Tourism Policy
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 29 December 2016
- Cite this living reference work entry

- María Velasco 2
333 Accesses
10 Citations
Tourism public action ; Tourism government decisions or nondecisions ; Public tourism objectives ; Tourism public planning
Tourism policy is a set of discourses, decisions, and practices driven by governments, sometimes in collaboration with private or social actors, with the intention to achieve diverse objectives related to tourism.

Introduction
Tourism is a relatively young phenomenon which involves the development of a singular and important economic sector. From the very beginning, that economic dimension of tourism has been the main priority for governments, and this has also been reflected in the tourism policy research. In fact it is very common considering tourism policy as a part of the economic policy, but tourism is much more than an economic sector. Tourism is probably one of the most determinant influences on our societies, and it will remain AS a key issue in the future.
The aim of the present text is to contribute to the debate on the nature, content,...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Allen MD, Edgell DL, Smith G, Swanson J (2007) Tourism policy and planning, 1st edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Amsterdam
Google Scholar
Bramwell B, Lane B (2000) Tourism collaboration and partnerships : politics, practice and sustainability, 1st edn. Channel View Publications, Clevedon
Bramwell B, Lane B (2013) Tourism governance : critical perspectives on governance and sustainability. Routledge, Hoboken
Burns PM, Novelli M (eds) (2007) Tourism and politics. Taylor & Francis Ltd., GB
Deegan, J., & Dineen, D. A. (1997). Tourism policy and performance (1. publ. ed.).London [u.a.]: Internat, Thomson Business Press
Dredge D, Jamal T (2015) Progress in tourism planning and policy: a post-structural perspective on knowledge production. Tour Manag 51:285–297. doi:10.1016/j.tourman.2015.06.002
Article Google Scholar
Dredge D, Jenkins J (eds) (2011) Stories of practice : tourism policy and planning. Ashgate, Burlington
Edgell DL (2015) International sustainable tourism policy. The Brown Journal of World Affairs 22(1):25
Edgell L, Swanson J, Allen D, Smith G (2013) Tourism policy and planning, Second edn. Routledge Ltd - M.U.A, GB. doi:10.4324/9780203113332
Gössling S (2002) Global environmental consequences of tourism. Glob Environ Chang 12(4):283–302
Hall CM (1994) Tourism and politics : policy, power and place. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester
Hall CM (2008) Tourism planning:policies, processes and relationships, 2nd edn. Pearson Education M.U.A, GB
Hall CM (2011) A typology of governance and its implications for tourism policy analysis. J Sustain Tour 19(4):437–457. doi:10.1080/09669582.2011.570346
Hall CM (2014) Introduction to tourism policies, planning, and governance. In: Lew AA, Hall CM, Williams AM (eds) The Wiley Blackwell companion to tourism. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Oxford
Hall CM, Jenkins JM (1995) Tourism and public policy (1. publ. ed.). New York, Routledge
Hood C (1986) The tools of government. Chatam House, Chatam
Hood C, Margetts H (2007) The tools of government in the digital age. Palgrave Macmillan, London
Book Google Scholar
Howlett M (1991) Policy instruments, policy styles, and policy implementation. Policy Studies Journal 19:1–21
Howlett M (2011) Designing public policies: principles and instruments. Routledge, Abingdon
ILO (2010) Developments and challenges in the hospitality and tourism sector. http://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---ed_dialogue/---sector/documents/meetingdocument/wcms_162202.pdf
Jeffries D (2001) Governments and tourism (1. publ. ed.). Oxford, Butterworth-Heinemann
Jenkins JM, Dredge D (eds) (2011) Stories of practice : tourism policy and planning. Ashgate, Farnham/Burlington
Johannesson GT, Ren C, Duim van der R (eds) (2015) Tourism encounters and controversies: Ontological politics of tourism development. Ashgate, Farnham/Burlington
Johnson P, Barry T (1992) Perspectives on tourism policy. Continuum International Publishing Group, London
MacCannell D (2013) The tourist. a new theory of the leisure class (With a new introduction). University of California Press, New York
McKercher B, Du Cros H (2002) Cultural tourism. Haworth Hospitality Press, New York
Moufakkir O (2012) Controversies in tourism. CABI, Wallingford
Scott, N (2011) Tourism policy: a strategic review. http://www.goodfellowpublishers.com/free_files/fileTourismPolicy.pdf
Velasco González M (2004) La política turística. Gobierno y Administración Turística en España. Tirant Lo Blanch, Valencia
Velasco González M (2011) La política turística una arena de acción autónoma. Cuadernos de Turismo 27:953–969
Wall G, Mathieson A (2006) Tourism: change, impacts, opportunities, 2nd edn. Pearson Education M.U.A, GB
WTO (1997) Towards new forms of public-private sector partnership : the changing role, structure and activities of national tourism administrations. World Tourism Organization, Madrid
WTO (1999) The future of national tourism administrations . Madrid, World Tourism Organization
WTO (2012a) Exploring the full economic impact of tourism for policy making . http://cf.cdn.unwto.org/sites/all/files/unwto_paper_t20_france.pdf
WTO (2012b) Positioning tourism in economic policy: evidence and some proposals. http://www2.unwto.org/es/node/30786
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, Spain
María Velasco
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to María Velasco .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, Florida, USA
Ali Farazmand
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Velasco, M. (2016). Tourism Policy. In: Farazmand, A. (eds) Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31816-5_2674-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31816-5_2674-1
Received : 26 June 2016
Accepted : 17 December 2016
Published : 29 December 2016
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-31816-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-31816-5
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Economics and Finance Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Tourism Policy, Planning, and Development
General overview.
Tourism policy, planning, and development are all very connected and do not just occur when a geographic area decides to be a tourism destination. Policy, planning, and development are included in numerous aspects of communities.
continue but from different perspectives. An example would be the use of the destination/product lifecycle, discussed later. It is important to understand what tourism planning and development are individually as well as collectively. Planning is essential to effective development. Tourism is not always a beneficial industry for a geographical area, but without planning tourism can damage the area, including natural and cultural resources (Morrison et al., 2018). A destination might consider “Who, What, When, Where, Why” when working on a tourism plan. The same can be considered for tourism development, as well as other topics included in this alternative textbook (e.g., marketing and promotion).
Tourism Policy
A policy is essentially a course of action taken by some organization or institution (e.g., government, business, educational institution). A tourism policy as defined by Edgell et al. (2008) “is a progressive course of actions, guidelines, directives, principles, and procedures set in an ethical framework that is issues-focused and best represents the intent of a community (or nation) to effectively meet its planning, development, product, service, marketing, and sustainability goals and objectives for the future grown of tourism” (p. 7). Stated more simply, Hall and Jenkins (1995) suggest “tourism public policy is whatever governments choose to do nor not to do with respect to tourism” (p. 7-8). A tourism policy is essentially a framework including guidelines, goals, and initiatives to work toward achieving the goals. Where as an act by government, such as the Travel Promotion Act of 2009 establishing Brand USA, is a law or statute.
A policy for international travel is having a current passport and for many countries a Visa. The application for a Visa to visit a foreign country allows countries to approve who may visit the country and not allow individuals for a variety of reasons (e.g., security threat). The U.S also has the Visa Waiver Program, which is an agreement with 40 countries allowing citizens of those countries to visit the U.S. for business or leisure travel purposes for up to 90 days without a Visa, provided they meet other requirements (U.S. Department of State – Bureau of Counsular Affairs, n.d.). The countries with the Visa Waiver Program also allows U.S. residents to travel to the respective countries with fairly similar criteria. The purpose of requiring a Visa is to regulate travel between countries. The Visa Waiver Program is an agreement to allow citizens of certain countries to visit without having to obtain a Visa if certain criteria are met. This essentially makes it easier to travel between the respective countries.
The International Trade Administration includes a Tourism Policy Council (TPC) to ensure national decision-making considers the national interests of travel and tourism (International Trade Administration, n.d.). The TPC provides resources to help with such issues or challenges as recovering from disaster, and links to Center for Disease Control (CDC), and many other potential issues or challenges for travel and tourism in the U.S.
At more local levels, Morrison et al. (2018) suggest tourism destinations can develop policies for development, marketing, tourist experiences, human resource issues, tourism organizations (e.g., structure), relationships throughout the community, quality assurance, and supporting services (e.g., safety and security).
Policy Setting Process
There are a series of recommended steps for the establishing policy (Morrison et al., 2018). First, identifying and assessing the circumstances related to the issue. This includes understanding contraints that you and/or will face. Constraints can be internal (e.g., locals’ awareness of tourism, training and education of employees in hospitality and tourism, budget) or external (e.g., economy, price of gas, natural disaster). The tourism organization/local industry has more control or ability to do something about internal constraints, while have little or no control over external constraints. For example, nothing can be done about bad weather or if a natural disaster occurs. However, if locals are not aware of tourism in the local community, education and information can be shared to make locals more aware. This step in the process can also make you aware of new opportunities (e.g., an attraction to develop, new target market).
The next step is typically to create a policy statement to provide guidelines, goals, and initiatives to help guide the organization, destination, etc. While not directly a policy statement, most CVB vision statements include something that provides a guideline with somewhat vague goals. For example, it might be to maintain and/or improve the quality of life for residents of the destination by promoting the destination for tourism and conventions, which would include an economic goal. A policy statement for this vision would be more specific with the goals and initiatives identified to fulfill the goals.
Consultation with government, local tourism businesses, and any other stakeholders is next. This step is to get feedback about the policy statement. Following the consultation and depending on the outcome, the policy statement might be rewritten or modified. Next would be another round of consultation and then rewriting until the the policy statement is approved.
Now is time to implement the policy statement. This will include identifying specific roles of individuals, committees, organizations, etc. This step also includes developing the budget and timeline for the initiative(s).
Finally, those involved evaluation the policy. Were the goals achieved? Why or why not? However, you do not wait until the end of the established timeline for the policy to evaluate. There should be constant assessment to identify if you are likely to achieve the goals. Remember there are numerous constraints that are external (e.g., weather, natural disaster) that might dictate the need to adjust the initiatives and other efforts related to the tourism policy.
Tourism Planning
Prior to tourism planning it is important to consider other types of planning for a community or geographic area. Planning is not new. Gunn and Var (2002) indicate physical planning goes back to early Greek and Roman times. Planning is done to manage visual appearance and land use. However, planning incorporates many disciplines and perspectives: “Planning is a multidimensional activity and seeks to be integrative. It embraces social, economic, political, psychological, anthropological, and technology factors. It is concerned with the past, present, and future” (Rose, 1984, p. 45).
Gunn and Var (2002) suggest when plans (not only tourism, but community, etc.) are created they often include very high or lofty goals and it is difficult to actually achieve such goals for numerous reasons. Planning is very vague and has no real theory behind it. For community plans the general goal is a better place to live. For tourism planning the goal might be to provide visitors with a good experience. As stated earlier, an effective tourism plan can also maintain or even improve the quality of life of residents, not just economically but the attractions provide activities for local residents as well as tourists.
Morrison et al. (2018) offer three primary reasons for tourism planning. The first two are related to impacts, to maximize the economic benefits and minimize damage to resources (i.e., natural, environmental, cultural). Another reason for a tourism plan is that tourism is constantly changing for many reasons (e.g., visitor expectations, needs, motives; politics; economy; technology). As a result, the plan needs to be adaptable.
Not all destinations have a tourism plan. Some reasons for not having a tourism plan include (Morrison et al., 2018):
- Objections – it should be taken care of by the private sector and there is no need for a formal plan.
- Cost – includes market research, consultations, and a lot of time.
- Complex – tourism is affected by numerous things, such as government policies, dynamic of the community and stakeholders.
- Diversity – various sectors involved directly or indirectly in tourism.
- Seasonality – in many destinations the jobs related to tourism can be seasonal (e.g., beach destinations, snow skiing destinations).
- Unpredictability – keep in mind the numerous things that affect and make tourism complex (e.g., natural disasters, crises, politics, economy).
Gunn and Var (2002) add the following tourism planning barriers:
- Lack of awareness of tourism impacts – which is ironic because it is a reason for a tourism plan.
- Do not understand tourism development – there needs to be a plan for developing tourism and then maintaining and even upgrading tourism (e.g., attractions, facilities, etc.).
- Inadequate infrastructure – might have deteriorated attractions, facilities, etc.
- Unorganized – no leadership to guide the process.
- Politics – usually various opinions among stakeholders (e.g., businesses, government, other stakeholders).
- Lack of hospitality training.
However, there can be serious consequences of unplanned tourism. In general, unplanned tourism is not likely to be sustainable tourism economically, environmentally, socially/culturally.
Tourism Planning Models or Approaches
Morrison et al. (2018) provide a seven step tourism destination planning model:
- Background analysis – including a SWOT analysis and assessments of government policies that affect tourism, inventory analysis (e.g., attractions, accommodations, restaurants, etc.), current demand for tourism at the destination.
- Research and analyses – identify/map locations of the inventory analysis, market survey of current visitors (e.g., motivations, what they like to do) and non-visitors (e.g., why have they not visited?, awareness of the destination, image/perception of the destination), competitive analysis (e.g., who are your competitors?, how can you differentiate your destination from competitors? what do and can you work to improve?).
- Where are we now? (position statement).
- Where would we like to be? (vision statement). Then, identify critical success factors or ways to measure and determine if you achieved your vision.
- Setting goals, establishing strategies, and setting objectives – develop a policy or (e.g., stimulate the economy). Set goals or achievable outcomes. Identify alternative strategies to achieve goals and select the most desired of the alternatives given environment or conditions (e.g., economy, resources, politics). Set objectives which are more short term goals to help monitor if you are going to achieve your longer term goals. If not, remember a tourism destination plan should be adaptable, which is the next step.
- Develop a plan – identify organizations and people to be involved and their roles, funding sources and budgets for different aspects of the plan, activities to implement your plan.
- Implement and monitor the plan – While the plan should be developed by input and participation by numerous stakeholders, it is generally implemented by a local tourism agency or organization (e.g., CVB). But, there should be committees derived of various stakeholders to which the agency is accountable. This helps monitor progress of implementing the tourism destination plan and adapt if needed.
- Evaluate the plan – measure performant of the various parts of the plan against the goals (e.g., did you achieve the goals? Why or why not?). Use the evaluation to see if and how you might adapt the plan moving forward.
Tourism Development
The tourism destination plan helps guide development of tourism. Destinations will be at various stages of development. So, it is not that the tourism plan is just for a destination just getting involved in tourism. As suggested by Mason (2003). development and change for destinations occurs as time progresses. The characteristics, motives, preferred activities and attractions, and many other things change over time and destinations redevelop to remain competitive. A fairly common way to view this is commonly referred to as “Butler’s Tourism Area Lifecycle”. There are five main stages to Butler’s Life Cycle (Butler, 1980):
- Exploration – at this stage there might be some tourism but not really an effort to provide traditional or common tourism attractions, facilities, etc. This stage mostly include tourists visiting facilities and local resources used by residents.
- Involvement – this is the beginning of the destination offering some facilities for tourists. The destination begins to more formally organize and provide or improve infrastructure, some attractions, and facilities for tourists at a local level.
- Development – the destination begins marketing and promoting the destination. This stage also begins development from outside organizations and/or businesses. The destination will begin to develop and look more like a noticeable tourist destination. More and more tourists will likely visit the destination as development progresses.
- Consolidation – at this stage the rate of increase in visitors will begin to decline. The rate of development will also begin to decline. Residents may become opposed to tourism with all of the non-locals who are in the community and there is more traffic and congestion. Some of the older attractions, facilities, etc. may also begin showing degradation.
- Decline – number of visitors will be begin to decrease as competitor destinations might have more appealing attractions, infrastructure, etc. The degradation of attractions, infrastructure, and other aspects of the destination will continue and possibly turn into what Butler (1980) refers to as a “veritable tourist slum” (p. 9).
- Rejuvenation – this outcome can occur by development of a new man-made attraction, which is likely to be followed by improvement of surrounding attractions, facilities, and other tourist needs. However, if competitor destinations also rejuvenate, the competition will remain and rejuvenation might be much less or possibly not rejuvenate and potentially decline. Another way Butler (1980) suggest rejuvenation can occur is to utilize natural resources that might not have been part tourism product throughout previous tourism development and marketing and promotion.
Butler (1980), as well as many other tourism scholars, suggest all of these efforts or stages of Tourism Area Life Cycle should be a collaborative effort within the community. For example, the government could offer incentives for private development of a new man-made attraction.
There are a number of potential ways to develop tourism. One way is to develop a “flagship” attraction, which are major attractions like a theme park (e.g., Disney Land, Disney World) and/or utilize natural attractions (e.g., ocean, lake, National Park). Gunn and Var (2002) offer recommendations for tourism destinations to develop destination zones. The zone would have clusters of attractions (e.g., museum districts) and a corridor connecting the clusters with some form of transportation. Clustering attractions provides tourists with more to do in a closer area so they spend more time at attractions and less traveling between attractions. The destination zone and clustering is a great example of planning and development and how integrated the two initiatives should be.
Morrison et al. (2018) suggest tourism involvement should be holistic. The holistic view would include consideration of the product (e.g., attractions, events, support facilities, transportation, infrastructure, etc.). Respective destinations could also ensure people (i.e., hosts, guests) are included to ensure there is community awareness and inclusion of local businesses, organizations, and residents. Morrison et al. (2018) also suggest visitor management (e.g., signage) and identifying the visitor mix of the destination. Packages (e.g., all inclusive, hotel and tickets to attraction) and programs (e.g., events, festivals, other activities) could also be developed to attract more tourists. However, destinations should approach tourism development and/or redevelopment from a sustainable approach to avoid overtourism (i.e., too many tourists).
Sustainable Tourism Development
Tourism development should also be sustainable and include the three impacts of tourism (i.e., economic, environmental, social/cultural).
The United Nations (n.d.) proposes 17 goals to consider for economic development, which include economic (e.g., “No Poverty”, “Decent Work and Economic Growth”, environmental (e.g., “Clean Water and Sanitation”, “Affordable and Clean Energy”), and social/cultural (e.g., “Good Health and Well Being”, Quality Education”) goals. The 17th goal is “Partnerships For the Goals”, which are very important for tourism destinations, not only in tourism destination planning and development, but other aspects such as marketing and promotion.
Relating development back to the impacts of tourism (i.e., economic, environmental, social/cultural). Sustainable development should include these impacts. Morrison et al. (2018) through applying the triple bottom line to tourism offers some examples of efforts for sustainable development in each of the three areas:
- Social – include residents, be sure development improves or at least maintains locals’ quality of life.
- Environmental – protect resources, educate visitors and residents of ways to protect resources.
- Economic – new employment opportunities, increase spending of visitors, find ways to have businesses purchase locally to minimize leakage.
Tourism Development Strategies
Various strategies exist to develop tourism. For example, flagship attractions (e.g., large amusement parks, National Parks) can provide something unique to market and promote. Development of clusters of attractions (e.g., museum districts) provide several attractions near each other so visitors do not have to drive long distances between attractions. Such districts could also include development of a circuit or trail for transportation via hiking or biking. Aside from man-made attractions, events can be developed by destinations to highlight such things as cultural or other unique aspects of a destination.
Considering all of the possible options of tourism development provides a holistic view. Not only the examples of attractions and events, but packages and programs can developed. Destinations need to also consider all of the elements of tourism in development (i.e., attractions, infrastructure, transportation, built/support facilities, service quality/hospitality). Again, not only businesses and organizations directly involved in tourism, but all stakeholders (e.g., residents, other local businesses) should be included and/or given the opportunity to provide feedback regarding the tourism development plan.
The general goals of tourism development should include improving visitors’ experiences, improving the local economy, not damaging natural resources, and integration throughout the destination so that tourism attractions and venues are not isolated from the rest of the community (Gunn & Var, 2002). Such goals of tourism development require all three sectors (i.e., private, non-profit, government) to be involved and collaborate.
Tourism Development Roles
The private sector, non-profit, government, and local community (e.g., residents) should be involved in tourism development. The private sector role is entrepreneurial and operations (Morrison et al., 2018). The entrepreneurial role is to identify investors to develop man-made attractions, accommodations, food and beverage, and other facilities for tourists. Once built their role becomes to hire workers, manage the operation and ensure it is successful. After all, they are taking a risk as entrepreneurs.
As discussed in the Tourism Organizations section, the non-profit organizations include CVBs to market and manage the destination, chambers of commerce, associations such as a local sports association to attract sporting events to the destination. The CVB typically works with all stakeholders and leads the marketing and sales (e.g., conventions, trade shows) for the destination. Chambers of commerce might be the tourism marketing and sales organization in smaller destinations. However, many of these non-profit types of organizations collaborate with each other, as well as with private or for-profit-sector (e.g., members of CVBs) and government (e.g., hotel tax dollars as a funding source). Non-profit organizations might also operate such things as museums and historical attractions, as well as festivals and events. Such organizations might be local cultural organizations.
The government really does not manage tourism attractions. However, there are exceptions, such as National Parks. Government roles are to stimulate development of tourism, as well as establish and enforce procedures, codes, such as zoning (e.g., business, residential). Government might also get involved for the following reasons: bankruptcy of an attraction where the government needs to help the business in some way, ensure cultural aspects of the community are conserved, encouraging private sector development, find ways to work with potential attractions and other elements of tourism provided through the private sector where businesses may have concerns about being profitable (Morrison et al., 2018).
Government might fulfill some of the above reasons for their role in tourism development by offering incentives (e.g., tax breaks) to entice development by the private sector. Government might also offer a piece of land for private sector development, which lowers the businesses cost to develop at attraction, supporting facilities, or other element of tourism.
While the sectors may have relatively unique roles in tourism development, it is also important the cooperate with each other for the good of the destination. Edgell and Haenisch (1995) offer a model whereby there are times each will work independently of the other two sectors, times when two sectors work together (e.g., private sector and government), and times when all three work together. Edgell and Haenisch (1995) call this “coopetition”. For example, while attractions compete within the destination for tourists to visit respective attractions, if all stakeholders cooperate the develop and manage tourism, the destination will do better overall.
Project Development Analyses
Prior to developing an attraction, hotel, or other element of tourism, there should be an assessment or analysis to determine the feasibility of being successful. Private sector developers who need be profitable will typically do feasibility studies. This may start with a pre-feasibility study, which is essentially to see if the project is even viable. For example, does the project make sense given what the destination already offers? Pre-feasibility studies might be conducted by whatever company or organization is interested in the project. If it does, the next step would be a more robust feasibility study to identify such things as potential sites for the product being considered, assess the market demand of the project, projected revenues and expenses, capital costs to develop the project, and will there be enough return on investment (ROI) if the project is developed. The full feasibility study is often conducted by an independent consulting company to minimize biases. The feasibility studies helps the company or organization identify if the project should move forward or not.
The market demand study within the full feasibility study would include secondary and primary research. Secondary research would include existing data, such as hotel metrics (e.g., supply, demand or rooms sold over a given period of time, occupancy, average daily rate (ADR), and revenue per available room (REVPAR) if the project is a hotel. Primary market analysis requires collection of data. This can include surveys (e.g., visitors of the destination to determine if the potential project is of interest), focus groups to get in-depth insight as to the interest of visitors. Surveys can also be conducted to potentially identify potential demand for the project.
If a project is not intended to be profitable, such as one being developed by the government or non-profit organization, a cost-benefit analysis can be conducted. Such a study essentially identifies the potential benefits to society are worth the cost of the investment.
Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area life cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. Canadian Geographer, XXIV (1), 5-12.
Draper, J., Woosnam, K. M., & Norman, W. C. (2011). Tourism use history: Exploring a new framework for understanding residents’ attitudes toward tourism. Journal of Travel Research, 50 (1), 64-77.
Edgell, D. L., Allen, M. D., Smith, G., & Swanson, L. E. (2008). Tourism policy and planning: Yesterday, today and tomorrow . Elsevier Inc.
Gunn, C. A., & Var, T. (2002). Tourism planning: Basics, concepts, cases (4th ed.). Routledge.
Hall, C. M., & Jenkins, J. M. (1995). Tourism and public policy . Routledge.
International Trade Administration. (n.d.). Tourism Policy Council (TPC). https://www.trade.gov/tourism-policy-council
Mason, P. (2003). Tourism impacts, planning and management . Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann.
Morrison, A. M., Lehto, X. Y., & Day, J. G. (2018). The tourism system (8th ed.). Kendall Hunt.
Rose, E. A. (1984). Philosophy and purpose in planning. In M. J. Bruton (Ed.), The spirit and purpose of planning (2nd ed., pp. 31-65). Hutchinson.
United Nations. (n.d.). Department of Economic and Social Affairs: Sustainable Development. https://sdgs.un.org/goals
U.S. Department of State – Bureau of Counsular Affairs. (n.d.) Visa Waiver Program. https://travel.state.gov/content/travel/en/us-visas/tourism-visit/visa-waiver-program.html
GHL 2365 - Tourism Copyright © 2024 by Jason Draper is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

U.S. Department of Commerce
- Fact Sheets
Was this page helpful?
Fact sheet: 2022 national travel and tourism strategy, office of public affairs.
The 2022 National Travel and Tourism Strategy was released on June 6, 2022, by U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina M. Raimondo on behalf of the Tourism Policy Council (TPC). The new strategy focuses the full efforts of the federal government to promote the United States as a premier destination grounded in the breadth and diversity of our communities, and to foster a sector that drives economic growth, creates good jobs, and bolsters conservation and sustainability. Drawing on engagement and capabilities from across the federal government, the strategy aims to support broad-based economic growth in travel and tourism across the United States, its territories, and the District of Columbia.
The federal government will work to implement the strategy under the leadership of the TPC and in partnership with the private sector, aiming toward an ambitious five-year goal of increasing American jobs by attracting and welcoming 90 million international visitors, who we estimate will spend $279 billion, annually by 2027.
The new National Travel and Tourism Strategy supports growth and competitiveness for an industry that, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, generated $1.9 trillion in economic output and supported 9.5 million American jobs. Also, in 2019, nearly 80 million international travelers visited the United States and contributed nearly $240 billion to the U.S. economy, making the United States the global leader in revenue from international travel and tourism. As the top services export for the United States that year, travel and tourism generated a $53.4 billion trade surplus and supported 1 million jobs in the United States.
The strategy follows a four-point approach:
- Promoting the United States as a Travel Destination Goal : Leverage existing programs and assets to promote the United States to international visitors and broaden marketing efforts to encourage visitation to underserved communities.
- Facilitating Travel to and Within the United States Goal : Reduce barriers to trade in travel services and make it safer and more efficient for visitors to enter and travel within the United States.
- Ensuring Diverse, Inclusive, and Accessible Tourism Experiences Goal : Extend the benefits of travel and tourism by supporting the development of diverse tourism products, focusing on under-served communities and populations. Address the financial and workplace needs of travel and tourism businesses, supporting destination communities as they grow their tourism economies. Deliver world-class experiences and customer service at federal lands and waters that showcase the nation’s assets while protecting them for future generations.
- Fostering Resilient and Sustainable Travel and Tourism Goal : Reduce travel and tourism’s contributions to climate change and build a travel and tourism sector that is resilient to natural disasters, public health threats, and the impacts of climate change. Build a sustainable sector that integrates protecting natural resources, supporting the tourism economy, and ensuring equitable development.
Travel and Tourism Fast Facts
- The travel and tourism industry supported 9.5 million American jobs through $1.9 trillion of economic activity in 2019. In fact, 1 in every 20 jobs in the United States was either directly or indirectly supported by travel and tourism. These jobs can be found in industries like lodging, food services, arts, entertainment, recreation, transportation, and education.
- Travel and tourism was the top services export for the United States in 2019, generating a $53.4 billion trade surplus.
- The travel and tourism industry was one of the U.S. business sectors hardest hit by the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent health and travel restrictions, with travel exports decreasing nearly 65% from 2019 to 2020.
- The decline in travel and tourism contributed heavily to unemployment; leisure and hospitality lost 8.2 million jobs between February and April 2020 alone, accounting for 37% of the decline in overall nonfarm employment during that time.
- By 2021, the rollout of vaccines and lifting of international and domestic restrictions allowed travel and tourism to begin its recovery. International arrivals to the United States grew to 22.1 million in 2021, up from 19.2 million in 2020. Spending by international visitors also grew, reaching $81.0 billion, or 34 percent of 2019’s total.
More about the Tourism Policy Council and the 2022 National Travel and Tourism Strategy
Created by Congress and chaired by Secretary Raimondo, the Tourism Policy Council (TPC) is the interagency council charged with coordinating national policies and programs relating to travel and tourism. At the direction of Secretary Raimondo, the TPC created a new five-year strategy to focus U.S. government efforts in support of the travel and tourism sector which has been deeply and disproportionately affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read the full strategy here
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Competitiveness.
- Market Intelligence
Policy and Destination Management
- Product Development
share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
UN Tourism works to provide guidance and share good practices on policies and governance models aimed to effectively support the tourism sector at the different levels: national, regional and local.
The development and management of tourism destinations requires a holistic approach to policy and governance.
Governance has two specific dimensions:
- Directive capacity of government , determined by coordination and collaboration as well as by the participation of networks of stakeholders.
- Directive effectiveness, determined by institutional skills and resources that support the ways in which processes are conducted to define goals and search for solutions and opportunities for relevant stakeholders, and by the provision of tools and means for their joint execution.
In this sense, UN Tourism works to support its Members in their efforts to develop efficient governance models / structures and policies, focusing among others on:
- Tourism policy and strategic planning
- Governance and vertical cooperation, i.e. national-regional-local levels
- Public Private Partnership (PPP)
Destination Management
Destination management consists of the coordinated management of all the elements that make up a tourism destination. Destination management takes a strategic approach to link-up these sometimes very separate elements for the better management of the destination. Joined up management can help to avoid overlapping functions and duplication of effort with regards to promotion, visitor services, training, business support and identify any management gaps that are not being addressed.
Destination management calls for a coalition of many organizations and interests working towards a common goal, ultimately being the assurance of the competitiveness and sustainability of the tourism destination. The Destination Management Organization’s (DMO) role should be to lead and coordinate activities under a coherent strategy in pursuit of this common goal.
Though DMOs have typically undertaken marketing activities, their remit is becoming far broader, to become a strategic leader in destination development. This is a vital ingredient for success in every tourism destination and many destinations now have DMOs to lead the way.
From a traditionally marketing and promotion focus the trend is to become leading organizations with a broader mandate which includes strategic planning, coordination and management of activities within an adequate governance structure with the integration of different stakeholders operating in the destination under a common goal. Destinations wherein such an organization is not still in place are increasingly creating or plan to create a DMO as the organizational entity to lead the way.
UN Tourism has identified three areas of key performance in destination management at DMO level: Strategic Leadership, Effective Implementation and Efficient Governance.
UN Tourism supports its Members and Destination Management/Marketing Organizations through the UN Tourism.QUEST - a DMO Certification System. UN Tourism.QUEST promotes quality and excellence in DMOs planning, management and governance of tourism, by means of capacity building. UN Tourism.QUEST Certification evaluates the three areas of key performance in destination management at DMO level: Strategic Leadership, Effective Implementation and Efficient Governance. With a training and capacity building component, UN Tourism.QUEST is a strategic tool which allows the DMOs to implement an improvement plan to achieve the criteria and standards of the Certification with the aim of enhancing their management processes and thus contribute to the competitiveness and sustainability of the destinations they represent.
Events & Publications
- International Seminar on Destination Management
- 2nd Conference on Destination Management in the Mediterranean
- 6th International Conference on Destination Management
UN Tourism Guidelines for Institutional Strengthening of Destination Management Organizations (DMOs) – Preparing DMOs for new challenges
Many factors account for the increased focus on effective destination management, all of them urging destination management organizations (DMOs) to face and adapt to new challenges. From traditional marketing and promotion boards the trend is for these entities to increasingly enlarge their scope to become all embracing DMOs, aiming to enhance the competitiveness and sustainability of destinations within a harmonious relationship between the residents and visitors.
Competitiveness Committee (CTC)
The Committee on Tourism and Competitiveness (CTC) is one of the technical committees of the UN Tourism and it is a subsidiary organ of the Executive Council . The Committee was established at the 95th session of the Executive Council in Belgrade, Serbia in May 2013 (CE/DEC/7(XCV). Its Rules of Procedure and the composition were approved by the Executive Council at its 96th session (Victoria Falls, Zimbabwe, August 2013) (CE/DEC/9(XCVI).
Since its establishment in 2013, CTC focused its work mainly on assessing the state of knowledge on the basic concept of “ tourism competitiveness ” and identifying its key factors . This process has also included identifying, developing and harmonizing concepts, models and operational definitions used in the tourism value chain .
Work priorities
(a) To support the Organization in fulfilling its normative role;
(b) To provide a dialogue mechanism between the public and private tourism stakeholders and academia to give guide in building and strengthening tourism competitiveness policies and strategies; and
(c) To build synergies and strategic alignments in the harmonization of the related activities of the Secretariat as well as other collaborating organizations/entities in order to ensure consistency and consensus in the delivery of the outputs and reinforce the official position of the Organization.
Provide UNWTO Members and other tourism stakeholders with a comprehensive and concise, operational, applicable and globally relevant conceptual framework to set the scene and contribute to establish a common ground for a clear harmonized understanding of:
i) concepts, models and operational definitions used in the tourism value chain;
ii) the quantitative and qualitative factors that explain competitiveness at the destination level which may be translated into technical guidelines facilitating a methodology for destinations to identify and evaluate their own factors of competitiveness.
As an outcome of the work of the CTC, the 22 nd Session of the General Assembly held in Chengdu, China (11-16 September 2017) adopted as Recommendations key definitions. Along with these definitions the Committee also focused on identifying the key quantitative and qualitative factors for “tourism competitiveness ” under two categories: i) governance, management and market dynamics, and ii) destination appeal, attractors, products and supply.
Full list of definitions adopted by the 22 nd Session of the General Assembly held in Chengdu, China (11-16 September 2017)
As part of the work of the UNWTO Committee on Tourism and Competitiveness (CTC) in its mandate for the period 2015-2019 prepared a paper on " Tourism Policy and Strategic Planning " which delves into this factor for tourism competitiveness. This paper (available below in pdf) aims to:
- Provide UNWTO Members with a comprehensive understanding on national tourism policies and contribute to their successful formulation and implementation;
- Explore key areas which need to be addressed in tourism policy and strategic planning in order to ensure the competitiveness and sustainable development of tourism;
- Assess the key areas addressed by UNWTO Members in their tourism policies and provide case studies to illustrate key elements of a sound tourism policy; and
- Serve as a practical tool for UNWTO Members and tourism policymakers by including a set of recommendations.
Composition of the CTC (2019-2023)
Full Members
Bahamas Bahrain Brazil Fiji (Vice-chair) India Israel Kenya Republic of Moldova Senegal (Chair)
Representative of the Associate Members Macao, China (2019-2021) Puerto Rico (2021-2023)
Representative of the Affiliate Members FITUR, Spain (2019-2021) Asociación Empresarial hotelera de Madrid (AEHM), Spain (2021-2023)
Meetings of the CTC:
1st Meeting: 25 August, 2013, Victoria Falls, Zambia /Zimbabwe (during 20th UN Tourism General Assembly) 1st Virtual Meeting: 27 March, 2014 2nd Virtual Meeting: 3 July, 2014 3rd Virtual Meeting: 22 October, 2014 2nd Meeting: 28 January, 2015, Madrid, Spain 3rd Meeting: 13 September, 2015, Medellin, Colombia (during 21st UN Tourism General Assembly) 4th Meeting: 22 January, 2016, Madrid, Spain 4th Virtual Meeting: 21 April, 2016 5th Meeting: 20 January, 2017, Madrid, Spain 5th Virtual Meeting: 2 March, 2017 6th Meeting: 11 September, 2017, Chengdu, China (during 22nd UN Tourism General Assembly) 7th Meeting: 19 January, 2018, Madrid, Spain 8th Meeting: 10 September 2019, Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation (during 23rd UN Tourism General Assembly) 9th Meeting: 24 January, 2020, Madrid, Spain 10th Virtual Meeting: 30 July 2020 11th CTC Meeting: 30 November 2021, Madrid, Spain (during the 24th UN Tourism General Assembly) 12th Virtual Meeting: 12 September, 2022
11th CTC Meeting: 30 November 2021, Madrid, Spain
During the 24th un tourism general assembly.

Download PDF
- Position Paper on Tourism Policyand Strategic Planning
- UN Tourism Tourism Definitions
- Composition of the Committee on tourism and competitiveness
Sustainable tourism
Related sdgs, promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable ....

Description
Publications.
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States (SIDS) and coastal least developed countries (LDCs) (see also: The Potential of the Blue Economy report as well as the Community of Ocean Action on sustainable blue economy).
The World Tourism Organization defines sustainable tourism as “tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities".
Based on General assembly resolution 70/193, 2017 was declared as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development.
In the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development SDG target 8.9, aims to “by 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism is also highlighted in SDG target 12.b. which aims to “develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”.
Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “by 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries” as comprised in SDG target 14.7.
In the Rio+20 outcome document The Future We want, sustainable tourism is defined by paragraph 130 as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities by supporting their local economies and the human and natural environment as a whole. ” In paragraph 130, Member States also “call for enhanced support for sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building in developing countries in order to contribute to the achievement of sustainable development”.
In paragraph 131, Member States “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small- and medium-sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”. In this regard, Member States also “underline the importance of establishing, where necessary, appropriate guidelines and regulations in accordance with national priorities and legislation for promoting and supporting sustainable tourism”.
In 2002, the World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg called for the promotion of sustainable tourism development, including non-consumptive and eco-tourism, in Chapter IV, paragraph 43 of the Johannesburg Plan of Implementation.
At the Johannesburg Summit, the launch of the “Sustainable Tourism – Eliminating Poverty (ST-EP) initiative was announced. The initiative was inaugurated by the World Tourism Organization, in collaboration with UNCTAD, in order to develop sustainable tourism as a force for poverty alleviation.
The UN Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD) last reviewed the issue of sustainable tourism in 2001, when it was acting as the Preparatory Committee for the Johannesburg Summit.
The importance of sustainable tourism was also mentioned in Agenda 21.
For more information and documents on this topic, please visit this link

UNWTO Annual Report 2016
In December 2015, the United Nations General Assembly declared 2017 as the International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development. This is a unique opportunity to devote a year to activities that promote the transformational power of tourism to help us reach a better future. This important cele...
UNWTO Annual Report 2015
2015 was a landmark year for the global community. In September, the 70th Session of the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a universal agenda for planet and people. Among the 17 SDGs and 169 associated targets, tourism is explicitly featured in Goa...
Emerging Issues for Small Island Developing States
The 2012 UNEP Foresight Process on Emerging Global Environmental Issues primarily identified emerging environmental issues and possible solutions on a global scale and perspective. In 2013, UNEP carried out a similar exercise to identify priority emerging environmental issues that are of concern to ...
Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
This Agenda is a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. It also seeks to strengthen universal peace in larger freedom, We recognize that eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for su...
Towards Measuring the Economic Value of Wildlife Watching Tourism in Africa
Set against the backdrop of the ongoing poaching crisis driven by a dramatic increase in the illicit trade in wildlife products, this briefing paper intends to support the ongoing efforts of African governments and the broader international community in the fight against poaching. Specifically, this...
Status and Trends of Caribbean Coral Reefs: 1970-2012
Previous Caribbean assessments lumped data together into a single database regardless of geographic location, reef environment, depth, oceanographic conditions, etc. Data from shallow lagoons and back reef environments were combined with data from deep fore-reef environments and atolls. Geographic c...
15 Years of the UNWTO World Tourism Network on Child Protection: A Compilation of Good Practices
Although it is widely recognized that tourism is not the cause of child exploitation, it can aggravate the problem when parts of its infrastructure, such as transport networks and accommodation facilities, are exploited by child abusers for nefarious ends. Additionally, many other factors that contr...
Natural Resources Forum: Special Issue Tourism
The journal considers papers on all topics relevant to sustainable development. In addition, it dedicates series, issues and special sections to specific themes that are relevant to the current discussions of the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development (CSD)....
Thailand: Supporting Sustainable Development in Thailand: A Geographic Clusters Approach
Market forces and government policies, including the Tenth National Development Plan (2007-2012), are moving Thailand toward a more geographically specialized economy. There is a growing consensus that Thailand’s comparative and competitive advantages lie in amenity services that have high reliance...
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal (NRF)
Natural Resources Forum, a United Nations Sustainable Development Journal, seeks to address gaps in current knowledge and stimulate relevant policy discussions, leading to the implementation of the sustainable development agenda and the achievement of the Sustainable...
Road Map on Building a Green Economy for Sustainable Development in Carriacou and Petite Martinique, Grenada
This publication is the product of an international study led by the Division for Sustainable Development (DSD) of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) in cooperation with the Ministry of Carriacou and Petite Martinique Affairs and the Ministry of Environment, Foreig...
UN Ocean Conference 2025
Our Ocean, Our Future, Our Responsibility “The ocean is fundamental to life on our planet and to our future. The ocean is an important source of the planet’s biodiversity and plays a vital role in the climate system and water cycle. The ocean provides a range of ecosystem services, supplies us with
UN Ocean Conference 2022
The UN Ocean Conference 2022, co-hosted by the Governments of Kenya and Portugal, came at a critical time as the world was strengthening its efforts to mobilize, create and drive solutions to realize the 17 Sustainable Development Goals by 2030.
58th Session of the Commission for Social Development – CSocD58
22nd general assembly of the united nations world tourism organization, world tourism day 2017 official celebration.
This year’s World Tourism Day, held on 27 September, will be focused on Sustainable Tourism – a Tool for Development. Celebrated in line with the 2017 International Year of Sustainable Tourism for Development, the Day will be dedicated to exploring the contribution of tourism to the Sustainable Deve
World Tourism Day 2016 Official Celebration
Accessible Tourism for all is about the creation of environments that can cater for the needs of all of us, whether we are traveling or staying at home. May that be due to a disability, even temporary, families with small children, or the ageing population, at some point in our lives, sooner or late
4th Global Summit on City Tourism
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and the Regional Council for Tourism of Marrakesh with support of the Government of Morroco are organizing the 4th Global Summit on City Tourism in Marrakesh, Morroco (9-10 December 2015). International experts in city tourism, representatives of city DMOs, of
2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference
The World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO) and Ulsan Metropolitan City with support of the Government of the Republic of Korea are organizing the 2nd Euro-Asian Mountain Resorts Conference, in Ulsan, Republic of Korea (14 - 16 October 2015). Under the title “Paving the Way for a Bright Future for Mounta
21st General Assembly of the United Nations World Tourism Organization
Unwto regional conference enhancing brand africa - fostering tourism development.
Tourism is one of the Africa’s most promising sectors in terms of development, and represents a major opportunity to foster inclusive development, increase the region’s participation in the global economy and generate revenues for investment in other activities, including environmental preservation.
- January 2017 International Year of Tourism In the context of the universal 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the International Year aims to support a change in policies, business practices and consumer behavior towards a more sustainable tourism sector that can contribute to the SDGs.
- January 2015 Targets 8.9, 12 b,14.7 The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development commits Member States, through Sustainable Development Goal Target 8.9 to “devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products”. The importance of sustainable tourism, as a driver for jobs creation and the promotion of local culture and products, is also highlighted in Sustainable Development Goal target 12.b. Tourism is also identified as one of the tools to “increase [by 2030] the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries”, through Sustainable Development Goals Target 14.7.
- January 2012 Future We Want (Para 130-131) Sustainable tourism is defined as a significant contributor “to the three dimensions of sustainable development” thanks to its close linkages to other sectors and its ability to create decent jobs and generate trade opportunities. Therefore, Member States recognize “the need to support sustainable tourism activities and relevant capacity-building that promote environmental awareness, conserve and protect the environment, respect wildlife, flora, biodiversity, ecosystems and cultural diversity, and improve the welfare and livelihoods of local communities” as well as to “encourage the promotion of investment in sustainable tourism, including eco-tourism and cultural tourism, which may include creating small and medium sized enterprises and facilitating access to finance, including through microcredit initiatives for the poor, indigenous peoples and local communities in areas with high eco-tourism potential”.
- January 2009 Roadmap for Recovery UNWTO announced in March 2009 the elaboration of a Roadmap for Recovery to be finalized by UNWTO’s General Assembly, based on seven action points. The Roadmap includes a set of 15 recommendations based on three interlocking action areas: resilience, stimulus, green economy aimed at supporting the tourism sector and the global economy.
- January 2008 Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria The Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria represent the minimum requirements any tourism business should observe in order to ensure preservation and respect of the natural and cultural resources and make sure at the same time that tourism potential as tool for poverty alleviation is enforced. The Criteria are 41 and distributed into four different categories: 1) sustainability management, 2) social and economic 3) cultural 4) environmental.
- January 2003 1st Int. Conf. on Climate Change and Tourism The conference was organized in order to gather tourism authorities, organizations, businesses and scientists to discuss on the impact that climate change can have on the tourist sector. The event took place from 9 till 11 April 2003 in Djerba, Tunisia.
- January 2003 WTO becomes a UN specialized body By Resolution 453 (XV), the Assembly agreed on the transformation of the WTO into a United Nations specialized body. Such transformation was later ratified by the United Nations General Assembly with the adoption of Resolution A/RES/58/232.
- January 2002 World Ecotourism Summit Held in May 2002, in Quebec City, Canada, the Summit represented the most important event in the framework of the International Year of Ecosystem. The Summit identified as main themes: ecotourism policy and planning, regulation of ecotourism, product development, marketing and promotion of ecotourism and monitoring costs and benefits of ecotourism.
- January 1985 Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code At the World Tourism Organization Sixth Assembly held in Sofia in 1985, the Tourism Bill of Rights and Tourist Code were adopted, setting out the rights and duties of tourists and host populations and formulating policies and action for implementation by states and the tourist industry.
- January 1982 Acapulco Document Adopted in 1982, the Acapulco Document acknowledges the new dimension and role of tourism as a positive instrument towards the improvement of the quality of life for all peoples, as well as a significant force for peace and international understanding. The Acapulco Document also urges Member States to elaborate their policies, plans and programmes on tourism, in accordance with their national priorities and within the framework of the programme of work of the World Tourism Organization.

Different levels of tourism policy and planning
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
What are the different levels of tourism policy and planning? Tourism policy and planning is a very complex issue involving a number of stakeholders and bodies. Research in this area can often be overwhelming and confusing for the untrained eye.
This post, therefore, intends to provide a basic introduction to tourism policy and planning, outlining the different levels of involvement by different organisations. At the end of the post I have included some recommend texts for further reading suitable for tourism industry stakeholders (those working in or interested in the industry) and those studying the tourism industry.
What is tourism policy and planning?
These two terms are largely interchangeable. Tourism policy can be defined as;
‘ A set of rules, regulations, guidelines, directives, and development/promotion objectives and strategies that provide framework within which the collective, as well as individual decisions directly affecting long-term tourism development and the daily activities within a destination are taken ’
Planning can be defined as;
‘the process of making decisions for the future , and not simply the physical preparation of a ‘plan’. Planning involves implementing decisions and monitoring the outcomes.’
Components of tourism
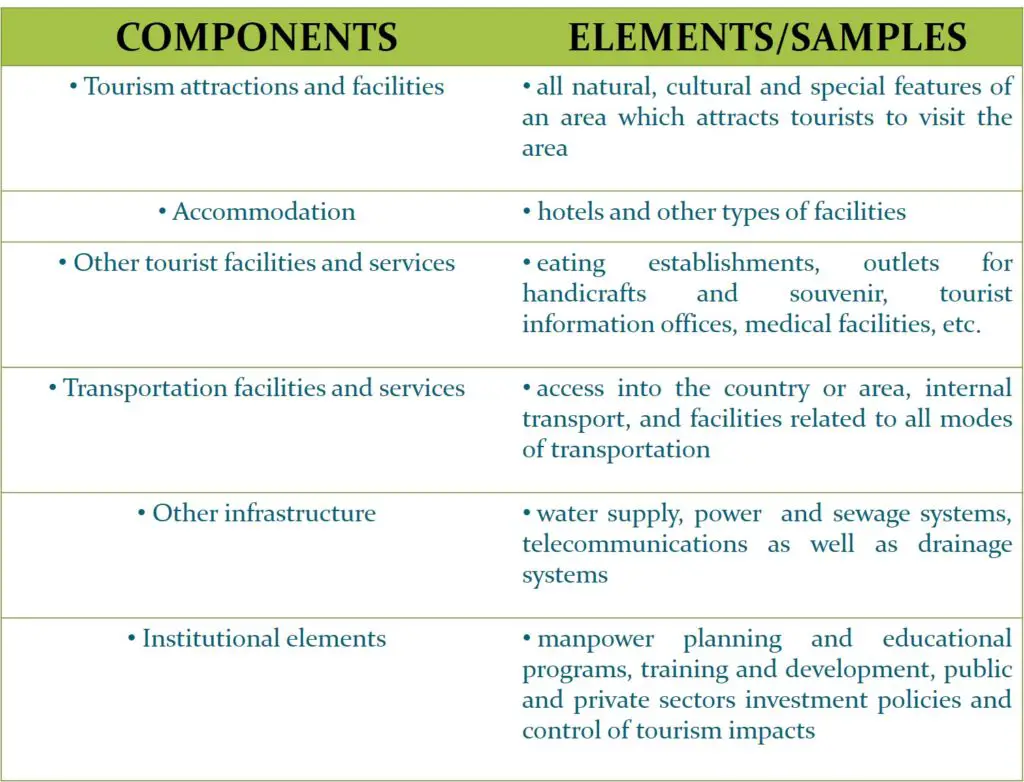
Tourism policy and planning typically involves a number of components, namely:
- Tourism attractions and activities
- Accommodation
- Other tourist facilities and services
- Transportation facilities and services
- Other infrastructure
- Institutional elements
You may also be interested in my post- ‘ Why tourism planning is important ‘
Levels of tourism planning
Tourism policy and planning takes place on different levels. This can take a top-down approach, for example by international or national bodies, or a bottom-up approach, from a local level.

International tourism planning
At the international level tourism planning typically involves; international transportation services; the movement and scheduling of the tours of tourists among different countries; the development of major tourist attractions and facilities in neighbouring countries and the working strategies and promotional programs of many countries.
Examples of international level participation groups include:
- International Government and Intra-government Org’s: g. World Tourism Organisation ; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
- International Producer Organisations: g. World Travel and Tourism Council
- International Non-Producer Organisations: g. Tourism Concern ; World Wildlife Fund (WWF); Greenpeace;
- International Single Interest Organisations: g. World Congress Against the Commercial Sexual Exploitation of Children
You may also be interested in my post- ‘ What is tourism? A definition of tourism ‘
The following organisations will consider similar issues, but not limited by the concerns or boundaries of a single nation. Decisions and influences from this level can be significant for tourism at a national and local level
- European Union
- of Caribbean States (ACS)
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
- The South Pacific Tourism Organization (SPTO)
- The “Tourism Program” of the Organization of American States (OAS)
National tourism planning
The national level of tourism planning is concerned with: tourism policy; infrastructure facilities and a physical structure plan which includes important tourist attractions, selected tourism development regions, international entry points, facilities, and services. It is also concerned with: the amount, kinds, and quality of accommodation and other required tourist facilities and services; the important tour routes in the country and their regional connections; tourism organisational entitles, laws and investment policies; tourism marketing strategies and promotion; education and training programs and environmental, economic, and socio-cultural analysis.
Examples of national level participation groups include:
- National Government and Intra-government Organisations- e.g. Visit Britain, Tourism New Zealand
- National Producer Organisations- e.g. Visit Scotland, ABTA, The Association of Independent Tour Operators (AITO)
- National Non-Producer Organisations- e.g. National Trust; The British Association for Nature Conservationists
- National Single Interest Organisations- e.g. The Wilderness Society; Society for the Protection of Birds
You may also be interested in my post- ‘ Volunteer tourism: The reasons why people volunteer ‘
Regional tourism planning
Regional planning looks at aspects including; regional policy: regional entry points and transportation facilities and services; kinds of tourist attractions and their locations; the amount, kinds, and location of tourist accommodation and other tourist facilities, and services and location of tourist development areas including resort areas.
In addition, they will manage: socio-cultural, environmental, economic, and impact analysis’s; education and training programs on the regional level; marketing techniques and promotion; organisational establishments, laws, regulations and investment policies and implementation methods which include project plans and regional zoning regulations.
Examples of regional level participation groups include:
- Regional Government and Intra-government Organisations – g. Caricom, Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS)
- Regional Producer Organisations – e.Caribbean Hotel & Tourism Association
- Regional Non-Producer Organisations – e.g. European Environmental Bureau (EEB), Regional Environmental Centre for Central and Eastern Europe
- Regional Single Interest Organisations- e.g. Coastwatch Europe, Climate Action Network Europe
Local tourism planning
Local level participants will consider tourism planning goals/objectives, analysis, plan preparation, outputs, outcomes, and evaluation at grass roots level.
Examples of local level participation groups include:
- Local Government and Intra-government Organisations- e.g. local government involvement in leisure and tourism provision, e.g. Visit Cornwall , Tourism South East
- Local Producer Organisations- e.g. local chambers of commerce and industry associations; local sporting clubs and private sport and leisure centres
- Local Non-Producer Organisations- e.g. ratepayers and resident associations,
- Single Interest Organisation – e.g. organisations such as ‘friends of a park’ or a group which has been formed in order to prevent particular developments such as a hotel or airport
The approach and implementation of tourism policy and planning differs considerably between destinations. It may, for example, be well organised and regulated in a developed country (or even over-regulated in some cases), and less resourced in developing countries.
Buy for others
Buying and sending ebooks to others.
- Select quantity
- Buy and send eBooks
- Recipients can read on any device
These ebooks can only be redeemed by recipients in the US. Redemption links and eBooks cannot be resold.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Tourism Economics and Policy (Aspects of Tourism Texts Book 5) 2nd Edition, Kindle Edition
Since the publication of the first edition of this seminal textbook, the tourism economics landscape has undergone many changes. In this concise revised edition, the authors have incorporated new approaches and ideas influencing tourism economics and policy. This includes discussions of the implications of the sharing economy and its effect on industry structure in accommodation and transport, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques that are being increasingly employed in tourism forecasting. It also includes new material on surface and marine transport, resident quality of life issues, the price mechanism, the economic contribution of tourism, tourism and economic growth, and tourism and sustainable development. It remains an important and accessible text for students, researchers and practitioners in tourism economics and tourism policy.
- ISBN-13 978-1845417314
- Edition 2nd
- Sticky notes On Kindle Scribe
- Publisher Channel View Publications
- Publication date January 14, 2020
- Part of series Aspects of Tourism Texts
- Language English
- File size 4554 KB
- See all details
- Kindle (5th Generation)
- Kindle Keyboard
- Kindle (2nd Generation)
- Kindle (1st Generation)
- Kindle Paperwhite
- Kindle Paperwhite (5th Generation)
- Kindle Touch
- Kindle Voyage
- Kindle Oasis
- Kindle Scribe (1st Generation)
- Kindle Fire HDX 8.9''
- Kindle Fire HDX
- Kindle Fire HD (3rd Generation)
- Fire HDX 8.9 Tablet
- Fire HD 7 Tablet
- Fire HD 6 Tablet
- Kindle Fire HD 8.9"
- Kindle Fire HD(1st Generation)
- Kindle Fire(2nd Generation)
- Kindle Fire(1st Generation)
- Kindle for Windows 8
- Kindle for Windows Phone
- Kindle for BlackBerry
- Kindle for Android Phones
- Kindle for Android Tablets
- Kindle for iPhone
- Kindle for iPod Touch
- Kindle for iPad
- Kindle for Mac
- Kindle for PC
- Kindle Cloud Reader

- Next 3 for you in this series $153.06
- All 5 for you in this series $225.06

Editorial Reviews
This revised edition covers a wide range of key topics in tourism economics updated to reflect latest trends in scholarship. The book provides students and researchers with tools to understand the latest changes affecting the tourism industry globally and to support private and public sector decision making to deliver desirable economic outcomes.
This second edition shows that the authors have been continuously improving the relevance and readability of the text with the latest research findings in tourism economics. It is very well written and the flow and logic of the writing is appropriate and easily accessible for students, researchers and practitioners.
I am pleased to recommend the second edition of Tourism Economics and Policy. This textbook is a rich resource for students, practitioners and scholars who want to enhance their knowledge and understanding on the subjects of tourism and economics. It provides a comprehensive picture of the main operations and activities in the tourism industry.
About the Author
Product details.
- ASIN : B083Y436ZJ
- Publisher : Channel View Publications; 2nd edition (January 14, 2020)
- Publication date : January 14, 2020
- Language : English
- File size : 4554 KB
- Text-to-Speech : Enabled
- Screen Reader : Supported
- Enhanced typesetting : Enabled
- X-Ray : Not Enabled
- Word Wise : Enabled
- Sticky notes : On Kindle Scribe
- Print length : 637 pages
- Page numbers source ISBN : 1845417313
- #1,012 in Hospitality, Travel & Tourism (Kindle Store)
- #1,479 in Development & Growth Economics (Kindle Store)
- #3,052 in Economic Policy & Development (Kindle Store)
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
No customer reviews
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tourism policy is an intentional course of action which goes beyond the level of theoretical reflection and political intention materialized into real actions, involving the use of public resources. It is also integrated by consistent actions or, at least, actions which were designed to be consistent.
1. Introduction. The tourism and hospitality industry creates an inflow of both local and foreign income and employment opportunities, prompting infrastructure development and positive economic growth (Comerio & Strozzi, 2019).In terms of social development, the industry also alleviates socio-economic challenges such as unemployment, inequality, and poverty by providing opportunities and ...
Policy Statement - Tourism Policies for Sustainable and Inclusive Growth. natural and cultural resources; iv) improve competitiveness; and, v) promote inclusive growth and development within and across countries. We agree that for whole-of-government policy responses to be effective, they should, as appropriate:
The social aspects of tourism policy were and still are also important for the European Union Parliament. It is reflected in the resolutions it issued, i.e., inter alia, the one of 27 September 2011 on Europe as the most popular tourist destination in the world—a new political framework for the European tourism sector, in which the European ...
Tourism policy, planning, and development are all very connected and do not just occur when a geographic area decides to be a tourism destination. Policy, planning, and development are included in numerous aspects of communities. continue but from different perspectives. An example would be the use of the destination/product lifecycle ...
Office of Public Affairs. [email protected]. The 2022 National Travel and Tourism Strategy was released on June 6, 2022, by U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina M. Raimondo on behalf of the Tourism Policy Council (TPC). The new strategy focuses the full efforts of the federal government to promote the United States as a premier destination ...
UN Tourism works to provide guidance and share good practices on policies and governance models aimed to effectively support the tourism sector at the different levels: national, regional and local. The development and management of tourism destinations requires a holistic approach to policy and governance. Governance has two specific dimensions:
Tourism is a major economic force whose development can have a fundamental impact on societies and the environment, both positive and negative. This guide shows governments how they can make tourism more sustainable. It sets out 12 aims for sustainable tourism and their implications for policy, and describes the collaborative structures and strategies that are needed at the national and local ...
Recent Trends. Tourism is an important part of OECD member and partner economies, and a key sector within a growing services economy. On average tourism directly contributes 4.4% of GDP, 6.9% of employment ( Figure 1.1) and 21.5% of service related exports to OECD countries. Global tourism has steadily expanded for over six decades.
1. Introduction. The balance between economic growth and sustainability contributes to the fact that sustainability and competitiveness represent the two major concepts in tourism policy from a modern perspective (Vanhove, 2002).The importance of sustainable tourism policies became obvious during the prolonged COVID-19 crisis.
As such, there is a need to rethink the policy framework supporting tourism growth, and to shift from a growth-paradigm that often values increasing visitor numbers as the primary objective, without considering the capacity of destinations to cope with increased tourism or other policy goals (Peeters et al., 2018), to one better reflecting the ...
The tourism industries are complex; this is particularly evident at the destination level, be that national, state, regional or local, where tourism planning and policy making is usually a complicated process involving a myriad of stakeholders with differing interests and objectives. This complexity is compounded when the regulatory aspects of tourism planning and development are factored into ...
In this research, tourism policy making is investigated from the perspectives of the people involved in the process to deepen understanding about its relational and contextual aspects. This approach draws attention to the importance of interactions and communications between people as policy is enacted, and is designed to encompass complexity ...
Tourism is one of the world's fastest growing industries and an important source of foreign exchange and employment, while being closely linked to the social, economic, and environmental well-being of many countries, especially developing countries. Maritime or ocean-related tourism, as well as coastal tourism, are for example vital sectors of the economy in small island developing States ...
Comprehensive textbook covering the latest approaches and ideas which influence tourism economics and policy globally. This revised edition incorporates new material on the sharing economy, AI, surface and marine transport, resident quality of life issues, the price mechanism, the economic contribution of tourism, and tourism and economic growth.
The national level of tourism planning is concerned with: tourism policy; infrastructure facilities and a physical structure plan which includes important tourist attractions, selected tourism development regions, international entry points, facilities, and services. It is also concerned with: the amount, kinds, and quality of accommodation and ...
Since the publication of the first edition of this seminal textbook, the tourism economics landscape has undergone many changes. In this concise revised edition, the authors have incorporated new approaches and ideas influencing tourism economics and policy. This includes discussions of the implications of the sharing economy and its effect on industry structure in accommodation and transport ...
tourism scholars that strive to explain the relationship between politics and tourism. One of the few political science scholars who acknowledges the interplay of politics and tourism is Political Scientist Harry G. Mathews, who advocates for the inclusion of international tourism within political science research. Mathews believes that there are
ASPECTS OF TOURISM TEXTS Series Editors: Chris Cooper (Leeds Beckett University, UK), C. Michael Hall (University of Canterbury, New Zealand) and Dallen J. Timothy (Arizona State University, USA) This new series of textbooks aims to provide a comprehensive set of titles for higher level under-
Social tourism policy should be considered as a contribution to the overall and sustainable development, not only economic aspects of development. The policy and especially tourism policy in the Eu are based on the principles of sustainability (with economic, social and environmental aspects) as well as competitiveness (Estol, Camilleri, & Font ...
Tourism Economics and Policy (Aspects of Tourism Texts Book 5) - Kindle edition by Dwyer, Larry, Forsyth, Peter, Dwyer, Wayne. Download it once and read it on your Kindle device, PC, phones or tablets. Use features like bookmarks, note taking and highlighting while reading Tourism Economics and Policy (Aspects of Tourism Texts Book 5).
In this concise revised edition, the authors have incorporated new approaches and ideas influencing tourism economics and policy. This includes discussions of the implications of the sharing economy and its effect on industry structure in accommodation and transport, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques that are being increasingly ...
Tourism Economics and Policy (Aspects of Tourism Texts Book 5) - Kindle edition by Dwyer, Prof. Larry, Forsyth, Prof. Peter, Dwyer, Wayne. Download it once and read it on your Kindle device, PC, phones or tablets. Use features like bookmarks, note taking and highlighting while reading Tourism Economics and Policy (Aspects of Tourism Texts Book 5).