuri Gripas for The New York Times
“In 2023, we drove the most transformative year for U.S. force posture in the Indo-Pacific region in a generation,” Ely S. Ratner, the assistant secretary of defense for Indo-Pacific security affairs, said in a statement following an interview.
The main change, he said, is having American forces distributed in smaller, more mobile units across a wide arc of the region rather than being concentrated at large bases in northeast Asia. That is largely intended to counter China’s efforts to build up forces that can target aircraft carriers or U.S. military outposts on Okinawa or Guam.
These land forces, including a retrained and refitted U.S. Marine littoral regiment in Okinawa, will now have the ability to attack warships at sea.
For the first time, Japan’s military will receive up to 400 of their own Tomahawk cruise missiles — the newest versions of which can attack ships at sea as well as targets on land from over 1,150 miles away.
The Pentagon has also gained access rights for its troops at four additional bases in the Philippines that could eventually host U.S. warplanes and advanced mobile missile launchers, if Washington and Manila agree that offensive weaponry can be placed there.
The United States has bilateral mutual defense agreements with several allied nations in the region so that an attack on the assets of one nation could trigger a response from the other. Bolstering the U.S. troop presence on the soil of allied countries strengthens that notion of mutual defense.
In addition, the United States continues to send weapons and Green Beret trainers to Taiwan, a de facto independent island and the biggest flashpoint between the United States and China. Mr. Xi has said his nation must eventually take control of Taiwan, by force if necessary.
“We’ve deepened our alliances and partnerships abroad in ways that would have been unthinkable just a few years ago,” Kurt Campbell, the new deputy secretary of state, told reporters last year, when he was the top Asia policy official in the White House.
What Deters China?
Taiwan’s foreign minister, Joseph Wu, said in an interview in Taipei that the strengthened alliances and evolving military force postures were critical to deterring China.
“We are very happy to see that many countries in this region are coming to the realization that they also have to be prepared for further expansions of the P.R.C.,” he said, referring to the People’s Republic of China.
To some Chinese military strategists, the U.S. efforts are aimed at keeping China’s naval forces behind the “first island chain” — islands close to mainland Asia that run from Okinawa in Japan to Taiwan to the Philippines.
U.S. military assets along these islands could prevent Chinese warships from getting into the open Pacific waters farther east if conflict were to break out.
Leaders in China’s People’s Liberation Army also talk of establishing military dominance of the “second island chain” — which is farther out in the Pacific and includes Guam, Palau and West Papua.
First Island Chain
Second Island Chain
philippines
But several conservative critics of the administration’s policies argue that the United States should be keeping major arms for its own use and that it is not producing new ships and weapons systems quickly enough to deter China, which is rapidly growing its military .
Some American commanders acknowledge the United States needs to speed up ship production but say the Pentagon’s warfighting abilities in the region still outmatch China’s — and can improve quickly with the right political and budget commitments in Washington.
“We have actually grown our combat capability here in the Pacific over the last years,” Adm. Samuel J. Paparo Jr., the incoming commander of the U.S. Indo-Pacific Command, said in an interview. “But our trajectory is still not a trajectory that matches our adversary. Our adversaries are building more capability and they’re building more warships — per year — than we are.”
Mr. Paparo said new American warships were still more capable than the ones China is building, and the U.S. military’s “total weight of fires” continued to outmatch that of the People’s Liberation Army, for now.

Warplanes on the flight deck of U.S.S. Carl Vinson, an aircraft carrier, during a joint U.S. and Japanese military exercise in the Philippine Sea in January.
Richard A. Brooks/Agence France-Presse — Getty Images
The Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty , a Cold War-era arms control agreement between Washington and Moscow, prohibited land-based cruise or ballistic missiles with ranges between 311 miles and 3,420 miles. But after the Trump administration withdrew from the pact, the United States was able to develop and field a large number of small, mobile launchers for previously banned missiles around Asia.
Even with the deployment of new systems, the United States would still rely on its legacy assets in the region in the event of war: its bases in Guam, Japan and South Korea, and the troops and arms there.
All of the senior U.S. officials interviewed for this story say war with China is neither desirable nor inevitable — a view expressed publicly by Defense Secretary Lloyd J. Austin III. But they also insist that a military buildup and bolstering alliances, along with diplomatic talks with China, are important elements of deterring potential future aggression by Beijing.
Wang Yi, China’s foreign minister, told Mr. Blinken on Friday in Beijing that “the negative factors in the relationship are still increasing and building, and the relationship is facing all kinds of disruptions.” He warned the United States “not to interfere in China’s internal affairs, not to hold China’s development back, and not to step on China’s red lines and on China’s sovereignty, security and development interests.”
U.S. military or
partner bases
The new deterrent effort is twofold for American forces: increasing patrolling activities at sea and the capabilities of its troop levels ashore.
To the former, the Pentagon has announced that U.S. Navy warships will participate in more drills with their Japanese counterparts in the western Ryukyu Islands near Taiwan and with Filipino ships in the South China Sea, where the Chinese coast guard has harassed ships and installations controlled by the Philippines .

A swarm of Chinese militia and Coast Guard vessels chased a Philippine Coast Guard ship in the South China Sea last year.
Jes Aznar for The New York Times
To the latter, Marine Corps and Army units already in the Pacific have recently fielded medium- and long-range missiles mated to small, mobile trucks that would have been prohibited under the former treaty.
These trucks can be quickly lifted by Osprey tilt-rotor aircraft or larger cargo planes to new locations, or they can simply drive away to evade a Chinese counterattack. A new flotilla of U.S. Army watercraft being sent to the region could also be used to reposition troops and launchers from island to island.
In an interview last year with The New York Times, Gen. David H. Berger, then the Marine Corps’ top general, said the service had begun analyzing strategic choke points between islands where Chinese forces were likely to transit throughout the Pacific. He said the service had identified sites where Marine assault forces like the new Okinawa-based littoral regiment could launch attacks on Beijing’s warships using these new weapons.
Philippines
Partner bases
The Pentagon announced in February last year a new military base-sharing agreement with Manila, giving U.S. forces access to four sites in the Philippines for use in humanitarian missions, adding to the five sites previously opened to the Pentagon in 2014. Most of them are air bases with runways long enough to host heavy cargo planes.
Plotting their locations on a map shows the sites’ strategic value should the United States be called upon to defend their oldest treaty ally in the region , if the Philippines eventually agrees to allow the U.S. military to put combat troops and mobile missile systems there.
One, on the northern tip of Luzon Island, would give missile-launching trucks the ability to attack Chinese ships across the strait separating Philippines from Taiwan, while another site about 700 miles to the southwest would allow the U.S. to strike bases that China has built in the Spratly Islands nearby.
In 2023, the United States committed $100 million for “infrastructure investments” at the nine bases, with more funds expected this year.
The Pentagon has forged closer military ties with Australia and Papua New Guinea , extending America’s bulwark against potential attempts by the Chinese military at establishing dominance along the “second island chain.”
The Obama administration moved a number of littoral combat ships to Singapore and deployed a rotating force of Marines to Darwin, on Australia’s north coast, giving the Pentagon more assets that could respond as needed in the region.
Last year, the Biden administration greatly elevated its commitment to Australia, which is one of America’s most important non-NATO allies.

The U.S.S. North Carolina, a Virginia-class submarine, docking in Perth, Australia last year.
Tony Mcdonough/Agence France-Presse — Getty Images
A new multibillion dollar agreement called AUKUS — for Australia, the United Kingdom and the United States — will permanently transfer some of the U.S. Navy’s newest Virginia-class attack subs to Canberra . The location of the new bases for those subs has not been announced, but the first group of Australian sailors who will crew them graduated from nuclear power training in America in January.
These stealthy submarines, which can fire torpedoes and Tomahawk missiles, will potentially add to the number of threats Beijing faces in case of a regional war.
Just north of Australia, an agreement in August gave U.S. forces more access to Papua New Guinea for humanitarian missions and committed American tax dollars to update military facilities there.
To Admiral Paparo, this growing network of partnerships and security agreements across thousands of miles of the Pacific is a direct result of what he calls China’s “revanchist, revisionist and expansionist agenda” in the region that has directly threatened its neighbors.
“I do believe that the U.S. and our allies and partners are playing a stronger hand and that we would prevail in any fight that arose in the Western Pacific,” the admiral said.
“It’s a hand that I would not trade with our would-be adversaries, and yet we’re also never satisfied with the strength of that hand and always looking to improve it.”
- Share full article
Advertisement
Ukraine is using long-range missiles secretly provided by the US to target Russian invaders, officials say
The United States has revealed it recently secretly shipped long-range missiles to Ukraine for use in that country's battle to fight off Russian invaders.
On Wednesday local time, a US official said Ukraine had now used them twice.
The missiles were contained in a $US300 million ($461 million) military aid package for Ukraine that US President Joe Biden approved on March 12, said the US official, speaking on condition of anonymity.
The official would not say how many of the missiles were sent.
White House national security adviser Jake Sullivan, at a briefing for reporters, confirmed that a "significant number" of the missiles had been sent to Ukraine and said "we will send more."
He said Ukraine has committed to only use the weapons inside Ukraine, not in Russia.
Some of the missiles were contained in a $US1 billion weapons package for Ukraine that Mr Biden approved on Wednesday, Mr Sullivan said.
The missiles were used for the first time in the early hours of April 17, launched against a Russian airfield in Crimea that was about 165 kilometres from the Ukrainian front lines, the official said.
The official said Ukraine used the weapon a second time overnight against Russian forces in south-eastern Ukraine.
Whether to send the Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS), with a range up to 300km, was a subject of debate within the Biden administration for months.
Mid-range ATACMS were supplied last September.
The Pentagon initially opposed the long-range missile deployment, fearing the loss of the missiles from the American stockpile would hurt US military readiness.
There were also concerns that Ukraine would use them to attack targets deep inside Russia.
Russia's use of North Korean-supplied long-range ballistic missiles against Ukraine in December and January, despite US public and private warnings not to do so, led to a change in heart, the US official said.
Also a factor in US decision-making was Russia's targeting of Ukraine's critical infrastructure, the official said.
"We warned Russia about those things," the official said.
"They renewed their targeting."
In late January the US military found a way to satisfy their concerns about military readiness, which enabled the administration to move forward.
They began acquiring new missiles coming off the Lockheed-Martin LMTN production line.
Mr Biden met with his national security team in mid-February and agreed to accept the unanimous recommendation of his advisers to send the missiles to Ukraine.
Involved in the discussion were Mr Sullivan, Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin, Secretary of State Antony Blinken and Joint Chiefs of Staff Chairman CQ Brown.
The challenge at that point was to figure out how to pay for the missiles.
The US had exhausted all of its funding options and congressional gridlock stymied further aid.
An opportunity arose in March, when several Pentagon contracts came in under bid.
Mr Biden was able to use the difference to send $US300 million in assistance to Ukraine.
Mr Biden told his team to include the long-range ATACMS in this funding package, but to do so secretly in order to maintain operational security and the element of surprise for Ukraine, the official said.
- X (formerly Twitter)
- Defence and National Security
- Russian Federation
- United States
- Unrest, Conflict and War
- World Politics
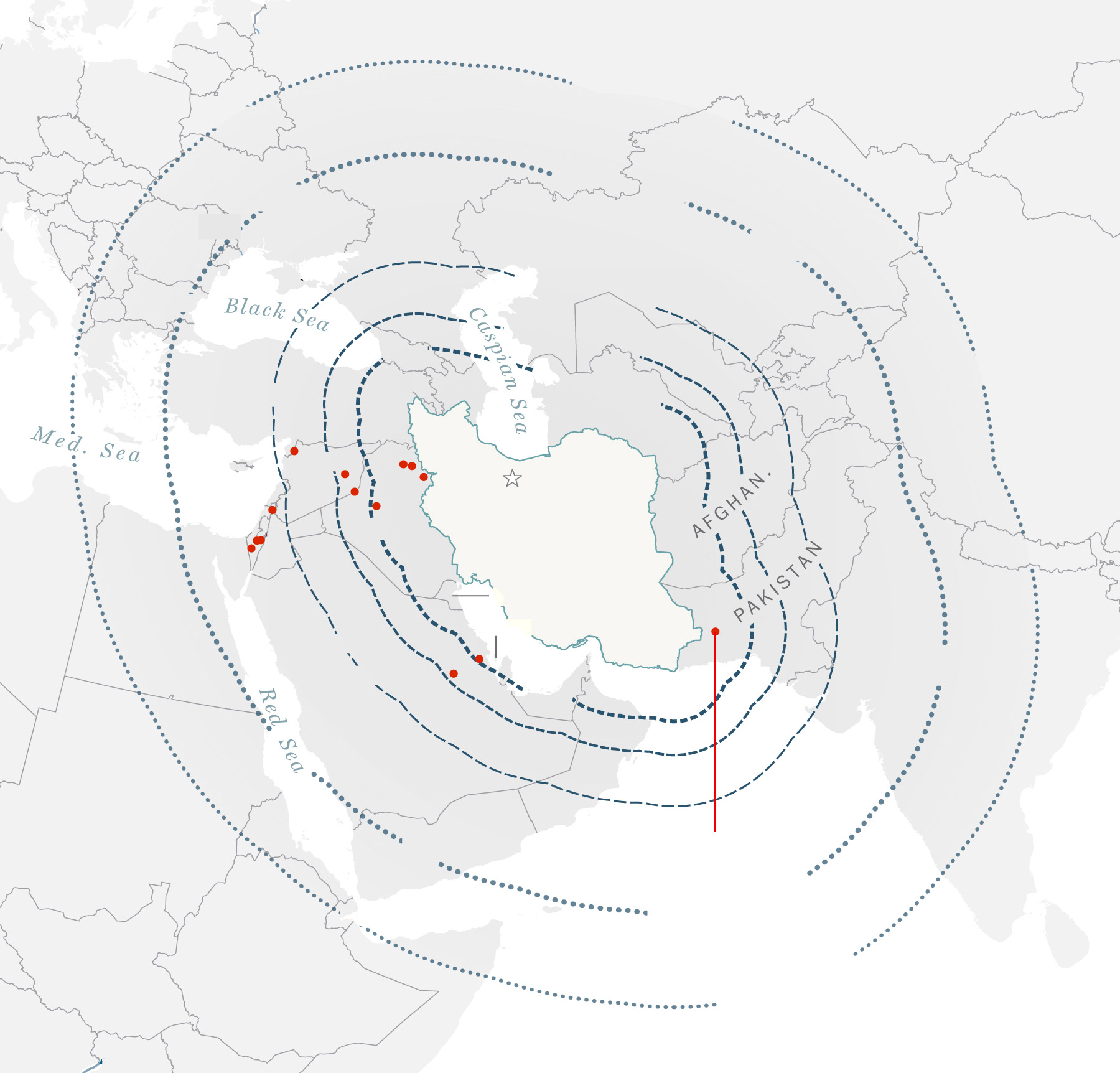
What Iran’s attack on Israel revealed about its weapons arsenal
Iran’s first direct attack on Israel overnight Saturday demonstrated the country’s military might and the advances of its domestic weapons program, analysts said, while also revealing the limitations of its arsenal.
With more than 300 drones and missiles launched in a layered onslaught, it was Iran’s largest-ever conventional show of force . That it inflicted only minimal damage was due in part to the choreographed nature of the attack — giving Israel and the United States ample time to prepare air defense systems — but may also be attributed to shortcomings in its medium- and long-range capabilities.
“The operation showed that our armed forces are ready,” Iranian president Ebrahim Raisi told crowds gathered Wednesday in Tehran to mark Army Day. Parades in the Iranian capital featured many of the same munitions used in the attack on Israel.

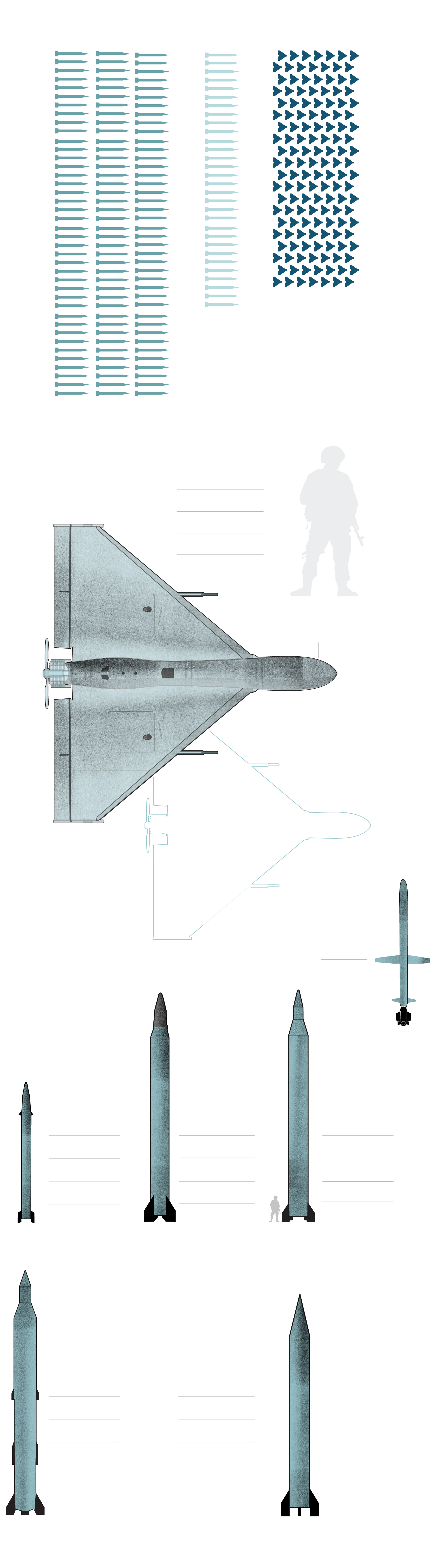
What Iran used against Israel
110 ballistic
Iranian drones
These drones can deliver small payloads of explosives in self-detonating attacks.
Length: 11.5 ft.
Width: 8 ft.
Max. take off weight: 440 lb.
Max. speed: 115 mph
Range: About 1,100 - 1,500 miles
Its nose contains a warhead and can be equipped with a camera.
Length: 8 ft.
Width: 7 ft.
Max. take off weight: 300 lb.
The Shahed-131 is an earlier version of Shahed-136 with a similar principle of operation. The layout and aerodynamics are also identical.
Ballistic missiles
KHEIBAR SHEKAN
The Kheibar Shekan MRBM is a solid-propellant ballistic missile designed by the IRGC.
Length: 34 ft.
Diameter: 2.6 ft.
Max. range: 900 miles
Warhead weight: 1,100 lb.
Introduction: 2022
The Emad MRBM is an Iranian-designed, liquid-fuel ballistic missile based on Shahab-3.
Length: 54 ft.
Diameter: 4.1 ft.
Max. range: 1,056 miles
Warhead weight: 1,650 lb.
Introduction: 2015
The Ghadr-1 MRBM seems to be an improved variant of the Shahab-3A. It is also referred to as the Ghadr-101 and the Ghadr-110.
Max. range: 1,211 miles
Warhead weight: 1,760 lb.
Introduction: 2007
Cruise missile
Max. range: 1,025 miles
Introduction: 2023
What Iran did not use
The Sejjil-1 Iranian MRBM is a two-stage, solid-propellant, surface-to-surface missile.
Length: 60 ft
Max. range: 1,243 miles
Warhead weight: 1,540 lb.
Introduction: 2011
The Shahab-3 is a MRBM developed by Iran and based on the North Korean Nodong-1.
Diameter: 4.1 or 4.5 ft.
Max. range: 808 miles
Warhead: Single or multiple
with 5 warheads of 617 lb.
Introduction: 2003
Sources: OE Data Integration Network (ODIN),
CSIS Missile Defense Project

120 ballistic
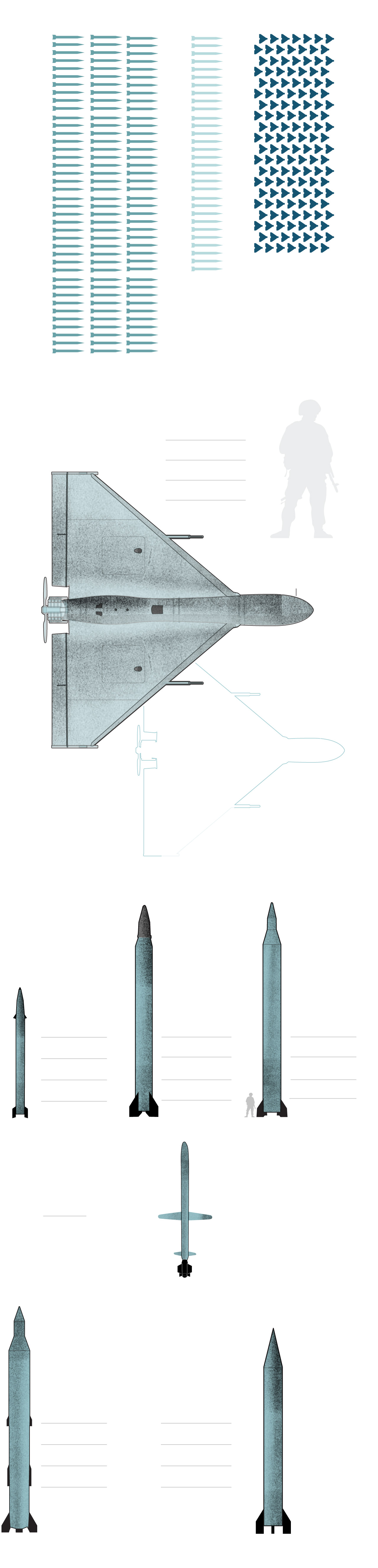
120 ballistic missiles
30 cruise missiles
Overhead view
1,211 miles
1,056 miles
Max. range:
Warhead weight:
Introduction:
Sources: OE Data Integration Network (ODIN), CSIS Missile Defense Project
Raisi hailed the attack as a resounding “success,” but was also quick to qualify the strikes as “limited” and “not comprehensive.”
“If it was supposed to be a large-scale action, nothing would have been left of the Zionist regime,” he said. And if Israel retaliates, Raisi pledged, “they will be dealt with fiercely and severely.”
Yet after analyzing the munitions used in Saturday’s assault and the success of regional defense systems, researchers say it’s unclear how Iran could inflict greater damage on Israel through conventional military means.
“Iran basically threw everything it had that could reach Israel’s territory,” said John Krzyzaniak, a researcher who studies Iran’s missile programs at the Wisconsin Project on Nuclear Arms Control. Like other analysts interviewed for this story, he has spent the past several days studying launch videos, imagery of debris and interception information to identify the Iranian munitions.
His conclusion is that Tehran “used some of every system they have.” And experts said it made sense that the Sejjil-1 and Shahab-3 missiles were excluded from the attack.
Shahab-3 “wasn’t used because it’s so old,” said Fabian Hinz, an Iran analyst at the International Institute for Strategic Studies in Berlin. “The Sejjil is a bit of a mysterious missile,” he said, adding that Iran has “used it very, very little during maneuvers.”
Other analysts noted the Sejjil was expensive to produce and may no longer be in production.
The quantity of munitions used also provides new insights into Iran’s capabilities. The deployment of over 100 ballistic missiles in a single wave suggests that previous estimates that Iran has about 3,000 ballistic missiles stockpiled are probably accurate, and could even be on the low end.
“If this is just round one of an unknown number of rounds to come, you wouldn’t fire a significant fraction of what you have just in the first round,” Krzyzaniak said.
The firing of over 100 ballistic missiles in the space of a few minutes suggests Iran has at least 100 launchers, he added — a new data point for researchers.
“This shows that Iran has really faced no limitation in domestically producing missiles and launchers,” he said.
Iran’s ballistic missile arsenal, the largest of any country in the Middle East, is almost entirely homegrown. In recent years Iran has demonstrated the ability to upgrade some systems, improving their range and precision.
The spokesman for Iran’s armed forces, Abolfazl Shekarchi, said the munitions used in the strikes against Israel only represented “a fraction of” the country’s military’s might, according to a statement published on state-run media.
The evolution of Iran’s
missile program
In the mid-1980s, Tehran acquired Scud missiles from Libya, Syria and North Korea and also began adapting the technology for their own missile variants. During the eight-year war with Iraq, Tehran countered primarily with Scud B missiles, which have a range of 185 miles.
Shahab-1 , 186 miles
1994 to 2001
Iran developed its own version of the Scud B, the Shahab-1, and from 1994 to 2001 fired it at bases in Iraq used by the opposition group Mujahedin-e Khalq.
A new generation of missiles
After 16 years without firing new missiles, Iran showed its technological advances in 2017 striking on an ISIS command center with 6 Zolfaghars with a range of 430 miles. In early 2024, it launched strikes against Islamic State targets in northwest Syria using Kheibar Shekan missiles that travelled 745 miles from Iran to Syria.
Fahteh 110 , 181 miles
Fahteh 313 , 310 miles
Zolfaghar , 435 miles
Qiam 1 , 497 miles
Kheibar Shekan , 900 miles
IRAN ATTACKS
Against ISIS
6 ballistic missiles
Deir ez-Zor, Syria
Against Kurdish dissidents
7 ballistic missiles
Abu Kamal, Syria
Against Oil fields and facilities
18 drones + 7 cruise missiles
Abqaiq, S. Arabia
Khurais, S. Arabia
3 cruise missiles
Against U.S. forces
Erbil, Iraq
1 ballistic missile
Ain Al Asad, Iraq
15 to 22 ballistic missiles
Against “Israeli strategic centers”
At least 10 ballistic missiles
73 launches + at least 20 drones
and suicide drones
Sulaimaniyah,
Against IS targets
Harem, Syria
Israeli “spy headquarters”
Against Jaish ul Adl
Balochistan,
Missiles and drones
Against Israel
120 ballistic missiles,
170 drones,
Sources: United States Institute of Peace, CSIS, IDF
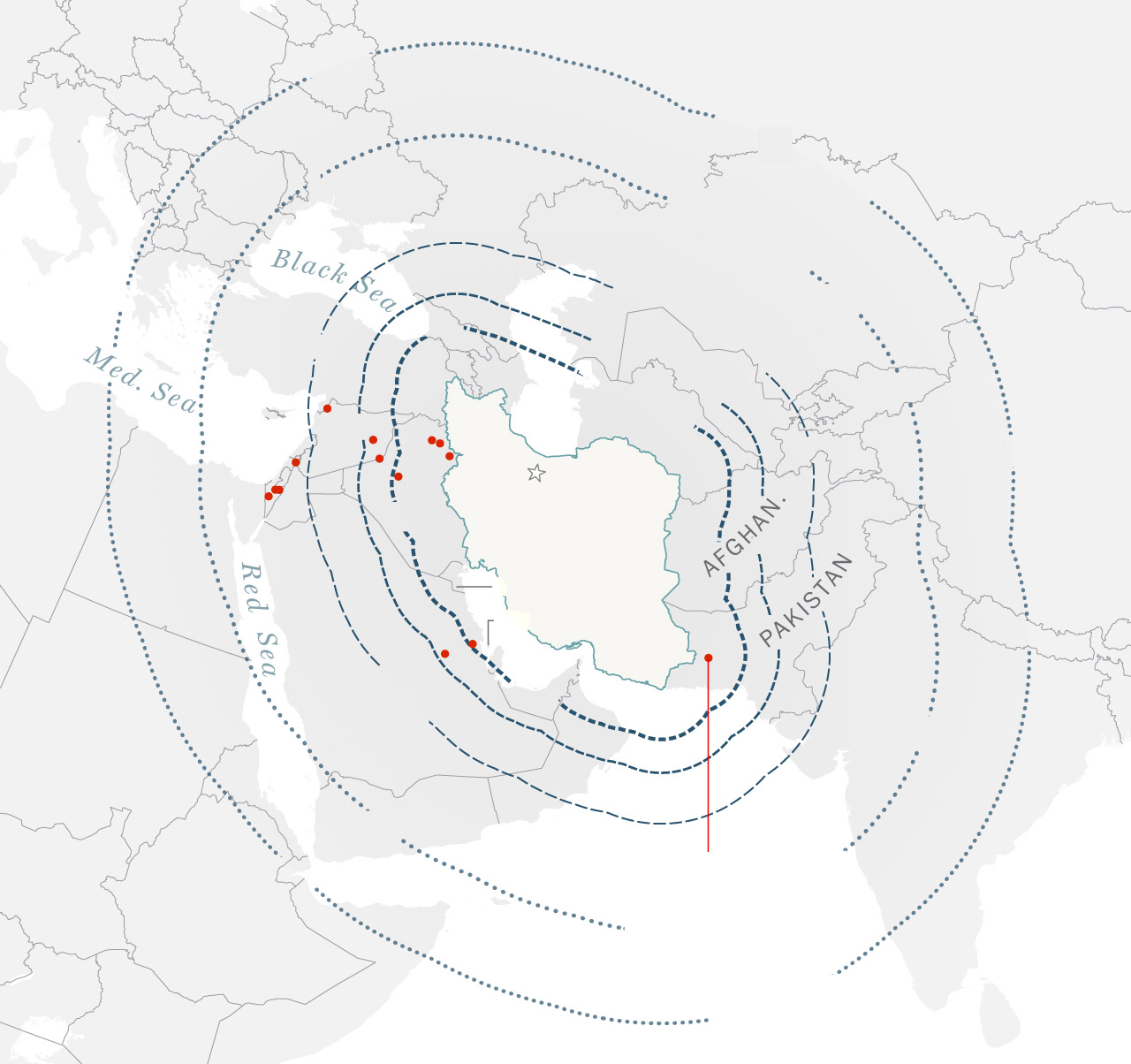
The evolution of Iran’s missile program
IRAN TARGETS
KNOWN MISSILE
Zolfaghars,
Abqaiq, Saudi Arabia
Khurais, Saudi Arabia
Zolfaghars and
potentially
Ballistic missiles and suicide drones
Sulaimaniyah, Iraq
Kheibar Shekan
Balochistan, Pakistan
Missiles and drones against Jaish ul Adl
170 drones, 30 cruise missiles
Before the attack on Israel, Iran’s most significant use of ballistic missiles was in 2020, after a U.S. drone attack killed the powerful Iranian commander Qasem Soleimani.
Iran launched more than a dozen ballistic missiles at two U.S. military bases in Iraq, one in the country’s west and one in the north. While there were no fatalities, dozens of U.S. service members suffered traumatic brain injuries.
Iran also used ballistic missiles in strikes this year on Pakistan, Syria and Iraq.
Iranian ballistic
missile ranges
1,240 miles
Locations of Iranian
missile strikes
INDIAN OCEAN
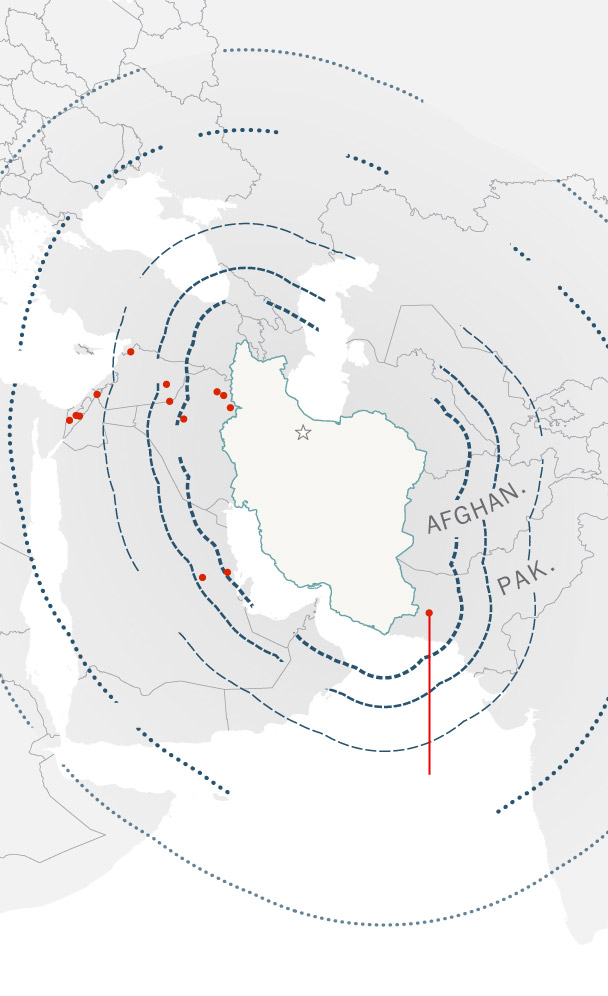
But the attack on Israel suggests that many of Iran’s munitions are of low quality. Israel’s military said 99 percent of the missiles and drones launched by Iran were intercepted or failed to launch.
“We saw that accuracy and precision are a work in progress,” said Behnam Ben Taleblu, a senior fellow at the Foundation for Defense of Democracies who has written extensively about Iran’s missile program. “These weapons alone won’t win a war for Iran.”
Iranian drones made up the first wave of the attack. Cheap, effective and easy to produce, Iranian drones have been used in attacks across the Middle East for years. Iran has also supplied drones to Russia for its war in Ukraine , where they have been deadly.
During the attack on Israel, the slow-moving drones were probably deployed to occupy air defenses and allow more advanced munitions to get through. All the drones were shot down before entering Israeli airspace, the Israel Defense Forces said.
Ali Hamie, a Lebanese military analyst, said Iran had probably gleaned important lessons about Israel’s aerial defenses. Commentators on Iranian state television have made similar points.
“It could be a testing attack,” Hamie said, “and the Iranians got what they want. Making it past the air defenses is not only a symbolic victory, but real victory.”
One of the few missiles to make it through the interceptors hit an Israeli air base in the Negev desert. Images of the strike were run on loop on many state-run Iranian broadcasters in the days after the attack. Israel characterized the damage as minor.
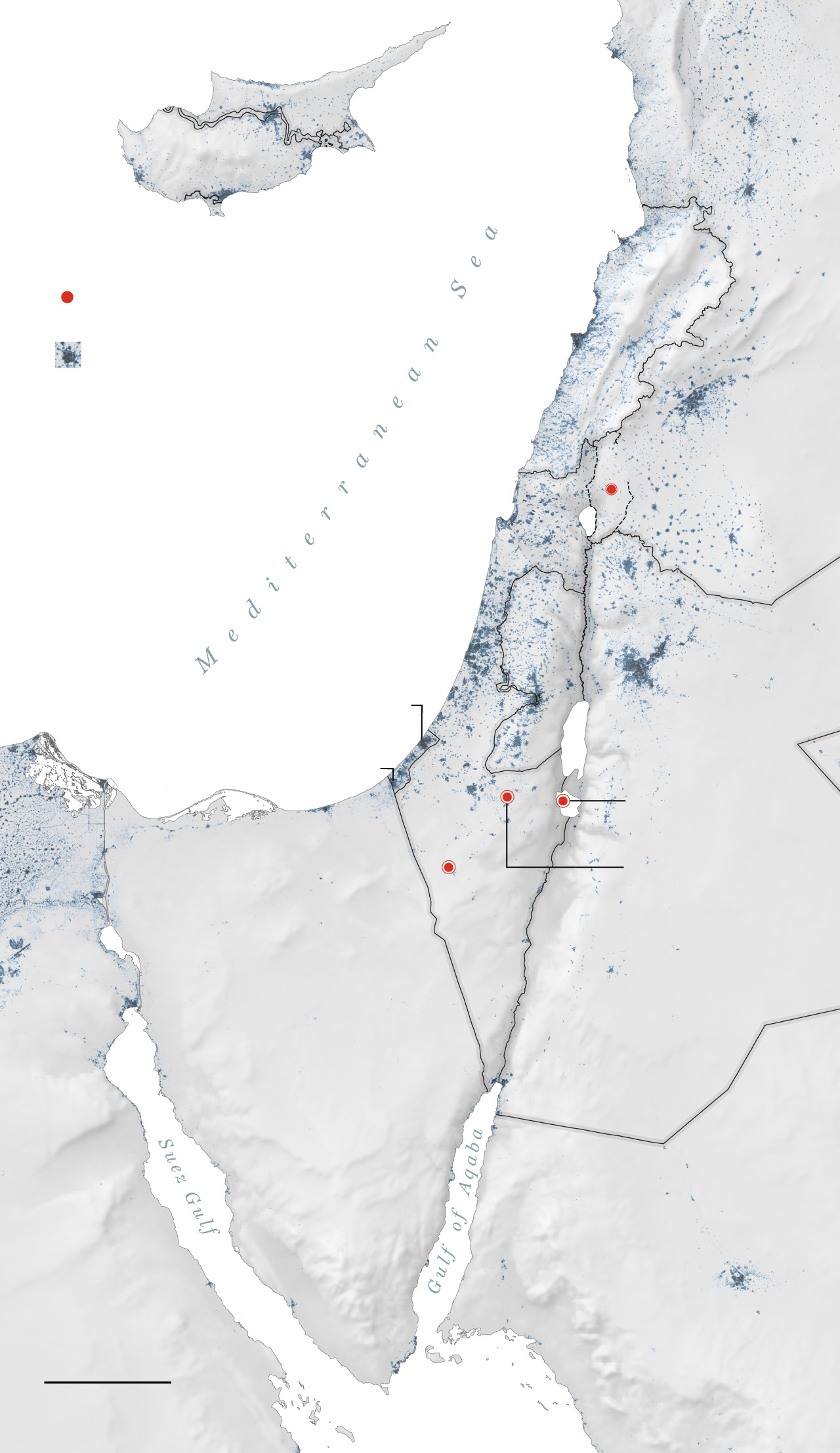
General location of missile strikes
that reached the ground.
Beirut—
Populated areas
Haifa—
Tel Aviv—
—Amman
—Jerusalem
An emad missile
was found here.
The barrage of
missiles from Iran
included targeting
the Nevatim
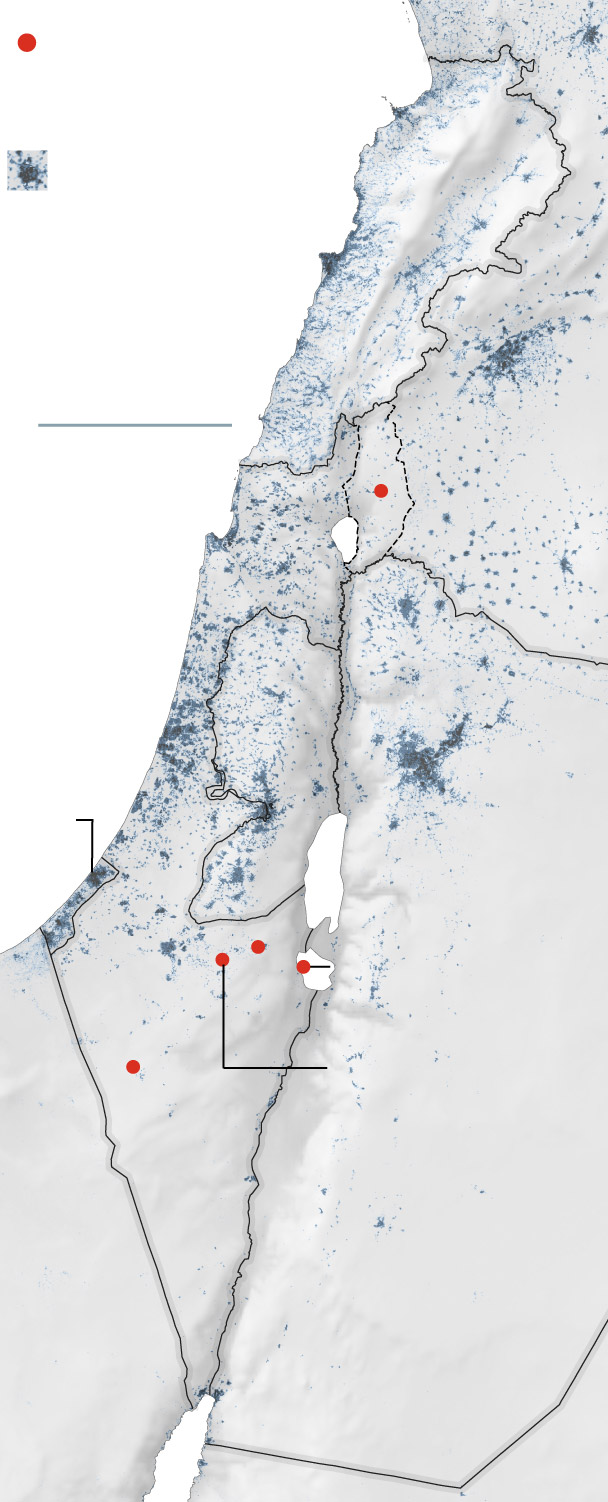
General location of
missile strikes that
reached the ground.
Mediterranean
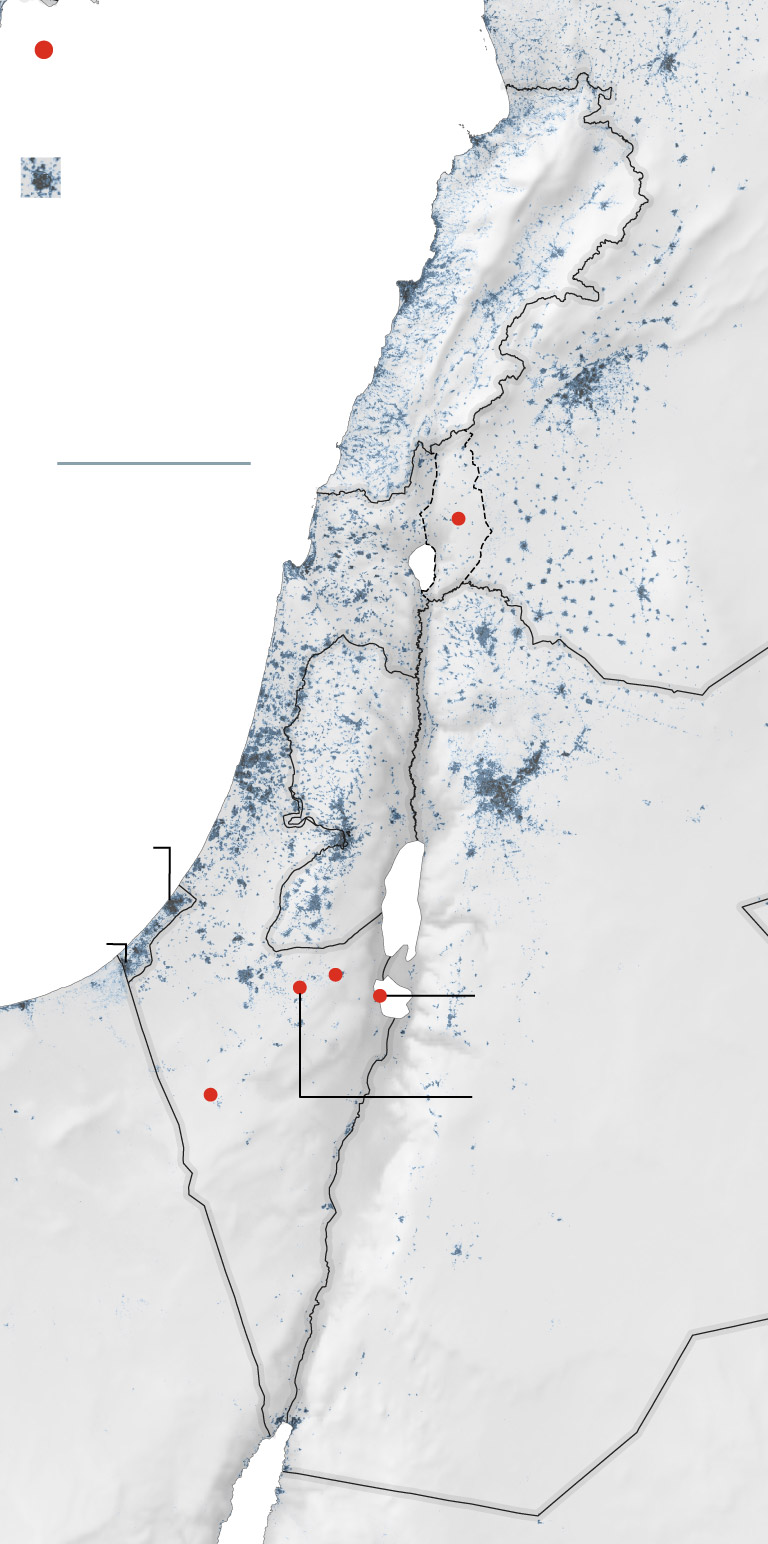
General location of missile
strikes that reached the
In addition to analyzing Israel’s air defenses, Tehran will probably also be studying the problems with its missile systems that reportedly led to failures at launch and in flight, according to Afshon Ostovar, a professor of national security affairs at the Naval Postgraduate School in California.
“Another attack could be more effective,” he said. But ultimately the kind of approach demonstrated in Saturday’s attack “is not really sustainable over a long-term conflict.”
Even if Iran changed the tempo of attacks and adjusted the munitions used, “they would still have to launch quite a lot of stuff for just a few [munitions] to get through,” he said.
Some Iranian officials have suggested they have held back their most dangerous weapons.
“We are prepared to use weapons we have never used before. We have plans for every scenario,” said Abolfazl Amoui, a parliamentary national security spokesman, in an interview with Lebanese broadcaster Mayadeen.
But analysts say it’s unlikely that any one type of munition could be a game changer. Rather, it’s more likely Iran would use the same kinds of munitions in a future attack, but in a different way: giving less warning, or launching the barrage in concert with allied militant groups in the region. The country’s proxy forces, from Lebanon to Iraq to Yemen, played little role in Saturday’s assault.
As Israel mulls its response , Tehran has warned that a counterattack would come in “a matter of seconds.”
“Iran will not wait for another 12 days to respond,” Deputy Foreign Minister Ali Bagheri Kani said Monday.
While the United States and Israel have celebrated the thwarting of Saturday’s attack, analysts are urging humility.
“The number of munitions it took to repel the attack was enormous, costly and could be difficult to replicate,” said Tom Karako, the director of the Missile Defense Project at the Center for Strategic and International Studies.
“Israel may have gotten lucky and Iran may have gotten very unlucky.”
William Neff and Suzan Haidamous contributed to this report.
Israel-Gaza war
The Israel-Gaza war has gone on for six months, and tensions have spilled into the surrounding region .
The war: On Oct. 7, Hamas militants launched an unprecedented cross-border attack on Israel that included the taking of civilian hostages at a music festival . (See photos and videos of how the deadly assault unfolded ). Israel declared war on Hamas in response, launching a ground invasion that fueled the biggest displacement in the region since Israel’s creation in 1948 .
Gaza crisis: In the Gaza Strip, Israel has waged one of this century’s most destructive wars , killing tens of thousands and plunging at least half of the population into “ famine-like conditions. ” For months, Israel has resisted pressure from Western allies to allow more humanitarian aid into the enclave .
U.S. involvement: Despite tensions between Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and some U.S. politicians , including President Biden, the United States supports Israel with weapons , funds aid packages , and has vetoed or abstained from the United Nations’ cease-fire resolutions.
History: The roots of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and mistrust are deep and complex, predating the establishment of the state of Israel in 1948 . Read more on the history of the Gaza Strip .
- Middle East conflict live updates: Hamas says it views cease-fire talks favorably; Blinken urges group to accept deal 11 minutes ago Middle East conflict live updates: Hamas says it views cease-fire talks favorably; Blinken urges group to accept deal 11 minutes ago
- Six months of the Israel-Gaza war: A timeline of key moments April 7, 2024 Six months of the Israel-Gaza war: A timeline of key moments April 7, 2024
- Colombia is the latest and largest country to sever ties with Israel May 1, 2024 Colombia is the latest and largest country to sever ties with Israel May 1, 2024

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
North Korea fires suspected short-range missiles into the sea in its latest weapons test
A TV screen shows a file image of North Korea’s missiles launch during a news program at the Seoul Railway Station in Seoul, South Korea, Monday, April 22, 2024. North Korea fired multiple suspected short-range ballistic missiles toward its eastern waters on Monday, South Korea’s military said, the latest in a recent series of weapons launches by the North. (AP Photo/Ahn Young-joon)
A TV screen shows a file image of North Korea’s missile launch during a news program at the Seoul Railway Station in Seoul, South Korea, Monday, April 22, 2024. North Korea fired multiple suspected short-range ballistic missiles toward its eastern waters on Monday, South Korea’s military said, the latest in a recent series of weapons launches by the North. (AP Photo/Ahn Young-joon)
FILE - In this photo provided by the North Korean government, North Korean leader Kim Jong Un, left, supervises artillery firing drills in North Korea Thursday, March 7, 2024. Independent journalists were not given access to cover the event depicted in this image distributed by the North Korean government. The content of this image is as provided and cannot be independently verified. Korean language watermark on image as provided by source reads: “KCNA” which is the abbreviation for Korean Central News Agency. (Korean Central News Agency/Korea News Service via AP, File)
- Copy Link copied
SEOUL, South Korea (AP) — North Korea on Monday test-fired suspected short-range ballistic missiles into the sea, the country’s neighbors said, as speculation swirled that it could soon launch a banned satellite into orbit.
South Korea’s Joint Chiefs of Staff said the weapons launched from the North’s capital region flew about 300 kilometers (185 miles) before crashing in the waters between the Korean Peninsula and Japan. The ranges suggest the weapons could likely target sites in South Korea.
The Joint Chiefs of Staff strongly condemned the launches, saying they were a “clear provocation” that threatens peace on the Korean Peninsula. It said it will maintain readiness to “overwhelmingly” respond to North Korean provocations in step with its military alliance with the United States.
Japan’s Chief Cabinet Secretary Yoshimasa Hayashi told reporters that North Korea launched at least one ballistic missile that flew 250 kilometers (155 miles) at a maximum altitude of about 50 kilometers (30 miles). He said that North Korea’s repeated missiles tests and other provocative actions threaten the peace and safety of Japan, the region and the international community.
Japan’s coast guard urged ships to use caution against falling objects, but there were no immediate reports of damage.
North Korea in recent months has maintained an accelerated pace in weapons testing as it continues to expand its military capabilities while diplomacy with the United States and South Korea remained stalled. Observers say North Korea likely believes an upgraded weapons arsenal would give it leverage to win greater concessions from the U.S. if negotiations resume.
North Korea said Saturday that it tested a “super-large” cruise missile warhead and a new anti-aircraft missile in a western coastal area earlier last week. In early April, North Korea also test-launched what it called a solid-fuel intermediate-range missile with hypersonic warhead capabilities, a weapon that experts say is meant to attack remote targets in the U.S. Pacific territory of Guam and beyond.
In past years, North Korea has test-fired nuclear-capable missiles designed to strike sites in South Korea, Japan and the mainland U.S. Many experts say North Korea already possesses nuclear missiles that can reach all of South Korea and Japan, but it has yet to develop functioning intercontinental ballistic missiles that can travel to the continental U.S.
In response to North Korea’s evolving nuclear threats, the United States and South Korea have been strengthening their bilateral military drills and trilateral exercises with Japan. On Monday, the chairman of South Korea’s Joint Chiefs of Staff, Kim Myung-soo, met with U.S. Space Command Commander Stephen N. Waiting for discussions on countering North Korean threats, according to South Korea’s military.
Some experts say North Korea could launch its second spy satellite this month to mark a key anniversary such as the April 15 birthday of its founder Kim Il Sung, the late grandfather of leader Kim Jong Un, or the April 25 founding anniversary of a predecessor of the North’s military.
U.N. Security Council resolutions ban North Korea from launching both ballistic missiles and satellites. The world body considers a satellite launch a test of its prohibited ballistic missile technology.
South Korea’s military said Monday that it had detected evidence that North Korea is preparing for a spy satellite launch but there are no signs that it’s imminent.
Last November, North Korea placed what it called its first military spy satellite into orbit, though there are widespread doubts about its capability. In late December, Kim Jong Un said North Korea would launch three additional military spy satellites in 2024.
Associated Press writer Mari Yamaguchi in Tokyo contributed to this report.

North Korea's Cruise Missile Tests Escalate Tensions Amidst Stalled Diplomacy
N orth Korea has once again ratcheted up tensions with the firing of several cruise missiles, according to South Korea’s military. The launches took place near Sinpo, a key military shipyard on the North’s east coast where missile-firing submarines are constructed. This latest demonstration of North Korea’s expanding arsenal raises concerns about regional security and the potential for escalated military confrontation.
The recent missile tests are part of a broader series of weapons demonstrations that include last week’s unveiling of a new cruise missile, Pulhwasal-3-31, and the test-firing of the country’s first solid-fuel intermediate-range ballistic missile on January 14. These activities underscore North Korean leader Kim Jong Un’s efforts to develop weaponry capable of evading missile defenses in South Korea and Japan, as well as targeting remote U.S. assets in the Pacific, such as Guam.
Pyongyang’s steady pace in cruise missile launches, at least ten rounds since 2021, demonstrates an aim to enhance its strike capabilities. The claimed range of these missiles, up to 2,000 kilometers, poses a stark threat to U.S. military bases in Japan. Although these cruise missile activities are not directly banned under United Nations sanctions, experts warn they pose a serious threat due to their ability to fly at low altitudes, making them harder to detect by radar.
Tensions on the Korean Peninsula have been on the upswing for months, with Kim Jong Un continuing to advance his weapons development and issuing threats of nuclear conflict against the U.S. and its Asian allies. In response, the U.S., South Korea, and Japan have been intensifying their military exercises and refining their deterrence strategies, involving nuclear-capable U.S. assets.
North Korea, meanwhile, has described its weapons tests as part of regular efforts to strengthen its military and indicated that some missiles have “strategic” purposes, suggesting they may be intended for nuclear armament.
The implications of these developments are far-reaching. On the one hand, they reflect North Korea’s determination to bolster its leverage in any potential future negotiations with the U.S. On the other hand, they complicate the already strained security situation in the region. North Korea’s actions have not only drawn sharp condemnation from South Korea and Japan but also from the U.S. These missile tests come at a time when diplomacy with the United States and South Korea remains stalled, with observers suggesting that Pyongyang believes an upgraded weapons arsenal could grant it greater concessions should talks resume.
Relevant articles:
– North Korea fires missile into ocean in its latest weapons launch, South Korea says , ABC News, 05/01/2024
– North Korea fires salvo of short-range ballistic missiles , Yahoo News UK, 04/29/2024
– North Korea fires ballistic missiles as Blinken visits Seoul , Yahoo News Canada, 04/29/2024

Israel hit Iran with a half-ton supersonic 'Rampage' missile, report says
- Israeli media reported that Israel used a "Rampage" missile in its strike on Iran.
- The supersonic missile is designed to strike ground targets such as military bases.
- However, officials and independent analyses are giving a range of other possibilities.

Israel used a long-range, supersonic missile in its strike on Iran last week, Israeli broadcaster Kan reported, per The Times of Israel .
US officials said Israel carried out a missile strike on a military base near the city of Isfahan on Friday.
Israel has not confirmed the reports, while Iran has sought to downplay the incident, only referencing small drones used in the attack, which, in an interview with NBC News , its foreign minister Hossein Amirabdollahian said were "like toys our children play with."
While it remains unclear what weapons were used in the strike, Israel's national broadcaster Kan reported that Israel used a "Rampage" air-to-surface missile, claiming it was identified in photos and that damage caused by the attack was consistent with a Rampage strike, per The Times of Israel.
The Rampage was designed by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) for use against targets such as "communication and command centers, air forces bases, maintenance centers and infrastructure," according to the company's website.
The company describes the missile, which weighs 1,250 pounds, as "a long-range, air-to-ground, seekerless, precision strike weapon."
Other reports, however, have pointed to another type of missile being used in the attack.
Related stories
Analyses by the BBC and the Financial Times , based on images of wreckage that landed in Iraq, suggest that the attack involved Israel's Blue Sparrow missile.
The wreckage was likely the missile's booster system that detached mid-journey, Justin Crump, a veteran and risk intelligence CEO, told the BBC.
Israel's Sparrow missile is an air-launched ballistic missile with a range of up to 1,240 miles, per the FT. It is normally used to test Israel's air defenses, per The War Zone .
A person briefed on the situation, who was not named, said that the Pentagon also believes the Blue Sparrow may have been involved, the FT reported.
Two Western officials said that the Israeli strike on Iran, which was launched in response to Iran's attack on Israel last week, was intended to show Tehran that it easily could evade its air-defense systems, The New York Times reported.
A much larger attack was considered, but was scaled back after discussions with President Joe Biden and British and German foreign ministers, the newspaper reported.
This was done to encourage Iran not to respond in kind, but still send a message about Israel's abilities, officials told the outlet.
Business Insider contacted the IDF and the IAI for comment.
It was reported last year that the UK's Royal Air Force was considering buying Rampage missiles to replenish its missile stocks after having donated many of its own Storm Shadow cruise missiles to Ukraine.
The Rampage is considered an economical alternative, costing hundreds of thousands of dollars each, compared with the $3 million price tag of each Storm Shadow, according to The National .
The missile has the ability to fly at 1,250 mph with a range of up to 190 miles. It can be fired from an aircraft or as a stand-alone system and uses GPS/INS guidance navigation and anti-jamming capabilities, according to the company, and has a blast fragmentation or general-purpose warhead.
A video shared on the company's YouTube channel simulates a strike by the missile.
Watch: Israel bombards Lebanon and Gaza in retaliatory attack
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A BGM-109 Tomahawk flying in November 2002. A cruise missile is an unmanned self-propelled guided vehicle that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path and whose primary mission is to place an ordnance or special payload on a target. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision.
The following is a list of cruise missiles. It doesn't include the specifically anti-ship missiles whose list is separate. Missile Type Country Max. range Max. Speed (Mach) Mass Warhead Warhead type Status Note AV-TM 300: Surface-to-surface missile
The air-launched cruise missile (ALCM) had a length of 6.3 m (20.7 feet); it attained a range of 2,500 km (1,500 miles). It was designed for deployment on the B-52 bomber. The Tomahawk sea-launched cruise missile (SLCM) and the Tomahawk ground-launched cruise missile (GLCM) had a length of 6.4 m (21 feet), a diameter of 53 cm (21 inches), and a ...
Surface ships. Submarines. TELs. The Tomahawk ( / ˈtɒməhɔːk /) Land Attack Missile ( TLAM) is a long-range, all-weather, jet-powered, subsonic cruise missile that is primarily used by the United States Navy and Royal Navy in ship and submarine-based land-attack operations. Developed at the Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins ...
Ballistic missiles can carry either nuclear or conventional warheads. There are four general classifications of ballistic missiles based on their range, or the maximum distance the missile can travel: Short-range: less than 1,000 kilometers (approximately 620 miles), also known as "tactical" ballistic missiles.
Credit: Cliff. Tomahawk is a long-range, all-weather, subsonic cruise missile in service with the surface ships and submarines of the US and the UK's Royal Navy. Originally produced by General Dynamics, Tomahawk is currently manufactured by Raytheon. The Tomahawk Land Attack Missile (TLAM) can strike high-value or heavily defended land targets.
The Tomahawk Land Attack Missile (TLAM) is an all-weather, long range, subsonic cruise missile used for deep land attack warfare, launched from U. S. Navy surface ships and U.S. Navy and United
Tomahawk cruise missile or BGM-109 (Show more) Related Topics: missile ... in high-risk environments where manned aircraft may be vulnerable to surface-to-air missiles. The Tomahawk is a long-range, unmanned weapon with an accuracy of about 5 metres (16 feet). The 5.6-metre- (18.4-foot-) long missile has a range of up to approximately 2,400 km ...
The Tomahawk is an intermediate-range, subsonic cruise missile that is launched from U.S. Navy ships and submarines. It provides a long-range, deep strike capability. The Tomahawk can carry either conventional or nuclear payloads, though policy decisions have phased out their nuclear role. Tomahawk Development The U.S. Navy began its development of sea-launched cruise missiles in 1972. The...
The longest-range nuclear-armed cruise missile in the inventory is the air-launched Kh-102 (RS-AS-23 Kodiak), which may have a maximum range of around 4,000 kilometres. A longer-range air-launched missile, known as the Kh-BD (long-range) or Item 506, is also in development. This may be an extended-range Kh-101.
The Basics. A cruise missile is basically a small, pilotless airplane. Cruise missiles have an 8.5-foot (2.61-meter) wingspan, are powered by turbofan engines and can fly 500 to 1,000 miles (805 to 1,610 km) depending on the configuration. A cruise missile's job in life is to deliver a 1,000-pound (450-kg) high-explosive bomb to a precise ...
The U.S. Air Force secretly test-fired a long-range variant of a stealthy cruise missile from a B-2 stealth bomber late last year, defense contractor Northrop Grumman revealed Thursday. The ...
The original JASSM was powered by a Teledyne CAE J402-CA-100 turbojet and had a range of 230 miles. JASSM-ER extended the missile's range to an estimated 500 miles using a more fuel efficient ...
The 3M14 Kalibr (NATO: SS-N-30A) is a Russian land attack cruise missile (LACM) and improved version of the 3M-14E "Club" LACM. The SS-N-30A has an estimated range of around 1,500 to 2,500 km and has become a mainstay in the Russian Navy's ground-strike capabilities. Kalibr Development Although commonly referred to as the Kalibr cruise missile...
Cruise missiles are capable of being launched from multiple ground, air, sea and submarine platforms. Both fighter and long-range bomber aircraft are capable of carrying and launching cruise missiles. [5] On the ground, cruise missiles are most commonly launched by road-mobile systems due to the inherent advantages of mobility, but they can ...
The U.S. Air Force has awarded Raytheon a contract to develop the service's next-generation stealth cruise missile. The Long Range Stand Off (LRSO) missile will arm B-21 Raider and B-52 ...
The Storm Shadow is a long-range cruise missile with stealth capabilities, jointly developed by the UK and France, which is typically launched from the air. With a firing range in excess of 250km ...
France will join Britain in supplying Ukraine with long-range cruise missiles, which can travel 250 km (155 miles), a move that allows Ukrainian forces to hit Russian troops and supplies deep ...
Iran has developed a cruise missile with a range of 1,650 km (1,025 miles) a top Revolutionary Guards commander said on Friday, in a move likely to raise Western concerns after Russia's use of ...
5 # System Country Year Range (km) 1 V-2 SRBM Germany 1942 320 2 SS-1 SRBM Soviet Union 1948 270 3 SS-2 SRBM Soviet Union 1949 1,200 4 SS-3 MRBM Soviet Union 1955 1,200
The Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty, a Cold War-era arms control agreement between Washington and Moscow, prohibited land-based cruise or ballistic missiles with ranges between 311 miles ...
Whether to send the Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS), with a range up to 300km, was a subject of debate within the Biden administration for months. Mid-range ATACMS were supplied last September.
30 cruise missiles. Sources: United States Institute of Peace, CSIS, IDF. ... Tehran countered primarily with Scud B missiles, which have a range of 185 miles. Shahab-1, 186 miles.
North Korea fired multiple suspected short-range ballistic missiles toward its eastern waters on Monday, South Korea's military said, the latest in a recent series of weapons launches by the North. (AP Photo/Ahn Young-joon) A TV screen shows a file image of North Korea's missiles launch during a news program at the Seoul Railway Station in ...
Pyongyang's steady pace in cruise missile launches, at least ten rounds since 2021, demonstrates an aim to enhance its strike capabilities. The claimed range of these missiles, up to 2,000 ...
An air-launched cruise missile ( ALCM) is a cruise missile that is launched from a military aircraft. Current versions are typically standoff weapons which are used to attack predetermined land targets with conventional, nuclear or thermonuclear payloads. Specific types of ALCMs (current, past and under development) include: AGM-28 Hound Dog ...
At the permanent exhibit of the Revolutionary Guard Aerospace Forces in western Tehran, dozens of long- and medium-range ballistic missiles stand tall along with cruise missiles and drones.
Israel's Sparrow missile is an air-launched ballistic missile with a range of up to 1,240 miles, per the FT. ... its missile stocks after having donated many of its own Storm Shadow cruise ...
The latest Ukrainian deep-strike weapon isn't a drone, a cruise missile or a ballistic missile. It's a balloon. In a recent speech, Russian defence minister Sergei Shoigu claimed Russian air ...